Components of Our Food Chapter Notes | Eureka Plus Class 6: Book Solutions, Notes & Worksheets PDF Download
Introduction
The human body requires various nutrients to stay healthy. These essential nutrients include carbohydrates, fats, proteins, vitamins, minerals, fiber, and water. Each type plays a unique role in keeping our bodies functioning properly.
Key Points
- Importance of Nutrients: Our bodies need different nutrients like carbs, fats, proteins, vitamins, minerals, fiber, and water for various functions.
- Variety in Foods: Nature offers us a wide range of foods, each containing its own set of nutrients. For example, fruits provide vitamins, while meat is a source of protein.
- Diet Diversity: It's crucial to have a diverse diet because no single food item can provide all the nutrients necessary for good health. By eating a variety of foods, we ensure we get all the essential nutrients our bodies need.
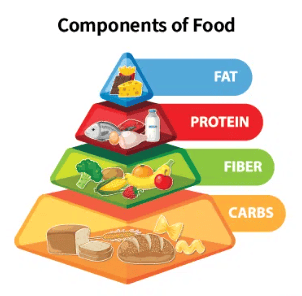
Carbohydrates for Energy
Carbohydrates are like fuel for our bodies, giving us the energy we need to stay active and function properly. They are found in many foods we eat, such as rice, wheat, and potatoes.
Here are some key points about carbohydrates:
- Carbohydrates are in foods like rice, wheat, potatoes, and bananas.
- They provide the energy our bodies need to do things like running, playing, and even thinking.
- Carbohydrates are also in foods like sugar cane and sweet potatoes.
- Most foods from plants have carbohydrates in them.
Fats, an Essential Part of Our Diet

Fats are another important type of nutrient that our bodies require for various reasons. They help with brain function, cell production, and even keeping us warm.
Here are some details about fats:
- Fats are needed to help our brains work well and to keep our bodies warm.
- They are in foods like nuts, seeds, oils, and fish.
- Small amounts of fats are all our bodies need to stay healthy.
- Fats are also important for helping our bodies absorb certain vitamins.
Proteins for Growth and Repair
- Proteins are like building blocks for our body, found in foods like milk, cheese, meat, fish, eggs, nuts, and beans.
- Our bones, muscles, and tissues are made up of proteins.
- The body needs proteins to grow and fix parts that are hurt or old.
Vitamins for Health
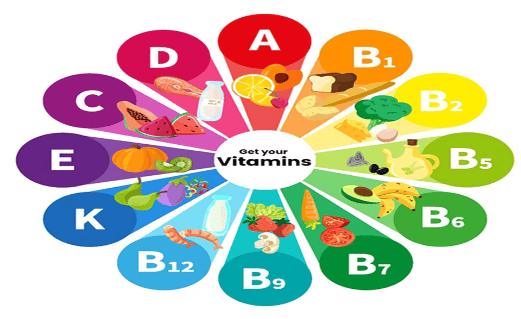
- Vitamins are important for helping us grow, stay healthy, and fight sickness.
- We only need a little bit of vitamins, and most foods have them.
Types of Vitamins, Their Functions, and Sources
- Vitamin A: Helps keep our eyes, skin, muscles, brain, and nerves healthy.
- Vitamin B Complex: Aids in making red blood cells, and keeps our gums and skin in good shape.
- Vitamin C: Assists in healing cuts and boosts our immunity.
- Vitamin D: Makes our bones and teeth strong and healthy.
Food Sources of Vitamins
- For Vitamin A: Carrots, leafy green vegetables, mangoes, tomatoes, papayas, liver, eggs, fish, and butter.
- For Vitamin B: Whole grains, nuts, beans, peas, soybeans, milk, curd, liver, meat, fish, eggs, and spinach.
- For Vitamin C: Fresh lemon, orange, sweet lime, tomato, spinach, and gooseberry.
- For Vitamin D: Fish, cod liver oil, eggs, mushrooms, and sunlight (your body makes Vitamin D when exposed to sunlight).
Minerals for growth and strength
Minerals are essential nutrients required by our bodies for growth and overall health. They are found in various foods we consume, each playing a specific role in maintaining our well-being.
Calcium
- Calcium is crucial for making our bones and teeth strong.
- Foods rich in calcium include milk, cheese, curd, ragi, green leafy vegetables, and soya beans.
- For example, think of calcium as the builder that constructs sturdy bones and teeth in our body.
Iron
- Iron is necessary for the production of red blood cells (RBCs).
- Good sources of iron are green leafy vegetables, whole wheat, nuts, pulses, apples, fish, liver, and meat.
- Imagine iron as the painter that colors our blood cells red, ensuring they can carry oxygen effectively throughout our body.
Potassium
- Potassium plays a role in maintaining the health of our brain, nerves, and muscles.
- It also helps in balancing the water content in our body.
- Foods like tomatoes, green leafy vegetables, bananas, dates, jaggery, beans, fruits, and fish are rich in potassium.
- Picture potassium as the conductor that harmonizes the activities of our brain, nerves, and muscles, ensuring they work in sync.
Iodine
- Iodine is essential for proper body growth.
- It can be sourced from fish, shellfish, vegetables, fruits grown in coastal areas, and iodized salt.
- Think of iodine as the architect that oversees the construction of a healthy body, ensuring all parts grow and develop as they should.
Fiber
- Fiber, found in fresh vegetables, fruits, and whole grains, is essential for our digestive system.
- On the other hand, animal-based foods lack fiber.
- While fiber itself doesn't give us nutrients, it plays a crucial role in eliminating waste from our bodies.
- Fiber is like the cleaning crew for your digestive system, sweeping out waste and keeping things moving smoothly.
- Examples: Spinach, apples, brown rice
Water
- Our bodies are about 60% water, and it's vital for keeping us healthy and functioning properly.
- We lose water through urine, sweat, and even in the water vapor we breathe out.
- Drinking enough clean water is crucial for our well-being.
- Reasons why we need water:
- It's a big part of our blood and every single cell in our bodies.
- Water helps regulate our body temperature, keeping us cool when it's hot and warm when it's cold.
- It aids in digestion, making it easier for our bodies to break down and absorb nutrients from food.
- Water is essential for cleaning our blood by forming urine, which carries away waste and toxins.
- Examples: Drinking water, eating water-rich foods like watermelon, cucumber
Balanced Diet

- A balanced diet is when you eat different types of foods that give your body all the nutrients it needs in the right amounts.
- A balanced diet helps your body grow properly and keeps you healthy. It's like giving your body all the tools it needs to work well.
- Factors Influencing Daily Diet:
- Age: Children need more protein for growth and energy from carbohydrates because they are active.
- Activity Level: People who do a lot of physical work, like athletes, need more carbohydrates for energy. Those with sedentary jobs, like office workers, should limit carb-rich foods and sugary drinks.
- Examples:
- Child: A child needs proteins for growth and carbohydrates for energy because they are always moving and playing.
- Athlete: A football player needs lots of carbohydrates to stay energized during games.
- Office Worker: Someone who sits at a desk most of the day needs less carbs and should avoid sugary drinks to stay healthy.
- Tips for a Balanced Diet:
- Choose a variety of foods to get different nutrients.
- Eat fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins.
- Limit sugary drinks and sweets.
Overweight and underweight
- Overweight: When you eat more food than your body needs for a long time, your body stores the extra nutrients and you gain weight. This can increase your risk of developing heart diseases and diabetes. For example, if you consistently eat large portions of unhealthy food like fast food and sugary snacks, you might become overweight over time.
- Underweight: Eating too little for an extended period means you're not taking in enough nutrients for your body's needs. This can lead to being underweight and suffering from malnutrition. For instance, if you're skipping meals regularly or not eating enough fruits and vegetables, you could become underweight and lack essential vitamins and minerals.
- Health Impact: Being either overweight or underweight can harm your health. It's essential to maintain a balanced diet with the right amount of nutrients to keep your body healthy and functioning properly. This means eating a variety of foods in appropriate portions to support your overall well-being.
Malnutrition
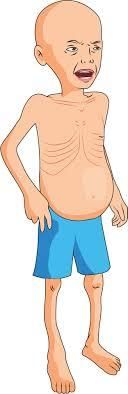
- Malnutrition: When the body lacks important nutrients like carbs, fats, proteins, vitamins, and minerals due to an inadequate diet.
- Protein-Energy Malnutrition: In children under two years old, a diet deficient in carbs, fats, and proteins can lead to this condition. Children with this form of malnutrition don't gain weight, appear weak with arms and legs looking very thin, lack energy, seem dull, and fall sick frequently. This type is known as marasmus.
- Kwashiorkor: Some children may have diets with enough carbs and fats but insufficient proteins. These children might have thin reddish hair, swollen feet and hands, and a protruding stomach. Even if they don't appear thin, they are not as active as other kids their age. This condition is called kwashiorkor.
- Recovery: By ensuring children receive adequate amounts of carbohydrates, fats, and proteins in their daily diets, they can recover from malnutrition and regain their health.
Deficiency Diseases
Deficiency diseases occur when the body lacks essential nutrients over a prolonged period, resulting in specific health issues. This includes conditions like night blindness, rickets, goitre, scurvy, and anemia. Let's delve into each of these diseases to understand their symptoms, causes, and prevention methods.
Night Blindness
- Symptom: Difficulty seeing clearly in low light.
- Cause: Night blindness is caused by a deficiency of vitamin A.
- Prevention: Consuming foods rich in vitamin A like carrots, papayas, mangoes, pumpkins, spinach, liver, and fish can help prevent night blindness.
Rickets
- Symptoms: Soft and twisted bones, 'bow legs', 'knock knees', 'pigeon chest', weak muscles, and susceptibility to infections.
- Cause: Rickets is caused by a deficiency of vitamin D and calcium in growing children.
- Prevention: Including vitamin D and calcium-rich foods like milk in the daily diet and ensuring exposure to sunlight for vitamin D synthesis can prevent rickets.
Goitre
- Symptoms: Enlarged thyroid gland leading to dwarfism in children, poor academic performance.
- Cause: Goitre is caused by iodine deficiency.
- Prevention: Including iodised salt and iodine-rich foods such as shrimp, fish, eggs, and potatoes in the diet can prevent goitre.
Scurvy
- Symptoms: Swollen or bleeding gums, slow wound healing, and in severe cases, it can be fatal.
- Cause: Scurvy is caused by a lack of vitamin C.
Anemia
- Symptoms: Pale skin, pale nails, dark patches under eyes, fatigue, headaches, and low hemoglobin levels.
- Cause: Anemia results from iron deficiency in the diet, which can be exacerbated by worm infections and malaria.
- Prevention: Preventing anemia involves consuming iron-rich foods like leafy vegetables, pulses, cereals, meat, liver, and fish. Additionally, controlling worm infections is crucial for effective treatment.
|
22 videos|80 docs|16 tests
|
FAQs on Components of Our Food Chapter Notes - Eureka Plus Class 6: Book Solutions, Notes & Worksheets
| 1. What are the main components of our food? |  |
| 2. Why are carbohydrates important in our diet? |  |
| 3. How do proteins help our body? |  |
| 4. Why do we need fats in our diet? |  |
| 5. What role do vitamins and minerals play in our diet? |  |
















