Worksheet: Rights | Political Science Class 11 - Humanities/Arts PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Fill in the Blanks |

|
| Match the Column |

|
| Assertion and Reason Based |

|
| Very Short Answer Type Questions |

|
| Short Answer Type Questions |

|
| Long Answer Type Questions |

|
Fill in the Blanks
Q1: Rights are legal, social, or ethical principles of ______ or entitlement.
Q2: According to political theorists in the 17th and 18th centuries, rights are derived from ______ law.
Q3: The three natural rights identified by early political theorists are the right to life, right to liberty, and right to ______.
Q4: The term "human rights" has become more popular than "natural rights" because of its ______ acceptability.
Q5: Rights are necessary for leading a life of ______ and dignity.
Q6: A bill of rights is a list of a country's most important rights granted to its ______.
Q7: Economic rights encompass basic needs such as food, shelter, clothing, and ______.
Q8: Cultural rights aim at ensuring the enjoyment of culture and its components in conditions of ______, human dignity, and non-discrimination.
Q9: Rights require individuals to respect the rights of ______.
Q10: Citizens must be vigilant about restrictions that may be placed on their rights, as they are the foundation of a ______ society.
Match the Column
Q1: Match the following types of rights with their descriptions:
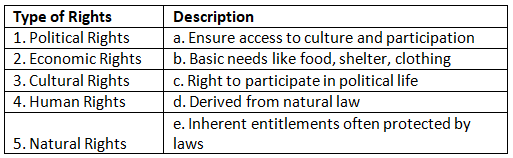
Assertion and Reason Based
Q1: Assertion: Human rights are more commonly used today than natural rights.
Reason: The idea of natural law appears radical and unacceptable in modern society.
(a) Both Assertion and Reason are correct.
(b) Assertion is correct, but the Reason is not.
(c) Assertion is not correct, but the Reason is.
(d) Both Assertion and Reason are incorrect.
Q2: Assertion: Economic rights include the right to participate in political life.
Reason: Economic rights are essential for leading a life of respect and dignity.
(a) Both Assertion and Reason are correct.
(b) Assertion is correct, but the Reason is not.
(c) Assertion is not correct, but the Reason is.
(d) Both Assertion and Reason are incorrect.
Q3: Assertion: Rights spell out what the government must do but not what it must avoid.
Reason: Legal recognition is the basis for asserting rights.
(a) Both Assertion and Reason are correct.
(b) Assertion is correct, but the Reason is not.
(c) Assertion is not correct, but the Reason is.
(d) Both Assertion and Reason are incorrect.
Q4: Assertion: Rights require individuals to respect the rights of others.
Reason: Balancing conflicting rights is not a requirement in a democratic society.
(a) Both Assertion and Reason are correct.
(b) Assertion is correct, but the Reason is not.
(c) Assertion is not correct, but the Reason is.
(d) Both Assertion and Reason are incorrect.
Very Short Answer Type Questions
Q1: What are rights?
Q2: Name three natural rights.
Q3: Why are human rights more popular today than natural rights?
Q4: How do political rights contribute to democracy?
Q5: Provide an example of an economic right.
Q6: What do cultural rights aim to ensure?
Q7: What is the basis for asserting rights?
Q8: Give an example of a situation where rights conflict.
Q9: Why is vigilance necessary to protect rights?
Q10: What is the role of rights in a democratic society?
Short Answer Type Questions
Q1: Explain the difference between natural rights and human rights.
Q2: How do political rights and civil liberties contribute to the democratic system of government?
Q3: Describe the concept of a bill of rights and its purpose.
Q4: Discuss the importance of economic rights in democratic societies.
Q5: Provide examples of cultural rights and their significance.
Q6: Why is it essential for individuals to respect the rights of others?
Q7: Give an example of a situation where individuals must balance their rights.
Q8: What are the challenges associated with protecting rights in the name of national security?
Long Answer Type Questions
Q1: Discuss the historical development of the concept of rights, from natural rights to human rights.
Q2: Explain the role of rights and responsibilities in a democratic society, emphasizing their interdependence.
Q3: Analyze the current global challenges to human rights and how they are addressed.
Q4: Provide a critical assessment of the limitations and constraints on rights in the name of national security, considering their impact on democratic societies.
You can access the solutions to this worksheet here.
|
43 videos|268 docs|39 tests
|
FAQs on Worksheet: Rights - Political Science Class 11 - Humanities/Arts
| 1. What are the main components of a Rights Humanities/Arts curriculum? |  |
| 2. How can students apply their learning from Rights Humanities/Arts in real-world situations? |  |
| 3. What skills do students develop through a Rights Humanities/Arts education? |  |
| 4. Why is it important to include diverse perspectives in the study of Rights Humanities/Arts? |  |
| 5. What types of assessments are commonly used in Rights Humanities/Arts courses? |  |




















