Textbook Solutions: Getting to Know Plants | Eureka Plus Class 6: Book Solutions, Notes & Worksheets PDF Download
I. Name the following:
1.
Ans: Taproot
2.
Ans: Fibrous root
3.
Ans: Stem
4.
Ans: Tendril
5.
Ans: Stamen
II. Tick (✔) the correct option.
1.
Ans: (c)
2.
Ans: (d)
3.
Ans: (b)
4.
Ans: (c)
5.
Ans: (a)
III. Answer the following questions in one sentence.
1.
Ans: The function of root hairs is to help the plant absorb water and minerals from the soil.
2.
Ans: The function of the xylem tubes is to transport water from the roots to other parts of the plant.
3.
Ans: The stem of cactus plants is modified to store water and make food.
4.
Ans: Pitcher plants are called insectivorous plants because they have leaves modified to trap insects as a source of nutrients.
5.
Ans: A flower that has sepals, petals, stamens, and pistil is called a complete flower.
6.
Ans: The female part of a flower is called the pistil (or carpel).
IV. Draw well-labeled diagrams of the following:
1.
Ans:

2.
Ans: 
3.
Ans: 
4.
Ans: 
V. Write short notes on the following topics. Support your note with a diagram or an activity wherever necessary.
1.
Ans: The shoot system is a critical component of a plant's anatomy, encompassing the above-ground parts involved in photosynthesis, reproduction, and transport of substances. It consists of the stem, leaves, and reproductive structures like flowers. The stem provides structural support and serves as a conduit for the transport of water, nutrients, and sugars. Leaves are the primary sites of photosynthesis, capturing sunlight and converting it into energy. Reproductive structures, like flowers, produce seeds for the plant's propagation. See the accompanying diagram for a visual representation of the shoot system.
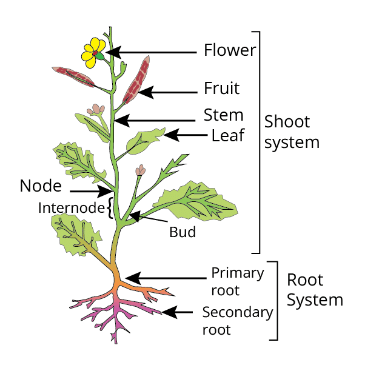
2.
Ans: Photosynthesis is the process by which green plants, algae, and some bacteria convert light energy into chemical energy in the form of glucose. It occurs in the chloroplasts of plant cells, primarily in the leaves. The process involves the absorption of sunlight, carbon dioxide (CO2) uptake, and water absorption. Through a series of complex chemical reactions, oxygen is released as a byproduct, and glucose is synthesized, providing energy for the plant. Photosynthesis sustains life on Earth by producing oxygen and serving as the foundation of the food chain. The diagram below illustrates the key steps of photosynthesis.

3.
Ans: Transpiration is the movement of water from the roots, through the plant, and into the atmosphere. It occurs primarily through small pores called stomata on the surface of leaves. This process helps in the absorption of nutrients and minerals from the soil. Transpiration also plays a crucial role in the regulation of water in plants and the ascent of water in the xylem vessels. It's a vital component of the water cycle, contributing to the continuous circulation of water on Earth. Engaging in a simple activity, such as placing a plastic bag over a leaf and observing the water droplets formed (transpiration experiment), can provide a hands-on understanding of this process.
|
22 videos|80 docs|16 tests
|
FAQs on Textbook Solutions: Getting to Know Plants - Eureka Plus Class 6: Book Solutions, Notes & Worksheets
| 1. What are the different parts of a plant and their functions? |  |
| 2. How do plants reproduce? |  |
| 3. What is photosynthesis and why is it important for plants? |  |
| 4. How do plants adapt to different environments? |  |
| 5. How can we promote plant growth and health in our gardens? |  |
|
22 videos|80 docs|16 tests
|

|
Explore Courses for Class 6 exam
|

|
















