Worksheet: Equality | Political Science Class 11 - Humanities/Arts PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Fill in the Blanks |

|
| Match the Column |

|
| Assertion and Reason Based |

|
| Very Short Answers Type Questions |

|
| Short Answer Type Questions |

|
| Long Answer Type Questions |

|
Fill in the Blanks
Q1: According to the Constitution of India, which of the following is a basis for discrimination? (Answer choices: Religion, Gender, Caste, All of the above)
Q2: Equality upholds the notion that every individual possesses equal worth, regardless of their __________, __________, __________, or __________.
Q3: __________ is a significant moral and political force inspiring human society.
Q4: Inequality still persists in various forms such as unequal distribution of wealth, limited opportunities, and unequal distribution of __________.
Q5: The ideal of equality is widely accepted, but inequality is still prevalent in almost all aspects of life, creating a significant __________.
Q6: Equality implies that the treatment we receive and the opportunities we have must not be predetermined by __________ or social circumstances.
Q7: Social inequalities are created by __________ and may treat people differently based on their race, color, gender, or caste.
Q8: __________ inequalities are distinct from socially-produced inequalities, which emerge due to inequalities of opportunity or exploitation.
Q9: Affirmative action is based on the idea that it is not sufficient to establish formal equality by law and may take many forms, such as __________ and __________.
Q10: Differential or special treatment may be considered to realize the goal of equality, but it requires justification and careful __________.
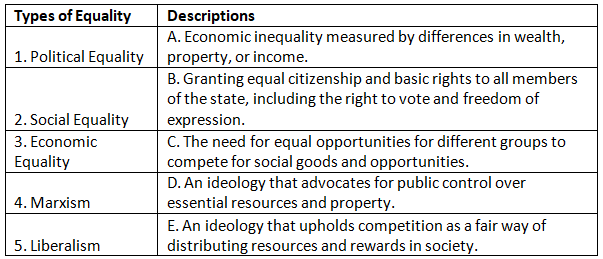
Match the Column
Q1: Match the types of equality with their descriptions.
Assertion and Reason Based
Q1: Assertion: Equality matters because it ensures fairness and justice in society.
Reason: Equality promotes unequal opportunities for individuals based on their background.
(a) Both the assertion and reason are true, and the reason is a correct explanation of the assertion.
(b) Both the assertion and reason are true, but the reason is not a correct explanation of the assertion.
(c) The assertion is true, but the reason is false.
(d) Both the assertion and reason are false.
Q2: Assertion: Affirmative action is based on the idea that it is not sufficient to establish formal equality by law.
Reason: Affirmative action aims to deny equal treatment to all sections of society.
(a) Both the assertion and reason are true, and the reason is a correct explanation of the assertion.
(b) Both the assertion and reason are true, but the reason is not a correct explanation of the assertion.
(c) The assertion is true, but the reason is false.
(d) Both the assertion and reason are false.
Q3: Assertion: Economic inequality can be measured by differences in wealth, property, or income.
Reason: Social equality focuses on granting equal citizenship and basic rights to all members of the state.
(a) Both the assertion and reason are true, and the reason is a correct explanation of the assertion.
(b) Both the assertion and reason are true, but the reason is not a correct explanation of the assertion.
(c) The assertion is true, but the reason is false.
(d) Both the assertion and reason are false.
Q4: Assertion: Differential or special treatment may be considered to realize the goal of equality.
Reason: Differential treatment is always unjust and should be avoided in all cases.
(a) Both the assertion and reason are true, and the reason is a correct explanation of the assertion.
(b) Both the assertion and reason are true, but the reason is not a correct explanation of the assertion.
(c) The assertion is true, but the reason is false.
(d) Both the assertion and reason are false.
Very Short Answers Type Questions
Q1: Define political equality.
Q2: What are natural inequalities?
Q3: Provide an example of a socially-produced inequality.
Q4: What is affirmative action?
Q5: How can equality be attained according to the Indian Constitution?
Q6: Why do some people argue against affirmative action?
Q7: What is the distinction between treating everyone in an identical manner and treating everyone as equal?
Q8: Give an example of differential treatment for achieving equality.
Q9: Why is it important to justify differential treatment in the pursuit of equality?
Q10: What role did the women's movement play in advocating for equality?
Short Answer Type Questions
Q1: Explain the concept of natural inequalities and their relevance in the pursuit of equality.
Q2: Describe the three dimensions of equality and provide examples for each.
Q3: Discuss the principles and arguments of Marxism and liberalism regarding economic inequality.
Q4: Why is affirmative action considered necessary to achieve equality, and what forms can it take?
Q5: What are the key provisions of the Indian Constitution in promoting equality?
Q6: What challenges and debates surround the policy of reservations in India?
Q7: Differentiate between formal equality and equality of opportunities.
Q8: How can society justify differential treatment in the pursuit of equality while avoiding unfairness and discrimination?
Long Answer Type Questions
Q1: Discuss the significance of the ideal of equality in society and its role in promoting fairness and justice.
Q2: Analyze the challenges and complexities of distinguishing between natural and socially-produced inequalities in the pursuit of equality.
Q3: Explore the different dimensions of equality, including political, social, and economic equality, and their role in creating a just society.
Q4: Examine the ethical and practical considerations surrounding affirmative action as a means to achieve equality, focusing on its potential benefits and criticisms.
You can access the solutions to this worksheet here.
|
44 videos|399 docs|50 tests
|
FAQs on Worksheet: Equality - Political Science Class 11 - Humanities/Arts
| 1. What is the concept of equality in humanities/arts? |  |
| 2. How does equality contribute to the development of arts and humanities? |  |
| 3. What are some challenges to achieving equality in humanities/arts? |  |
| 4. How can individuals contribute to promoting equality in humanities/arts? |  |
| 5. What are some initiatives or organizations working towards equality in humanities/arts? |  |




















