Overview: Progressions (Sequences & Series) | Quantitative Aptitude (Quant) - CAT PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Introduction |

|
| Sequence and Series Definition |

|
| Types of Sequence and Series |

|
| Sequence and Series Formulas |

|
| Difference Between Sequences and Series |

|
| Sequence and Series Examples |

|
Introduction
Sequence and series are the basic topics in Arithmetic. An itemized collection of elements in which repetitions of any sort are allowed is known as a sequence, whereas a series is the sum of all elements. An arithmetic progression is one of the common examples of sequence and series.
- In short, a sequence is a list of items/objects which have been arranged in a sequential way.
- A series can be highly generalized as the sum of all the terms in a sequence. However, there has to be a definite relationship between all the terms of the sequence.
Sequence and Series Definition
A sequence is an arrangement of any objects or a set of numbers in a particular order followed by some rule. If a1, a2, a3, a4,……… etc. denote the terms of a sequence, then 1,2,3,4,…..denotes the position of the term.
A sequence can be defined based on the number of terms i.e. either finite sequence or infinite sequence.
If a1, a2, a3, a4, ……. is a sequence, then the corresponding series is given by
SN = a1+a2 + a3 + .. + aN
Note: The series is finite or infinite depending if the sequence is finite or infinite.
Types of Sequence and Series
Some of the most common examples of sequences are:
- Arithmetic Sequences
- Geometric Sequences
- Harmonic Sequences
- Fibonacci Numbers
Arithmetic Sequences
A sequence in which every term is created by adding or subtracting a definite number to the preceding number is an arithmetic sequence.
Geometric Sequences
A sequence in which every term is obtained by multiplying or dividing a definite number with the preceding number is known as a geometric sequence.
Harmonic Sequences
A series of numbers is said to be in harmonic sequence if the reciprocals of all the elements of the sequence form an arithmetic sequence.
Fibonacci Numbers
Fibonacci numbers form an interesting sequence of numbers in which each element is obtained by adding two preceding elements and the sequence starts with 0 and 1. Sequence is defined as, F0 = 0 and F1 = 1 and Fn = Fn-1 + Fn-2
Sequence and Series Formulas
List of some basic formula of arithmetic progression and geometric progression are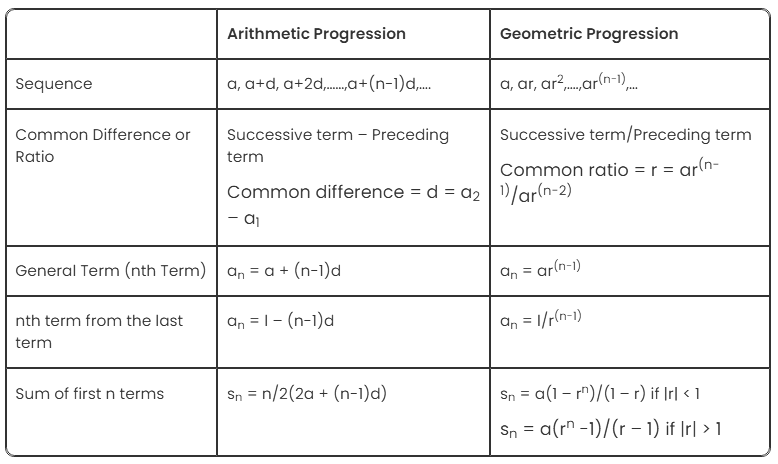
*Here, a = first term, d = common difference, r = common ratio, n = position of term, l = last term
Difference Between Sequences and Series
Let us find out how a sequence can be differentiated with series.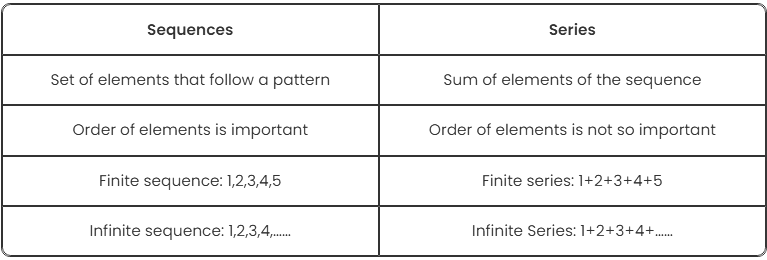
Sequence and Series Examples
Question 1: If 4,7,10,13,16,19,22……is a sequence, Find:
(a) Common difference
(b) nth term
(c) 21st term
Sol: Given sequence is, 4,7,10,13,16,19,22……
(a) The common difference = 7 – 4 = 3
(b) The nth term of the arithmetic sequence is denoted by the term Tn and is given by Tn = a + (n-1)d, where “a” is the first term and d is the common difference.
Tn = 4 + (n – 1)3 = 4 + 3n – 3 = 3n + 1
(c) 21st term as: T21 = 4 + (21-1)3 = 4+60 = 64.
Q2: Consider the sequence 1, 4, 16, 64, 256, 1024….. Find the common ratio and 9th term.
Sol: The common ratio (r) = 4/1 = 4
The preceding term is multiplied by 4 to obtain the next term.
The nth term of the geometric sequence is denoted by the term Tn and is given by Tn = ar(n-1) where a is the first term and r is the common ratio.
Here a = 1, r = 4 and n = 9
So, 9th term is can be calculated as T9 = 1* (4)(9-1)= 48 = 65536.
|
166 videos|231 docs|95 tests
|
FAQs on Overview: Progressions (Sequences & Series) - Quantitative Aptitude (Quant) - CAT
| 1. What is the difference between a sequence and a series? |  |
| 2. What are the types of sequences? |  |
| 3. How can I differentiate between a geometric sequence and an arithmetic sequence? |  |
| 4. What is the formula for a geometric sequence? |  |
| 5. What can the GMAT ask us to do with sequences and series? |  |















