Worksheet Solutions: Citizenship | Political Science Class 11 - Humanities/Arts PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Fill in the Blanks |

|
| Match the Column |

|
| Assertion and Reason Based |

|
| Very Short Answer Type Questions |

|
| Short Answer Type Questions |

|
| Long Answer Type Questions |

|
Fill in the Blanks
Q1: Citizenship is granted to an individual by __________.
Ans: the national government of the country
Citizenship is typically granted by the national government of the country, not the United Nations or local government.
Q2: Full and equal membership in a political community defines __________.
Ans: citizenship
This statement defines the essence of citizenship, emphasizing that it involves being a full and equal member of a political community.
Q3: What are the three types of rights typically included in democratic countries?
Ans: political, civil, and socio-economic rights
In democratic countries, citizens generally have political, civil, and socio-economic rights, such as the right to vote, freedom of speech, minimum wage, and education.
Q4: The struggle for securing citizens' rights in European countries, like the French Revolution in 1789, was sometimes __________.
Ans: violent
The French Revolution was a violent struggle for securing citizens' rights, highlighting that the struggle for rights can involve violence.
Q5: In South Africa, black Africans waged a prolonged struggle against the ruling white minority for equal citizenship until the __________.
Ans: early 1990s
This statement emphasizes the long and persistent struggle for equal citizenship by black Africans in South Africa.
Q6: Freedom of movement is a right granted to __________ in many countries.
Ans: citizens
Freedom of movement is a right typically granted to citizens, allowing them to move within their country and, in some cases, internationally.
Q7: The right to protest is guaranteed under the Constitution as long as it does not cause harm to __________.
Ans: people, property, or the State
The Constitution guarantees the right to protest as long as it is peaceful and does not cause harm to people, property, or the state.
Q8: Equal rights and opportunities for all citizens can be challenging because different groups may have varying __________.
Ans: needs
Different groups may have unique needs, making it challenging for governments to provide equal rights and opportunities to all citizens.
Q9: The concept of universal citizenship is supported, but each state sets its own criteria for granting citizenship in their __________.
Ans: laws
Universal citizenship is a concept that promotes inclusivity, but each state sets its own criteria for granting citizenship through its laws.
Q10: Statelessness is a major issue facing the world today, and the United Nations has appointed a High Commissioner for __________.
Ans: Refugees
Statelessness is a significant global issue, where individuals are not considered citizens of any nation, leaving them without legal protection and rights.
Match the Column
Q1: Match the concepts on the left with their descriptions on the right.
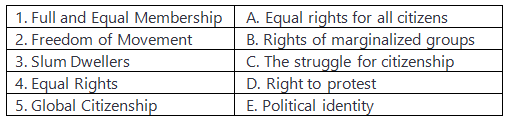 Ans: 1. Full and Equal Membership - E. (Global Citizenship)
Ans: 1. Full and Equal Membership - E. (Global Citizenship)
"Full and Equal Membership" typically relates to the idea of being recognized as a global citizen. Global citizenship involves a sense of identity that transcends national boundaries and emphasizes the idea that all individuals have certain rights and responsibilities in a global context.
2. Freedom of Movement - D. (Right to protest)
"Freedom of Movement" refers to the right of individuals to move freely within their country or even across borders. While it is not directly related to the "Right to protest," it can be associated with this concept because freedom of movement can also encompass the ability to assemble and move about freely, including for the purpose of peaceful protests.
3. Slum Dwellers - B (Rights of marginalized groups)
"Slum Dwellers" typically refers to people living in impoverished urban areas, often marginalized and facing socio-economic challenges. Therefore, it is associated with the "Rights of marginalized groups" as they are a vulnerable population that may require specific rights and support.
4. Equal Rights - A (Equal rights for all citizens)
"Equal Rights" directly corresponds to the concept of ensuring equal rights for all citizens. This includes the principle that all individuals should have the same rights and opportunities, regardless of their background, race, or social status.
5. Global Citizenship - C (The struggle for citizenship)
While "Global Citizenship" does not directly correspond to "The struggle for citizenship," it is the closest match among the given options. The term "Global Citizenship" reflects the idea that individuals can identify as members of a global community, even though they may not necessarily have a direct struggle for national citizenship. The match isn't perfect, but it's the best option based on the given choices.
Assertion and Reason Based
Q1: Assertion: Citizenship extends beyond the relationship between states and their members.
Reason: Citizenship is only about political identity and rights.
(a) Both the assertion and reason are true, and the reason is the correct explanation of the assertion.
(b) Both the assertion and reason are true, but the reason is not the correct explanation of the assertion.
(c) The assertion is true, but the reason is false.
(d) The assertion is false, but the reason is true.
Ans: (c)
In this case, the assertion is true, but the reason is false. The assertion is accurate because citizenship indeed extends beyond the relationship between states and their members. It includes citizen-citizen relations and citizens' obligations to one another and society, as mentioned in the provided text. The reason is false because citizenship is not solely about political identity and rights; it encompasses various aspects, including social, cultural, and economic dimensions, as discussed in the text. Therefore, the reason is not the correct explanation of the assertion.
Q2: Assertion: Full and equal membership in a political community is a fundamental aspect of citizenship.
Reason: Citizenship only applies to democratic countries.
(a) Both the assertion and reason are true, and the reason is the correct explanation of the assertion.
(b) Both the assertion and reason are true, but the reason is not the correct explanation of the assertion.
(c) The assertion is true, but the reason is false.
(d) The assertion is false, but the reason is true.
Ans: (b)
Both the assertion and reason are true, but the reason is not the correct explanation of the assertion. The assertion correctly states that full and equal membership in a political community is a fundamental aspect of citizenship, as mentioned in the provided text. However, the reason is not entirely accurate because citizenship is not limited to democratic countries only. While democratic countries typically offer a broader range of rights and protections, citizenship exists in various political systems, and the fundamental concept of full and equal membership applies universally. Therefore, the reason does not correctly explain the assertion.
Q3: Assertion: Global citizenship is the same as national citizenship.
Reason: People already feel connected to each other beyond national boundaries.
(a) Both the assertion and reason are true, and the reason is the correct explanation of the assertion.
(b) Both the assertion and reason are true, but the reason is not the correct explanation of the assertion.
(c) The assertion is true, but the reason is false.
(d) The assertion is false, but the reason is true.
Ans: (d)
In this case, the assertion is false, but the reason is true. The assertion is incorrect because global citizenship is not the same as national citizenship. Global citizenship refers to the idea that individuals are members of not only their own nation but also the global community, emphasizing the interconnectedness of people beyond national boundaries. The reason is true because the reason provided correctly states that people already feel connected to each other beyond national boundaries, which is a key element of the concept of global citizenship. However, the reason does not explain why global citizenship is not the same as national citizenship, making the assertion false.
Q4: Assertion: In India, the state should not discriminate against citizens on grounds only of religion, race, caste, sex, place of birth, or any of them.
Reason: India defines itself as a secular, democratic nation-state.
(a) Both the assertion and reason are true, and the reason is the correct explanation of the assertion.
(b) Both the assertion and reason are true, but the reason is not the correct explanation of the assertion.
(c) The assertion is true, but the reason is false.
(d) The assertion is false, but the reason is true.
Ans: (a)
Both the assertion and reason are true, and the reason is the correct explanation of the assertion. The assertion correctly states that in India, the state should not discriminate against citizens on grounds only of religion, race, caste, sex, place of birth, or any of them, as mentioned in the Indian Constitution. The reason is also true because India defines itself as a secular, democratic nation-state, as stated in the provided text. The reason correctly explains why India has provisions against discrimination on these grounds. Therefore, both the assertion and reason are accurate, and the reason is the correct explanation of the assertion.
Very Short Answer Type Questions
Q1: What are the three types of rights typically included in democratic countries?
Ans: The three types of rights in democratic countries are political, civil, and socio-economic rights.
Q2: Give an example of a violent struggle for equal citizenship.
Ans: The French Revolution in 1789 is an example of a violent struggle for equal citizenship.
Q3: What is the significance of freedom of movement for workers?
Ans: Freedom of movement is crucial for workers who often migrate for employment opportunities, as it allows them to seek better job prospects without restrictions.
Q4: How does the Constitution guarantee the right to protest?
Ans: The Constitution guarantees the right to protest as long as it is peaceful and does not cause harm to people, property, or the state, ensuring the protection of citizens' freedom of expression.
Q5: What challenges do governments face regarding tribal people and forest dwellers?
Ans: Governments face the challenge of protecting the rights and habitats of tribal people and forest dwellers while managing commercial interests and the tourism industry.
Q6: What is the problem of statelessness?
Ans: Statelessness is a condition where individuals are not considered citizens of any nation, leaving them without legal protection and rights.
Q7: Provide an example of India providing refuge to persecuted individuals.
Ans: India provided refuge to the Dalai Lama and his followers in 1959, fleeing from persecution in Tibet.
Q8: Why is global citizenship important in the modern world?
Ans: Global citizenship is essential in the modern world because it promotes interconnectedness and emphasizes collective action to address global challenges that transcend national boundaries.
Q9: What is the main focus of a democratic state's national identity?
Ans: The main focus of a democratic state's national identity is inclusivity, which allows diverse groups within the state to identify with and participate in the broader national identity.
Q10: How does the Indian Constitution protect against discrimination based on religion, race, and caste?
Ans: The Indian Constitution protects against discrimination based on religion, race, and caste through Article 15, which explicitly prohibits discrimination on these grounds.
Short Answer Type Questions
Q1: Explain the concept of global citizenship and its significance in today's world.
Ans: Global citizenship refers to being a member of not only one's own nation but the global community, emphasizing interconnectedness and collective responsibility. It is significant in addressing global issues and promoting cooperation.
Q2: Discuss the challenges governments face in providing equal rights and opportunities to all citizens, considering diverse needs.
Ans: Governments face challenges because different groups may have varying needs, making it complex to ensure equal rights. Policies must consider diversity to avoid discrimination.
Q3: Describe the idea of a nation-state and its role in defining national identity.
Ans: A nation-state defines itself based on geographical borders and cultural identity, and its national identity plays a role in creating a sense of belonging for citizens.
Q4: Explain the criteria for granting citizenship in India.
Ans: India's citizenship can be acquired by birth, descent, registration, naturalization, or inclusion of territory. The criteria prioritize inclusivity and non-discrimination.
Q5: What are some of the struggles and controversies despite inclusive provisions in the Indian Constitution?
Ans: Despite inclusive provisions, there are struggles related to women's rights, the dalit movement, and displacement due to development projects, where citizens feel they are being denied full rights.
Q6: What is the problem of statelessness, and why is it a significant issue globally?
Ans: Statelessness is when individuals are not considered citizens of any nation, leading to a lack of legal protection and rights. It is significant because it affects millions globally and can result from wars, persecution, or migration.
Q7: How has India provided refuge to persecuted individuals, and why is this significant?
Ans: India has provided refuge to persecuted individuals, like the Dalai Lama in 1959, which is significant as it demonstrates humanitarian values and solidarity with those in need.
Q8: Discuss the importance of global citizenship in addressing issues that transcend national boundaries.
Ans: Global citizenship is essential as it promotes an understanding of interconnectedness and encourages people to collaborate across borders to address global challenges, such as climate change and pandemics.
Long Answer Type Questions
Q1: Define and elaborate on the concept of universal citizenship, considering the criteria for granting citizenship and the challenges it poses for states.
Ans:
- Universal citizenship is a concept that emphasizes granting citizenship to individuals without discrimination, primarily based on principles of inclusivity and equal rights. However, despite supporting the idea of universal citizenship, each state typically sets its own criteria for granting citizenship. These criteria are often established in the country's constitution and legal framework. Universal citizenship acknowledges the interconnectedness of people globally and seeks to ensure that individuals are not left stateless or without legal protection.
- Universal citizenship poses several challenges for states. First, states must strike a balance between national security concerns and humanitarian considerations. They need to prevent the entry of unwanted visitors, such as potential threats or illegal migrants, while also fulfilling their obligations towards those in need, such as refugees fleeing persecution or conflict. This challenge is particularly pronounced in countries dealing with mass displacement crises.
- Second, states may be concerned about the economic and social impacts of granting citizenship universally. Admitting a large number of people into a country can strain resources, infrastructure, and social services, potentially affecting the well-being of existing citizens.
- Furthermore, there is the issue of cultural and social cohesion. States may worry about how the integration of new citizens from diverse backgrounds might affect their national identity and societal norms. Striking a balance between ensuring universal citizenship and addressing these challenges is a complex task for governments.
Q2: Discuss the relationship between citizens and the nation-state, with a focus on how democratic states aim to define their national identity.
Ans: The relationship between citizens and the nation-state is a fundamental aspect of political science and citizenship studies. In a democratic state, this relationship is characterized by a shared bond that extends beyond mere legal status. Here, citizens identify with the nation-state and its values, contributing to the concept of national identity.
Democratic states aim to define their national identity in an inclusive manner, allowing diverse groups within their borders to identify with the state. This inclusivity is essential because democratic values prioritize individual rights and equality.
To achieve this inclusive national identity, democratic states often adopt the following strategies:
- Cultural Pluralism: Democratic states acknowledge and celebrate the cultural, religious, and linguistic diversity within their borders. They respect the rights of various communities to practice their customs and traditions while upholding democratic values. This approach allows citizens to retain their unique identities while also participating in the broader national identity.
- Civic Nationalism: Democratic states promote civic nationalism, which emphasizes shared values, principles, and political institutions as the basis for national identity. This approach focuses on citizenship as a unifying factor, regardless of one's cultural or ethnic background. In such states, the allegiance to democratic ideals becomes the primary bond between citizens and the nation.
- Inclusivity in Political Participation: Democratic states encourage all citizens to participate in the political process, irrespective of their background. This participation allows citizens to actively contribute to shaping the nation's identity through democratic means, such as elections and public discourse.
- Equal Rights and Protections: Democratic states ensure that all citizens have equal rights and protections under the law, regardless of their background. This commitment to equality fosters a sense of belonging and loyalty to the nation-state.
While democratic states strive for an inclusive national identity, in practice, challenges may arise. Striking the right balance between preserving cultural diversity and fostering a cohesive national identity can be complex. Additionally, external factors, such as globalization and immigration, may influence the evolution of national identities over time. Nevertheless, democratic states aim to create a sense of shared identity that accommodates their diverse populations while upholding democratic values.
Q3: Explain the provisions of the Indian Constitution related to citizenship and how they aim to protect against discrimination.
Ans: The Indian Constitution contains provisions related to citizenship that emphasize inclusivity and the protection of citizens from discrimination. These provisions are primarily outlined in Part II of the Constitution, which deals with citizenship.
Here are some key provisions and how they aim to prevent discrimination:
- Acquisition of Citizenship: The Indian Constitution outlines various modes of acquiring citizenship, including by birth, descent, registration, naturalization, or the incorporation of territory. These provisions ensure that individuals from diverse backgrounds can become Indian citizens.
- Prohibition of Discrimination: Article 15 of the Indian Constitution explicitly prohibits discrimination on grounds of religion, race, caste, sex, place of birth, or any of them. This provision ensures that all citizens are treated equally under the law, regardless of their background.
- Equality Before the Law: Article 14 guarantees equality before the law, ensuring that all citizens are subject to the same legal framework and have equal protection of their rights.
- Protection of Minorities: The Indian Constitution contains provisions to protect the rights of religious and linguistic minorities. Article 29 and Article 30 safeguard the educational and cultural rights of minorities, ensuring that they can preserve their distinct identity within the broader Indian society.
- Right to Freedom of Religion: Article 25 to Article 28 of the Constitution protect the freedom of religion, allowing individuals to practice their faith without interference. This protection is crucial for religious minorities.
These provisions in the Indian Constitution aim to create a fair and inclusive citizenship framework, preventing discrimination based on various factors such as religion, caste, gender, or place of birth. They reflect India's commitment to ensuring equal rights and protection for all its citizens, regardless of their diverse backgrounds.
Q4: Analyze the idea that national citizenship should be complemented with global citizenship, emphasizing the need for collaboration and interconnectedness beyond national borders.
Ans: The idea of complementing national citizenship with global citizenship emphasizes that individuals should not only identify with their own nation but also recognize their membership in a broader global community. This concept underscores the need for collaboration, interconnectedness, and a shared responsibility to address global challenges that transcend national borders.
Here's an analysis of this idea:
- Interconnected World: In today's highly interconnected world, events and issues in one part of the globe can have far-reaching consequences for people in other regions. This interdependence highlights the need for individuals to view themselves as global citizens who are part of a broader human family.
- Addressing Global Challenges: Many global challenges, such as climate change, pandemics, poverty, terrorism, and human rights violations, require collective action by people and governments across different countries. Global citizenship fosters a sense of responsibility to contribute to solutions for these challenges, transcending national interests.
- Human Rights and Universal Values: Global citizenship promotes the idea that certain rights and values, such as the protection of human rights and environmental sustainability, should be universal. This perspective encourages individuals to advocate for these principles beyond their national boundaries.
- Cultural Exchange and Understanding: Global citizenship encourages cultural exchange, fostering understanding and empathy between people from diverse backgrounds. It emphasizes the importance of respecting cultural differences while finding common ground based on shared values.
- Social and Economic Development: Collaborative efforts on a global scale can lead to social and economic development for all. Global citizenship involves recognizing the interconnectedness of economies and working to reduce global inequalities.
- Humanitarian Assistance: Global citizenship emphasizes the obligation to provide assistance to individuals in crisis, whether due to natural disasters, conflicts, or other emergencies. It calls for international solidarity and support.
- Transnational Challenges: Many challenges, such as cybercrime and cyber warfare, transcend national borders. Global citizenship involves recognizing the need for international cooperation to address these issues effectively.
In conclusion, the concept of global citizenship complements national citizenship by emphasizing interconnectedness, shared responsibility, and a commitment to addressing global challenges. It promotes collaboration beyond national borders and recognizes the importance of working together for the well-being of all humanity. This perspective is essential in an increasingly globalized world where local and global issues are intertwined.
|
43 videos|268 docs|39 tests
|




















