Worksheet Solutions: Nationalism | Political Science Class 11 - Humanities/Arts PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Fill in the Blanks |

|
| Match the Column |

|
| Assertion and Reason Based |

|
| Very Short Answer Type Questions |

|
| Short Answer Type Questions |

|
| Long Answer Type Questions |

|
Fill in the Blanks
Q1: Nationalism has played a significant role in shaping history over the past __________ centuries.
Ans: two
The text mentions that nationalism has been significant in shaping history over the past two centuries.
Q2: In the 19th century, nationalism led to the unification of small kingdoms into larger __________ in Europe.
Ans: nation-states
The 19th-century nationalism resulted in the formation of larger nation-states.
Q3: Nationalists in India invoked its ancient cultural heritage and __________.
Ans: achievements
Nationalists in India emphasized India's cultural heritage and achievements to bolster their claims.
Q4: Nations identify with a particular __________ that they claim as their own.
Ans: territory
Nations have a strong association with a specific geographical territory.
Q5: The aspiration for a homeland has been a major cause of __________ in the world.
Ans: conflict
The text discusses how the desire for a homeland often leads to conflicts due to competing claims.
Q6: National self-determination refers to a nation's right to __________ themselves.
Ans: govern
Self-determination implies a nation's right to govern itself.
Q7: After World War I, the Treaty of Versailles led to the establishment of several small, newly independent __________.
Ans: states
The Treaty of Versailles resulted in the establishment of new states.
Q8: Most states in the world have multiple ethnic and cultural communities within their __________.
Ans: borders
The text mentions that states have various communities within their borders.
Q9: Creating new states may not be the solution; instead, making existing states more __________ and equitable is key.
Ans: democratic
The text argues that improving the existing states' democratic and equitable aspects is a solution to self-determination issues.
Q10: Some countries have granted group rights to safeguard the language, cultures, and religion of __________ groups.
Ans: minority
Group rights are often granted to protect the interests of minority communities.
Match the Column
Q1: Match the terms in Column A with their corresponding definitions in Column B.
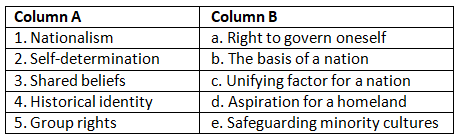 Ans: 1. Nationalism - c. Unifying factor for a nation
Ans: 1. Nationalism - c. Unifying factor for a nation
Nationalism is the ideology or sentiment that promotes the interests and culture of a particular nation. It often serves as a unifying force, bringing people with a shared identity, culture, and history together to work towards common goals.
2. Self-determination - a. Right to govern oneself
Self-determination is the concept that a nation or a group of people has the right to determine their own political status, make their own choices, and govern themselves without external interference. It's about the right to control one's own destiny.
3. Shared beliefs - b. The basis of a nation
Shared beliefs refer to the common values, ideas, and principles that bring a group of people together and serve as the foundation of a nation. These shared beliefs can include political, cultural, or moral values that bind a nation's citizens.
4. Historical identity - d. Aspiration for a homeland
Historical identity is often linked to a group of people's collective memory and their shared historical experiences. It can include the desire to have a homeland where people from that group can live and preserve their cultural heritage, which aligns with the aspiration for a homeland.
5. Group rights - e. Safeguarding minority cultures
Group rights are rights that pertain to specific communities or minority groups within a larger society. These rights are often aimed at protecting and preserving the cultural, linguistic, and social identities of these minority groups, which includes safeguarding minority cultures.
Assertion and Reason Based
Q1: Assertion: Nationalism has played a significant role in shaping history.
Reason: It has been a source of both unity and division among people.
(a) Both assertion and reason are true, and the reason is the correct explanation of the assertion.
(b) Both assertion and reason are true, but the reason is not the correct explanation of the assertion.
(c) The assertion is true, but the reason is false.
(d) Both assertion and reason are false.
Ans: (b)
Nationalism has indeed shaped history, and the reason is true, but it doesn't directly explain why nationalism has played this role.
Q2: Assertion: The right to self-determination has led to border conflicts and violence in many countries.
Reason: Creating new states is the only solution to issues of self-determination.
(a) Both assertion and reason are true, and the reason is the correct explanation of the assertion.
(b) Both assertion and reason are true, but the reason is not the correct explanation of the assertion.
(c) The assertion is true, but the reason is false.
(d) Both assertion and reason are false.
Ans: (b)
While self-determination can lead to conflicts, the assertion that creating new states is the only solution is not entirely accurate.
Q3: Assertion: Many movements strive for the recognition of group identities, using the language of nationalism.
Reason: In a democratic system, political identity should encompass various identities.
(a) Both assertion and reason are true, and the reason is the correct explanation of the assertion.
(b) Both assertion and reason are true, but the reason is not the correct explanation of the assertion.
(c) The assertion is true, but the reason is false.
(d) Both assertion and reason are false.
Ans: (a)
The reason explains why movements use nationalism to seek recognition for group identities in a democratic system.
Q4: Assertion: Granting independent statehood to every distinct cultural group would be practical and wise.
Reason: It ensures the protection of cultural diversity.
(a) Both assertion and reason are true, and the reason is the correct explanation of the assertion.
(b) Both assertion and reason are true, but the reason is not the correct explanation of the assertion.
(c) The assertion is true, but the reason is false.
(d) Both assertion and reason are false.
Ans: (c)
Granting independent statehood to every distinct cultural group is often impractical and unwise due to various reasons, including the potential for conflict.
Very Short Answer Type Questions
Q1: Define nationalism.
Ans: Nationalism is a belief in and loyalty to one's nation, often involving a shared cultural, historical, or political identity.
Q2: What is the basis of a nation's historical identity?
Ans: A nation's historical identity is based on the sense of continuing historical identity and unity of its people.
Q3: How does territory contribute to a sense of collective identity?
Ans: Territory provides a physical space where people with a shared identity live, contributing to their collective identity.
Q4: Explain the concept of "one culture, one state."
Ans: "One culture, one state" is the idea that each cultural group should have its own independent state, which can lead to conflicts over territory.
Q5: What is the right to self-determination?
Ans: The right to self-determination is a nation's right to govern itself and control its own development.
Q6: What challenges do minority communities within states often face?
Ans: Minority communities often face disadvantages, including unequal treatment and lack of representation.
Q7: Why is creating new states not always the solution to self-determination issues?
Ans: Creating new states can lead to conflicts, migrations, and other problems. It may not address self-determination effectively.
Q8: What are group rights in the context of nationalism?
Ans: Group rights involve safeguarding the language, cultures, and religion of minority groups and their members through constitutional protection.
Q9: Why is it important to recognize different groups as part of the national community?
Ans: Recognition of different groups promotes inclusivity, diversity, and social harmony within a nation.
Q10: Why is it risky to allow intolerant and homogenizing forms of identity and nationalism to emerge in a democratic system?
Ans: Tolerant and inclusive forms of identity and nationalism are essential for democratic values and peaceful coexistence.
Short Answer Type Questions
Q1: Discuss the role of nationalism in shaping history and its impact on unity and division.
Ans: Nationalism has both united and divided people, leading to the formation of nation-states and conflicts.
Q2: Explain the concept of an "imagined" community as it relates to nations.
Ans: Nations are "imagined" communities based on shared beliefs, not physical attributes, as people believe they belong together.
Q3: Describe the historical basis of a nation and how it is invoked by nationalists.
Ans: Nations are based on a sense of continuing historical identity, and nationalists often emphasize this historical identity to support their claims.
Q4: Discuss the challenges that arise when multiple cultural groups lay claim to the same territory.
Ans: Competing claims to the same territory can lead to conflicts and disputes, making it a challenge to establish clear borders.
Q5: Analyze the consequences of the "one culture, one state" ideal in Europe after World War I.
Ans: The "one culture, one state" ideal resulted in mass migrations, border conflicts, and the creation of new states in Europe.
Q6: How has the right to self-determination led to conflicts and migrations in the world?
Ans: The right to self-determination has often led to conflicts and migrations when different groups seek their own independent states.
Q7: What is the paradox concerning self-determination and nation-states?
Ans: The paradox is that nation-states that have achieved independence sometimes oppose self-determination for minority groups within their borders.
Q8: Why is making existing states more democratic and equitable considered a solution to self-determination issues?
Ans: This approach can address self-determination concerns while maintaining the integrity of existing states and promoting inclusivity.
Long Answer Type Questions
Q1: Provide a detailed explanation of the different elements that constitute a nation, including shared beliefs, history, territory, shared political ideals, and common political identity.
Ans: A nation is a complex entity formed by various elements that contribute to its identity and coherence.
These elements include:
- Shared Beliefs: Shared beliefs are the cornerstone of a nation. They encompass common values, cultural practices, and a collective identity that binds individuals together. These beliefs can be religious, cultural, or ideological. For example, a shared belief in democracy, freedom, or a particular religion can be a unifying factor within a nation.
- History: History plays a crucial role in defining a nation. It encompasses a sense of continuing historical identity, which means that people within a nation share a common historical narrative. They often refer to historical events, figures, and achievements as a source of pride and identity. For instance, Indian nationalists invoke the rich history and achievements of ancient India to assert their national identity.
- Territory: A specific territory is another defining element of a nation. People who identify as part of a nation typically reside in a particular geographical region or territory. Living together in this space over a long period of time contributes to a sense of collective identity. The aspiration for a homeland is a powerful force in the formation of nations, and disputes over territory can lead to conflicts.
- Shared Political Ideals: Nations often share a set of political values and ideals that they aspire to uphold. These values can include principles like democracy, human rights, and the rule of law. A collective vision for the future and the aspiration to have an independent political existence distinguish nations from mere social or cultural groups.
- Common Political Identity: A common political identity is an integral aspect of a nation. It involves citizens of a nation identifying themselves with the political institutions and legal framework that govern their lives. In a democratic context, individuals are bound by a set of obligations to each other through the shared political identity, which includes being part of the same nation-state.
The interaction and interplay of these elements are what create a nation. These elements are not static but evolve over time, adapting to changing circumstances and historical events. Together, they form the foundation of a nation's identity and serve as a source of unity and shared purpose among its people.
Q2: Discuss the challenges faced by minority communities within states and the importance of accommodating them as equal citizens.
Ans: Minority communities within states often face a range of challenges due to their distinct cultural, religious, or ethnic identities.
These challenges can include:
- Discrimination: Minority communities may face discrimination, prejudice, and unequal treatment in various aspects of life, including education, employment, and access to public services. Discrimination can hinder their social and economic progress.
- Marginalization: Minority communities may be marginalized in the political process, leading to underrepresentation in legislative bodies and decision-making institutions. This can result in a lack of influence and a feeling of exclusion.
- Cultural Preservation: Minority communities often strive to preserve their distinct cultures, languages, and traditions. However, assimilationist policies may threaten these efforts, causing concern about the loss of cultural heritage.
- Lack of Access to Resources: Minority communities may have limited access to resources, economic opportunities, and infrastructure development. This can perpetuate poverty and socio-economic disparities.
- Violence and Conflict: In some cases, minority communities face violence, persecution, or even ethnic or religious conflict. These conflicts can have devastating consequences for the affected communities.
Accommodating minority communities as equal citizens is crucial for several reasons:
- Promoting Inclusivity: Inclusivity ensures that all members of society, regardless of their cultural or ethnic backgrounds, can participate in the social, economic, and political life of the nation.
- Strengthening Social Cohesion: Accommodating minority communities fosters social harmony and unity. It reduces the likelihood of inter-group conflicts and promotes peaceful coexistence.
- Respecting Human Rights: Equal treatment and respect for minority rights are fundamental principles of human rights. States are expected to protect and promote these rights as signatories to international agreements.
- Enriching Diversity: Diversity within a nation enriches its cultural tapestry and can be a source of strength. It allows for the exchange of ideas, traditions, and perspectives, leading to a more vibrant society.
- Fostering Economic Development: Empowering minority communities can enhance economic development by leveraging the skills, knowledge, and contributions of all citizens.
Accommodating minority communities requires policies and practices that ensure equal rights, representation, and opportunities for all citizens, regardless of their background. It also involves recognizing and valuing the contributions of minority communities to the nation's cultural and social fabric.
Q3: Explain why granting independent statehood to every distinct cultural group is considered impractical and unwise. Provide examples.
Ans: Granting independent statehood to every distinct cultural group is considered impractical and unwise for several reasons:
- Border Complexities: Creating numerous small states can lead to complex border issues. Identifying and demarcating clear borders can be challenging, and disputes may arise over territory.
- Resource Distribution: Dividing a region into multiple states can lead to disputes over the distribution of resources, including land, water, and natural resources. These disputes can escalate into conflicts.
- Economic Viability: Smaller states may struggle to achieve economic viability. They may lack the resources and infrastructure needed for sustainable development.
- Interconnected Communities: Many regions have interconnected communities with shared histories and familial ties. Dividing these communities can lead to social disruption and migration.
- Security Concerns: Small states may have limited capacity to defend themselves, making them vulnerable to external threats or influence.
- Ethnic Conflict: Granting independence solely based on ethnicity can lead to ethnic conflict and violence as different groups may lay claim to the same territory. For example, the breakup of Yugoslavia in the 1990s resulted in ethnic conflict and the creation of several new states.
- International Recognition: The international community may not readily recognize every new state, leading to diplomatic and geopolitical challenges. Some states may face isolation if not recognized.
- Fragmentation: Excessive state fragmentation can lead to administrative and governance challenges. It may become difficult to maintain effective governance and deliver public services.
- Economic Interdependence: In a globalized world, states are often economically interdependent. Creating multiple small states may disrupt economic relationships, trade, and cooperation.
- Political and Legal Complexities: The process of creating new states involves complex legal and political procedures, including constitutional reforms, recognition by the international community, and establishing governance structures.
An example of the challenges of granting independent statehood is the case of South Sudan. While South Sudan gained independence from Sudan in 2011, it has faced significant political and economic challenges, including internal conflicts and a struggling economy.
Q4: In the context of the right to self-determination, discuss the idea that creating new states may not be the ultimate solution and how making existing states more democratic and equitable can address the issues.
Ans: The right to self-determination is often linked to the desire for independence and the creation of new states. However, creating new states is not always the ultimate solution to issues of self-determination.
Several factors make this approach less practical:
- Border Disputes: Creating new states often involves redrawing borders, which can lead to border disputes and conflicts. Neighboring states may resist the creation of a new state, leading to tension and potential violence.
- Resource Conflicts: New states may vie for control of valuable resources, such as oil, water, or land, leading to disputes and resource-related conflicts.
- Ethnic and Minority Groups: Within the new state, ethnic and minority groups may continue to face discrimination or oppression, perpetuating the same issues that the self-determination movement sought to address.
- Economic Viability: Newly formed states may struggle to achieve economic viability, as they often lack the infrastructure and resources needed for sustainable development.
- Global Recognition: Not all new states may gain international recognition, which can impact their diplomatic relations and economic interactions with the rest of the world.
Instead of solely focusing on creating new states, an alternative approach is to make existing states more democratic and equitable. This approach has several advantages:
- Inclusivity: Ensuring that all citizens have equal rights and opportunities within an existing state promotes inclusivity and social harmony.
- Diverse Representation: A more democratic state can accommodate the diverse voices and perspectives of its citizens, reducing the feeling of marginalization among minority groups.
- Peaceful Coexistence: A democratic and equitable state is more likely to foster peaceful coexistence among different communities and reduce the potential for conflicts.
- Resource Sharing: Equitable resource-sharing arrangements can address grievances related to access to resources and mitigate resource-based conflicts.
- International Standing: Established states with a commitment to democracy and equity are more likely to gain international recognition and support.
- Administrative Efficiency: Maintaining existing states can be administratively more efficient, as established institutions and governance structures are already in place.
A case in point is post-apartheid South Africa, which transitioned from a system of racial segregation to a democratic, inclusive state. The process of making the existing state more democratic and equitable, instead of creating separate racial states, helped resolve many of the nation's long-standing issues.
In summary, while self-determination is a valid aspiration, creating new states is not always the most practical solution. A focus on improving the governance and inclusivity of existing states can often address the issues associated with self-determination more effectively, leading to peaceful coexistence and stability.
|
43 videos|268 docs|39 tests
|
FAQs on Worksheet Solutions: Nationalism - Political Science Class 11 - Humanities/Arts
| 1. What is nationalism and why is it important in the context of humanities/arts? |  |
| 2. How does nationalism impact the field of humanities/arts? |  |
| 3. Can nationalism lead to cultural homogeneity in the field of humanities/arts? |  |
| 4. How does nationalism impact the global art scene? |  |
| 5. How can nationalism be balanced with internationalism in the field of humanities/arts? |  |















