Worksheet Solutions: Government Budget and the Economy- 1 | Economics Class 12 - Commerce PDF Download
Q1: Which of the following is Revenue expenditure?
(a) Construction of school
(b) Borrowings
(c) Grants given to the state governments.
(d) Loans given to the state governments
Ans: c
Q2: ………………………………. Indicates the borrowing requirement of the govt.
(a) Revenue deficit
(b) Budgetary deficit
(c) Fiscal deficit
(d) Primary deficit
Ans: c
Q3: Identify which of the following is not an example of tax revenue for the government. (Choose the correct alternative)
(a) Wealth Tax
(b) Special Assessments
(c) Income Tax
(d) Corporate Tax
Ans: b
Q4: Find out incorrect statement from the following:
(a) A government budget is an estimation of receipts and expenditure for current year.
(b) A government budget is an estimation of receipts and expenditure for next financial year.
(c) Capital receipts decreases assets of the government.
(d) Subsidies are not treated as capital expenditure of the government.
Ans: a
Q5: Which of the following is a basis for comparison between direct and indirect taxes?
(a) Impact
(b) Shift of burden
(c) Coverage
(d) All of the above
Ans: d
Q6: Identify the correct formula to calculate Fiscal Deficit.
(a) Total expenditure - Total Receipt (other than borrowings)
(b) Revenue Expenditure- Revenue Receipt
(c) Capital Expenditure- Capital Receipt
(d) Revenue Expenditure + Capital expenditure - Revenue Receipt.
Ans: A
Q7: Match the item in column A to those in column B and choose the correct option:
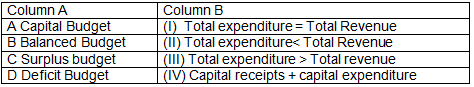
(a) A-(iv), B-(i), C-(ii), D- (iii)
(b) A-(iv), B-(i), C-(iii), D- (ii)
(c) A-(iv), B-(iii), C-(ii), D- (i)
(d) A-(i), B-(iv), C-(ii), D- (iii)
Ans: a
Q8: In a govt. budget, revenue deficit is Rs. 50000 crores and borrowings are Rs.75000 crores. The fiscal deficit will be:
(a) Rs. 25000 crores
(b) Rs.125000 crores
(c) Rs.50000 crores
(d) Rs.75000 crores
Ans: d
Q9: Read the following statements carefully and choose the correct alternatives given below:
Statement 1 – Tax Revenue and non-tax revenue are increasing but recovery of loan is reducing.
Statement 2 –Revenue receipts and capital receipts are decreased from 2019 to 2021
Alternatives:
(a) Both the statements are true.
(b) Both the statements are false.
(c) Statement 1 is true and Statement 2 is false
(d) Statement 2 is true and Statement 1 is false
Ans: c
Q10: Read the following statements – Assertion (A) and Reason (R). Choose one of the correct alternatives given below
Question. Assertion (A): GST is imposed on goods and services and it is an indirect tax.
Reason (R): Indirect taxes are those tax whose money burden cannot be shifted.
(a) Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true, (R) is correct explanation of (A).
(b) Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true but (R) is not correct explanation of (A).
(c) Assertion (A) is true and Reason (R) is false.
(d) Assertion (A) is false and Reason (R) is true.
Ans: c
Q11: Assertion (A): Recovery of loan by the government is capital receipts.
Reason (R): Disinvestment is revenue receipts of the government.
(a) Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true, (R) is correct explanation of (A).
(b) Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true but (R) is not correct explanation of (A).
(c) Assertion (A) is true and Reason (R) is false.
(d) Assertion (A) is false and Reason (R) is true.
Ans: c
Read the following paragraph carefully and Answer: the given questions
Every govt. seeks to control and give direction to economic activities. For this purpose, it may exercise a large number of instruments available to it. Among these instruments, the most important is the fiscal policy, which operates through the financial operations of the government. In modern times the responsibilities and functions of a government have been gradually increasing as the areas of the activity are expanding continuously. It requires more and more finance as the corresponding expenditures are moving northwards. The government has to perform innumerable functions for ensuring economic growth and development of the country for which it has to take care of public revenue and public expenditure.
Q12: Fiscal policy is the policy of the …….
(a) Government
(b) Central Bank
(c) Both govt. and central bank
(d) None of these.
Ans: a
Q13: During the time of inflation, govt. should go for ____ budget.
(a) Deficit
(b) Surplus
(c) Balanced
(d) Capital
Ans: b
Read the following paragraph and Answer: the given questions
In the modern world, govt. aims at maximizing the welfare of the people and the country. It requires various infrastructure and economic welfare activities. These activities require huge govt. spending through appropriate planning and policy. Budget provides a solution to all these concerns. Budget is prepared by the government at all levels.
Estimated expenditure and receipts are planned as per the objectives of the government. In India, budget is prepared by the parliament on such a day as the president may direct. The parliament approves the budget before it can be implemented. The receipts and expenditures as shown in the budget are only the estimated values for the upcoming fiscal year, and not the actual figure.
Q14: Which of the following is not an objective of the govt. budget?
(a) Reallocation of resources.
(b) Re distribution of income
(c) Reducing expenditure
(d) Economic stability.
Ans: c
Q15: Govt. budget is a statement of actual receipts and payments of the govt. (True/False)
a) True
b) False
Ans: b
Short Answer: Question and Answer
Q1: What are the different sources of nontax revenue?
Ans:
- Non tax revenue refers to revenue receipts of the govt. other than the tax revenue.
- Major sources are: - Administrative revenue (Fess, Fines & penalties, Escheats, License fees, forfeitures etc.) Gift & grants, Income from govt. properties, special assessments, interest received, dividends etc.
Q2: Distinguish between revenue receipt and capital receipt.
Ans: Revenue Receipts (RR):
Receipts which neither creates liability nor reduces the assets of the govt.
Major features are:
- It does not create liability to the govt. It does not reduce the assets of the govt.
- They are regular and recurring in nature.
- Major sources are: Tax revenue and Non- tax revenue
Capital Receipts (CR):
- Receipts which either creates liability or reduces the assets of the govt.
Major features:
- It creates liability for the govt. It reduces the assets of the govt.
- They are irregular and non-recurring in nature. For example; disinvestment, recovery of loans, small savings etc.
Q3: Define fiscal deficit and write any three implications of fiscal deficit.
Ans: Fiscal deficit refers to the excess of Budgetary Expenditure over Budgetary receipts, excluding borrowings, during an accounting year.
FD = BE- BR (Excluding borrowings)
Major implications:
- Leads to Debt trap:- Borrowings not only involves repayment of borrowed amount but it also requires payment of interest. Interest payments increases revenue expenditures which leads to revenue deficits, ultimately leads to debt trap.
- Creates inflationary situation in the economy:- Borrowings leads to increase in money supply in the economy creates inflation.
- Foreign dependence:- Govt. borrows money from the foreign countries and foreign financial institutions, which ultimately increases its dependences on these countries and institutions.
- Financial burden on future generations:- If the country did not repay the borrowed amount in time, its burden will go to the future generations, which will hamper the future growth of the country.
Q4: Explain how the govt. is using as an instrument for reducing the inequalities in income.
Ans: Reducing inequality is an inherent part of every economic system.
- By imposing taxes on the rich and through providing welfare programs to the poor people govt. is achieving this goal.
- Also known as redistribution of income & wealth
- Progressive taxes on the rich and through providing job opportunities and also through transfer payments govt. is achieving this goal.
- Govt. also aims to achieve regional equality by providing facilities to the rural areas, basically infrastructural Facilities for bringing balanced growth.
Q5: What do you mean by deficit budget? What are its types?
Ans: Deficit Budget: If Budgetary Receipts are LESS THAN the Budgetary Expenditure of the govt., then it is known as Deficit budget.
BR < BE or TR < TE
Types of budgetary deficits: -
- Revenue Deficit (RD)
- Fiscal Deficit (FD)
- Primary Deficit (PD)
Q6: ‘’Through its budgetary policy govt. allocates resources in accordance with the requirements of the country.’’ Do you agree? Justify your Answer: with valid reason.
Ans: Re-allocation of resources is the major objectives of the govt. Govt. aims to reallocate resources in accordance with the economic and social priorities of the country.
- To encourage investment, govt. gives tax concessions and subsidies etc., to the producers.
- Govt. discourages the production of the harmful goods by imposing heavy taxes and encourages the production of needful goods like ‘khadi products’ by providing subsidies.
- Also undertake production of those goods where private sector does not take interest.
Q7: What do you mean by revenue deficit? Write its implications.
Ans: If Revenue Expenditures are MORE THAN the Revenue Receipts of the govt., then it is known as REVENUE DEFICIT (RD) during an accounting year.
RD = RE - RR or RD= RE > RR
Major implications are: -
- It is a warning signal to the govt. either to reduce the revenue expenditure or to increase the revenue receipts.
- It indicates the inability of the govt. to meet its regular and recurring expenditure.
- It also implies that the govt. has to make up this deficit from capital receipts which may lead to inflationary situation in the economy.
Q8: What do you mean by unbalanced budget? What are its types?
Ans: Un- balanced budget:
If Budgetary Receipts are not equal to the Budgetary Expenditure of the govt., then it is known as un balanced budget. Major TYPES of unbalanced budget are: Surplus Budget & Deficit Budget
Surplus Budget
If Budgetary Receipts are MORE THAN the Budgetary Expenditure of the govt., then it is known as Surplus budget.
BR > BE or TR > TE
Deficit Budget
If Budgetary Receipts are LESS THAN the Budgetary Expenditure of the govt., then it is known as Deficit budget.
BR < BE or TR < TE
Long Answer: Questions
Q1: Define govt. budget and explain its major objectives.
Ans: An annual statement of estimated receipts and estimated expenditure of the govt. during an accounting year (fiscal year).
Major objectives are:
- Re-allocation of resources:
Govt. aims to reallocate resources in accordance with the economic and social priorities of the country.- To encourage investment, govt. gives tax concessions and subsidies etc., to the producers.
- Govt. discourages the production of the harmful goods by imposing heavy taxes and encourages the production of needful goods like ‘khadi products’ by providing subsidies.
- Also undertake production of those goods where pvt. Sector does not take interest.
- Economic equality:
Reducing inequality is an inherent part of every economic system.- By imposing taxes on the rich and through providing welfare programs to the poor people govt. is achieving this goal.
- Also known as redistribution of income & wealth
- Progressive taxes on the rich and through providing job opportunities and also through transfer payments govt. is achieving this goal.
- Govt. also aims to achieve regional equality by providing facilities to the rural areas, basically infrastructural Facilities for bringing balanced growth.
- Economic stability:
- Govt. budget is used to prevent the business fluctuations like booms or depressions (inflations or deflations) to achieve the goal of balanced growth (economic stability).
- The policy of surplus budget during the time of inflation and deficit budget during the time of deflation helps the govt. to achieve this goal.
- Economic Growth:
- Economic growth depends on the rate of saving and investment in the economy. Increase in GDP
- Govt. budget aims to mobilise sufficient resources for investment in the economy.
- Various provisions are making in the govt. budget for increasing the investment in the economy.
- Management of public sector enterprises:
- All public sector enterprises are managed through the govt. budget, functioning for social welfare
Q2: Define tax and differentiate between direct and indirect tax. Give examples
Ans: Tax is a compulsory contribution made by individuals and institutions to the govt. without any direct return.
Direct Tax:
- Taxes that are imposed on property and income of individuals and firms and are directly paid by them to the govt.
- The burden of tax cannot be shifted.
- The Impact and incidence of tax falls on same person.
- For e.g.: - Income tax, property tax etc.
Indirect Tax:
- Taxes that are levied on goods and services.
- The burden of tax can be shifted.
- The Impact and incidence of tax falls on different persons.
- For e.g.: - GST (Goods & Service tax)
Q3: What are the different sources of capital receipts? Explain. 4 marks
Ans: Major sources of capital receipts are:
- Borrowings:
- These are the funds raised by the govt. to meet the excess expenditures.
- Govt. borrows funds from internal sources (RBI, Open market) External sources (Foreign governments, foreign financial institutions like IMF, IBRD etc.)
- Borrowings are capital receipts as they create liability and reduce the assets of the government.
- Disinvestment:
- It refers to the act of selling a part or the whole unit of selected public sector undertakings held by the government to the private agencies.
- It reduces the assets of the govt.
- It leads to transfer of ownership of PSU’s to the private enterprises
- Recovery of loans:
- Govt. provides various loans to the state government’s or UT’s or even to foreign countries.
- Recovery of such loan is a capital receipt as it reduces the assets of the govt.
- Small Savings: Small savings in the form of Post office deposits, NSC are other sources of capital receipts as it leads to an increase in liability.
Q4: Questions are to be Answered on the basis of the data given below (in ₹ Crores) Budget at a Glance
Ans: 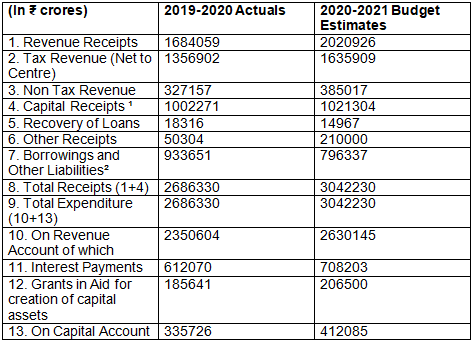
Q5: The percentage change in the Tax Revenue, between 2019- 20 (Actual) and 2020-21 (Budgeted Estimate), taking the 2019-20 as base, would be ____________. (Fill up the blank with correct alternative)
(a) 15.02%
(b) 20.56%
(c) 17.06%
(d) 20.01%
Ans: b
Q6: The value of borrowings and other liabilities has ___________ crores between 2019-20 (Actual) and 2020- 21 (Budgeted Estimate). (Fill up the blank with correct alternative)
(a) Fallen by ₹ 137314
(b) Risen by ₹ 137314
(c) Fallen by ₹ 137324
(d) Risen by ₹ 137324
Ans: a
Q7: The value of borrowings for the year 2020-21, would be ₹ _____________ crores. (Fill up the blank with correct alternative))
(a) 88134
(b) 796337
(c) 933651
(d) 666545
Ans: b
Q8: The percentage change in the Total receipts, between 2019- 20 (Actual) and 2020-21 (Budgeted Estimate), taking the 2020- 21 as base, would be ____________. (Fill up the blank with correct alternative)
(a) 11.70%
(b) 13.14%
(c) 13.24%
(d) 10.01%
Ans: a
Numerical illustrations:
Q1: Estimate the value of RD, FD, & PD (For practice)
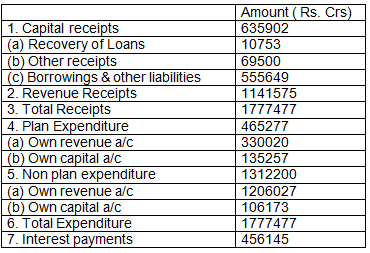
Ans: RD = 394472 Crs FD = 555649 crs PD = 99504 Crs
Q2: Define Balanced, Surplus and Deficit Budgets.
Ans: (a) Balanced Budget:- It is one where the estimated revenue EQUALS the estimated expenditure.
(b) Surplus Budget:- It is one where the estimated revenue is GREATER THAN the estimated expenditures.
(c) Deficit Budget:- It is one where the estimated revenue is LESS THAN the estimated expenditure.
Q3: Explain the four different concepts of Budget deficit.
Ans: These are the four different concepts of Budget Deficit.
(a) Budget Deficit: It is the difference between the total expenditure, current revenue and net internal and external capital receipts of the government.
Formulae: B.D = B.E > B.R (B.D= Budget Deficit, B.E. Budget Expenditure B.R= Budget Revenue
(b) Fiscal Deficit: It is the difference between the total expenditure of the government, the revenue receipts PLUS those capital receipts which finally accrue to the government.
Formulae: F.D = B.E - B.R (B.E > B.R. other than borrowings) F.D=Fiscal Deficit, B.E= Budget Expenditure, B.R. = Budget Receipts.
(c) Revenue Deficit: It is the excess of governments revenue expenditures over revenue receipts.
Formulae: R.D= R.E – R.R., When R.E > R.R., R.D= Revenue Deficit, R.E= Revenue Expenditure, R.R. = Revenue Receipts.
(d) Primary Deficit: It is the fiscal deficit MINUS Interest payments.
Formulae: P.D= F.D – I.P, P.D= Primary Deficit, F.D= Fiscal Deficit, I.P= Interest Payment.
Q4: How is tax revenue different from administrative revenue?
Ans: (a) Tax Revenue:-
(i) It is the main source of revenue of the government
(ii) It is the revenue that arises on account of taxes levied by the government.
(iii)Taxes of two types i.e., Direct and Indirect.
(iv) Direct taxes are those taxes levied immediately on the property and income of persons. Examples: Income Tax, Corporate Tax, Wealth Tax etc., Incidence and impact falls on same person.
(v) Indirect taxes are those taxes levied on the production and sale of the goods.
Examples: Sales Tax, Excise Duty etc. Tax paid by one person but burden taken by another person.
(b) Administrative Revenue:-
(i) It is the revenue that arises on account of the administrative function of the Government.
(ii) (It includesa) Fees
(b) License fees
(c) Fines and penalties
(d) Forfeitures of surety by courts
(e) Escheat – means claim of the government on the property of a person who dies without having any legal heirs.
Q5: What is a balanced government budget? Explain the multiplier effect of a balanced budget.
Ans: (a) Balanced Budget:
It is one where the estimated revenue of the government equals the estimated expenditure.
(b) Effect of Multiplier on the Balanced Budget:
(i) If only source of revenue is a lump sum tax, a balanced budget will then mean that the amount of tax equals the amount of expenditure (T=E)
(ii) A balanced budget has an expansionary effect on the economy.
(iii) Under balanced budget, the increase in income is equalent to the amount of government expenditure financed by tax revenue (i.e., Δ Y =ΔG/ΔT)
(iv) The multiplier effect of a balanced budget is ONE (Unitary)
(v) A balanced budget is a good policy to bring the economy, which is under employment to a full employment equilibrium.
Q6: What are the three levels at which the budget impacts the economy?
Ans: These below are the three levels at which the budget impacts the economy.
(a) Aggregate fiscal discipline:- This means having control over expenditures, given the quantum of revenues. This is necessary for proper macro-economic performance.
(b) Allocation of resources: - The allocation of resources based on social priorities.
(c) Effective and efficient provision of programmes:- Effectiveness measures the extent to which goods and services the government provides its goals.
|
69 videos|380 docs|57 tests
|
FAQs on Worksheet Solutions: Government Budget and the Economy- 1 - Economics Class 12 - Commerce
| 1. What is a government budget and how does it affect the economy? |  |
| 2. What are the components of a government budget? |  |
| 3. How does government spending impact the economy? |  |
| 4. What is the relationship between government budget deficits and national debt? |  |
| 5. How does the government budget impact different sectors of the economy? |  |





















