Worksheet Solutions: Financial Statements - II | Accountancy Class 11 - Commerce PDF Download
MCQs
Q1: The object of non-trading concerns ______.
(a) Social service
(b) Profit earning
(c) Both of these
(d) None of the above
Ans: (a) Social service
Q2: Which of the following is recorded in income and expenditure accounts?
(a) Revenue items
(b) Capital items
(c) Revenue and capital items
(d) None of the above
Ans: (a) Revenue items
Q3: If the rent of one month is still to be paid, the adjustment entry will be _______.
(a) Debit outstanding rent account and Credit rent account
(b) Debit profit and loss account and Credit rent account
(c) Debit rent account and Credit profit and loss account
(d) Debit rent account and Credit outstanding rent account
Ans: (d) Debit rent account and Credit outstanding rent account
Q4: If a person fails to pay his debt, such an amount is considered as ______.
(a) Bad debts
(b) Bad debts recovered
(c) Provision for bad debt
(d) None of the above
Ans: (a) Bad debts
Q5: If the insurance premium paid Rs. 1,000 and prepaid insurance Rs. 300. The amount of insurance premium shown in the profit and loss account will be ______.
(a) Rs. 1,300
(b) Rs. 1,000
(c) Rs. 300
(d) Rs. 700
Ans: (d) Rs. 700
Short Answer Questions
Q1: Why do we need adjustments when preparing financial statements?
Ans: Adjustments are needed in financial statements to show the true profit or loss of a business. This is because some money earned or spent may not be received or paid in cash during the year. If we do not make these adjustments, the financial statements will not reflect the real situation of the business.
Q2: What is the accrual basis of accounting?
Ans: The accrual basis of accounting means we record income when it is earned and expenses when they occur, not when cash is received or paid. This helps to give a clearer picture of a business's financial health, showing all money owed and owed to the business, even if not yet paid.
Q3: What are outstanding expenses?
Ans: Outstanding expenses are costs that a business has incurred but has not yet paid. For example, if a company uses electricity in December but pays the bill in January, that expense is outstanding for December and needs to be recorded in that month’s financial statements.
Q4: What are prepaid expenses?
Ans: Prepaid expenses are payments a business makes for goods or services it will receive in the future. For instance, if a company pays for a year's insurance in advance, that payment is a prepaid expense until the insurance coverage is used over the year.
Q5: What is the effect of not adjusting for accrued incomes?
Ans: If a business does not adjust for accrued income, it will understate its revenue. This means the financial statements will show less money earned than what the business actually made, leading to a misleading view of its profitability and financial position.
Numerical Questions Solutions
Q1: Prepare a trading and profit and loss account for the year ending March 31, 2017. from the balances extracted of M/s Rahul Sons. Also prepare a balance sheet at the end of the year.
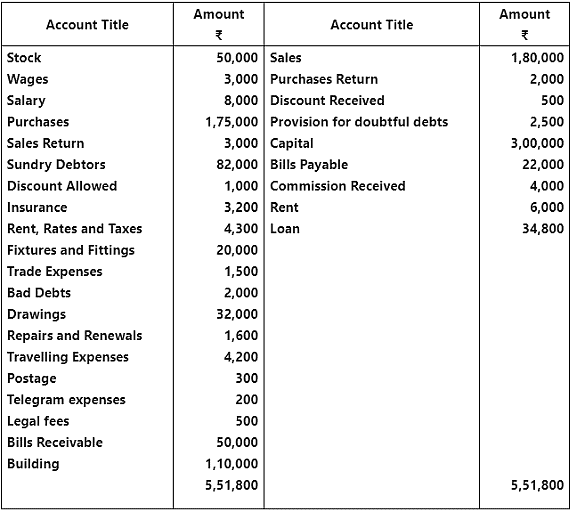
Adjustments:
- Commission received in advance ₹ 1,000.
- Rent receivable ₹ 2,000.
- Salary outstanding ₹ 1,000 and insurance prepaid ₹ 800.
- Further bad debts ₹ 1,000 and provision for doubtful debts @ 5% on debtors and discount on debtors @ 2%.
- Closing stock ₹ 32,000.
- Depreciation on building @ 6% p.a.
Trading and Profit and Loss Account of M/s Rahul Sons for the year ending
Ans:
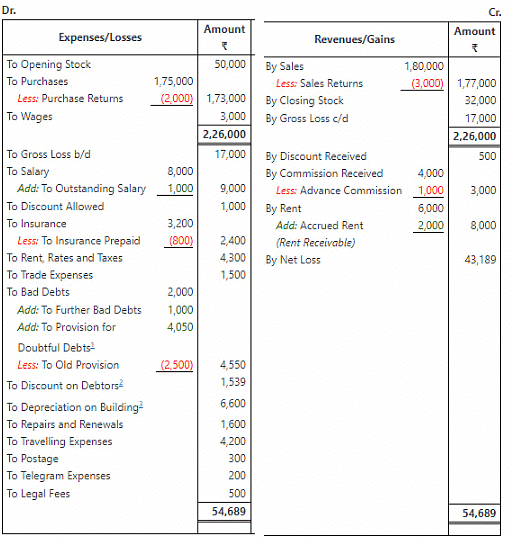
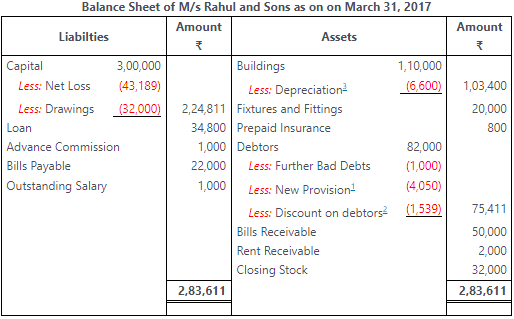
Working Notes:
1. Provision for Doubtful Debts=5% of (Debtors – Further Bad Debts)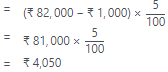
2. Discount on Debtors=2% of (Debtors – Provision for Doutful Debts – Further Bad Debts)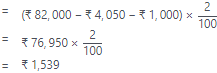
= ₹ 1,10,000×6100₹6,600
Q2: Prepare a trading and profit and loss account of M/s Green Club Ltd. for the year ending March 31, 2017. from the following figures taken from his trial balance :
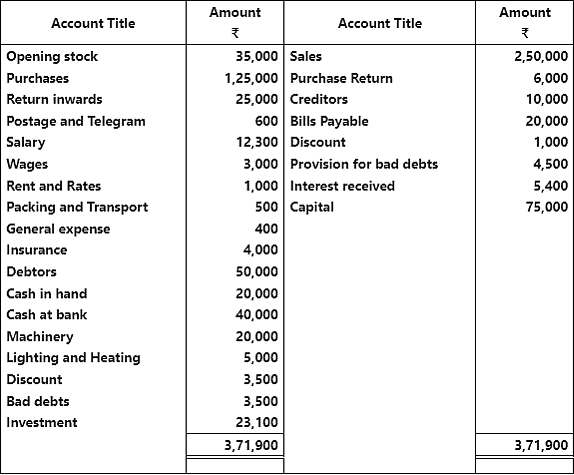
Ajustments:
- Depreciation charged on machinery @ 5% p.a.
- Further bad debts ₹ 1,500, discount on debtors @ 5% and make a provision on debtors @ 6%.
- Wages prepaid ₹ 1,000.
- Interest on investment @ 5% p.a.
- Closing stock ₹ 10,000.
Trading and Profit and Loss Account of M/s Green Club Ltd. for the year ending
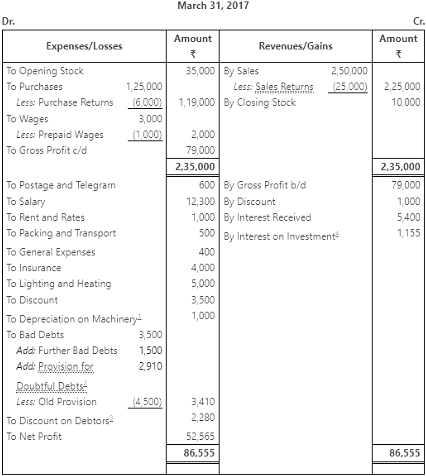
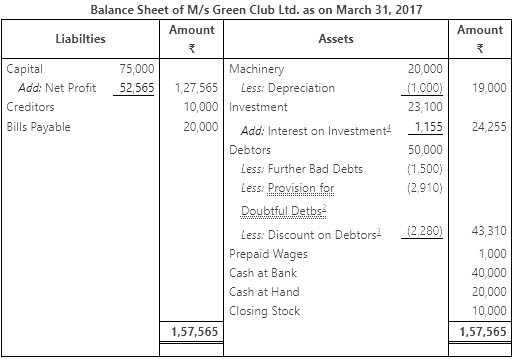
Working Notes: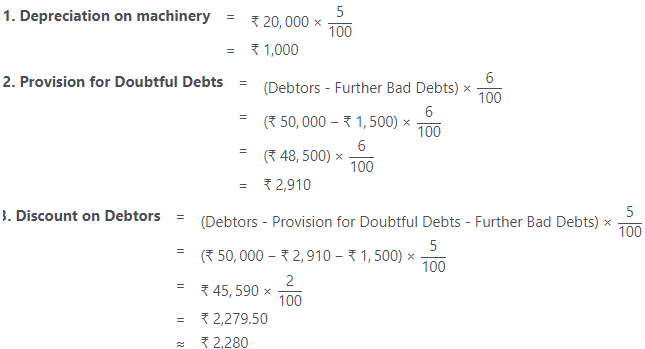
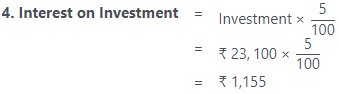
Q3: The following balances has been extracted from the trial of M/s Runway Shine Ltd. Prepare a trading and profit and loss account and a balance sheet as on March 31, 2017.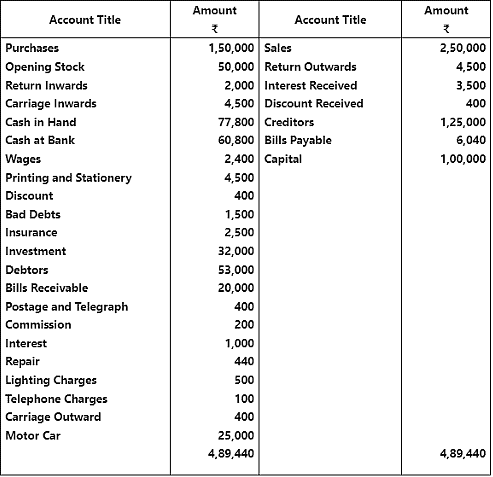
Adjustments:
- Further bad debts ₹ 1,000. Discount on debtors ₹ 500 and make a provision on debtors @ 5%.
- Interest received on investment @ 5%.
- Wages and interest outstanding ₹ 100 and ₹ 200 respectely.
- Depreciation charged on motor car @ 5% p.a.
- Closing Stock ₹ 32,500.
Ans: Trading and Profit and Loss Account of M/s Runway Shine Ltd. for the year ending March 31, 2017
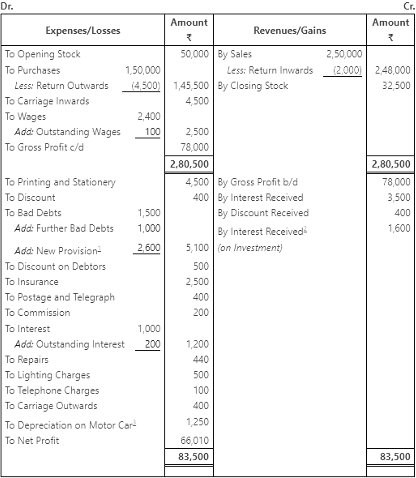
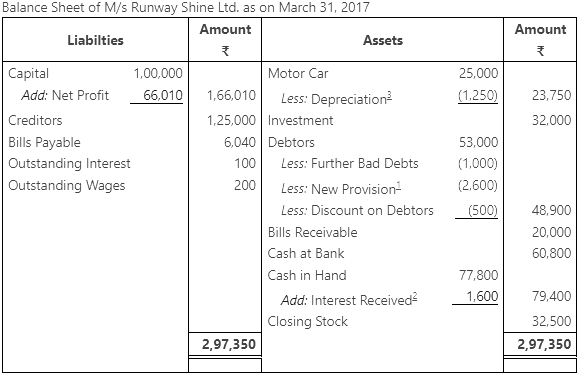
Working Notes: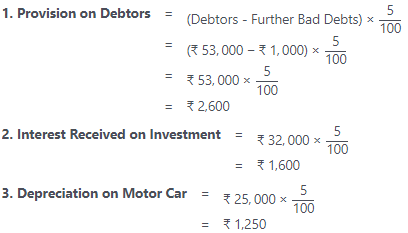
Q4.1: From the following Trial Balance you are required to prepare trading and profit and loss account for the year ending March 31, 2017 and Balance Sheet on that date.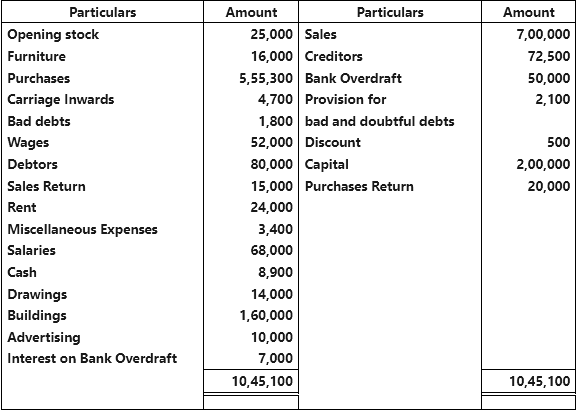
Adjustments
- Closing stock valued at ₹ 36,000.
- Private purchases amounting to ₹ 5000 debited to purchases account.
- Provision for doubtful debts @ 5% on debtors.
- Sign board costing ₹ 4,000 includes in advertising.
- Depreciate furniture by 10%.
Ans: Trading and Profit and Loss Account for the year ending March 31, 2017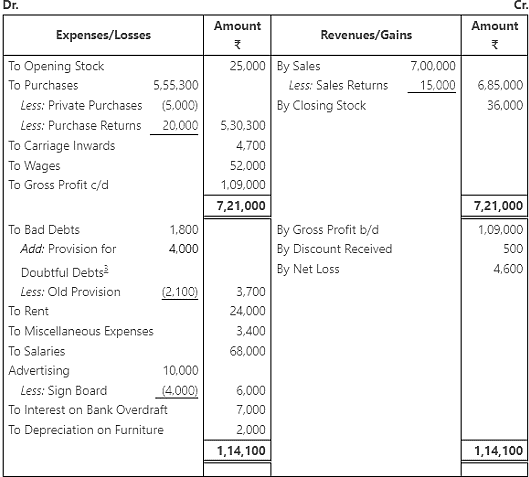
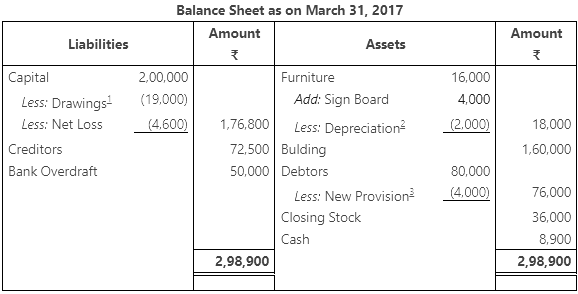
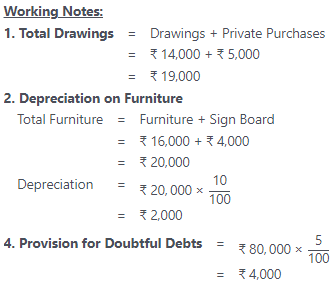
Q4.2: The following balances have been extracted from the trial of M/s Haryana Chemical Ltd. You are required to prepare a trading and profit and loss account and balance sheet as on March 31, 2017 from the given information.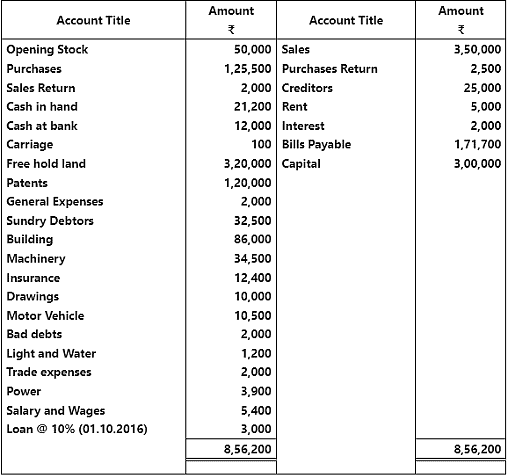
Adjustments:
- Closing stock was valued at the end of the year ₹ 40,000.
- Salary amounting ₹ 500 and trade expense ₹ 300 are due.
- Depreciation charged on building and machinery are @ 4% and @ 5% respectively.
- Make a provision of @ 5% on sundry debtors.
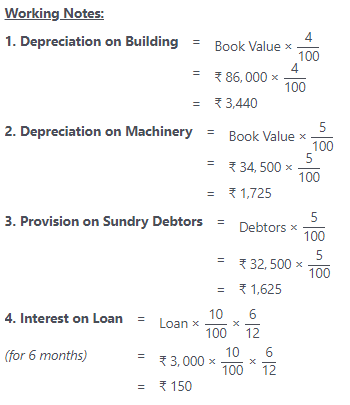
Note:
- If you do not find this problem in the text book, do not worry. This is from an old version of the text book. In the current text book, this problem is replaced with a different one (you can find it above)
- Note: In the text book, it is giving that the Loan @ 15% (01.09.2016) (it has to be calculated for 7 months from 1-Sep-2016 to 31-Mar-2017). However, if we consider that value we’re getting the accrued interest on the loan as 262.50 which will make the Net profit as ₹ 1,85,672.50. To make it equal to the answer given in the book i.e. ₹ 1,85,560, we’ve considered that the Loan @10% (01.10.2016), which will make the acrued interest on loan as ₹ 150 and the answers for net profit and the balance sheet totals match.
Ans: Trading and Profit and Loss Account of M/s Haryana Chemical Ltd. for the year ending March 31, 2017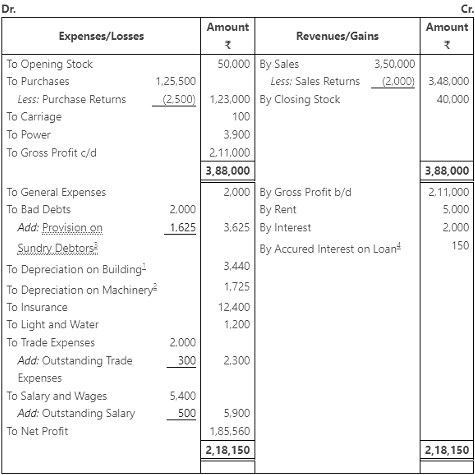
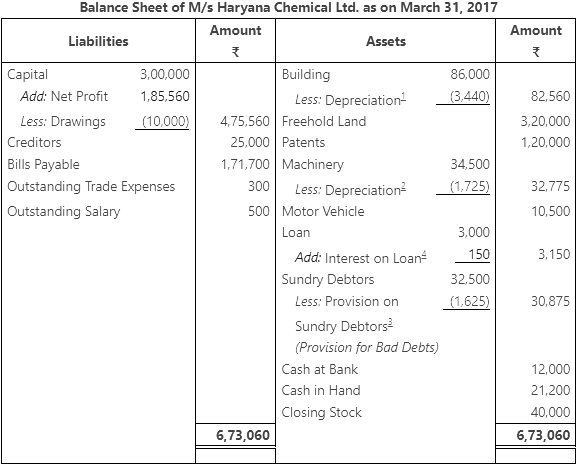
Q5: From the following information prepare trading and profit and loss account of M/s Indian sports house for the year ending March 31, 2017.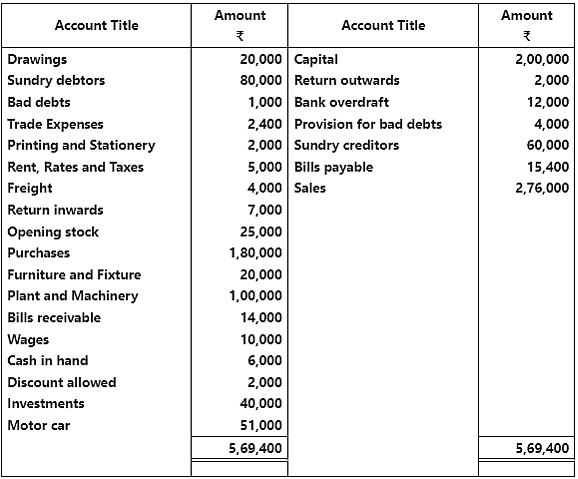
Adjustments:
- Closing stock was ₹ 45,000.
- Provision for doubtful debts is to be maintained @ 2% on debtors.
- Depreciation charged on : furniture and fixture @ 5%, plant and Machinery @ 6% and motor car @ 10%.
- A Machine of ₹ 30,000 was purchased on July 01, 2016.
- The manager is entitled to a commission of @ 10% of the net profit after charging such commission.
Ans: Trading and Profit and Loss Account of M/s Indian Sports House for the year ending March 31, 2017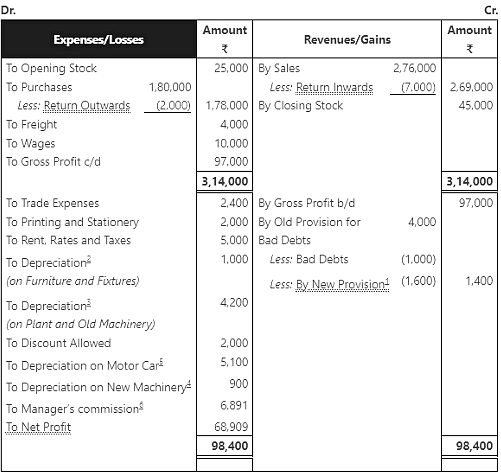
Note: In the text book answers, the gross profit is given with a typo as ₹ 1,01,000. However, as per our calculation, we got ₹ 97,000.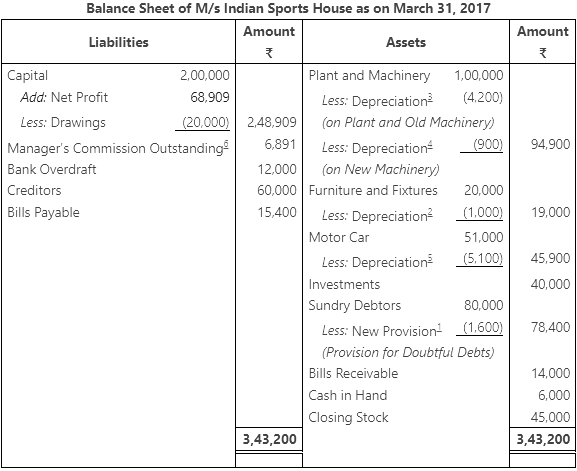
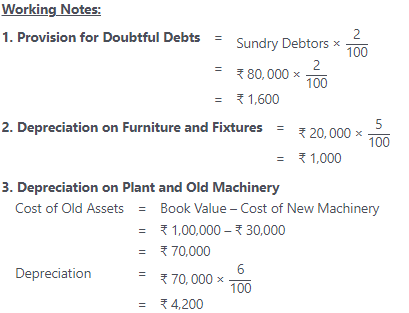
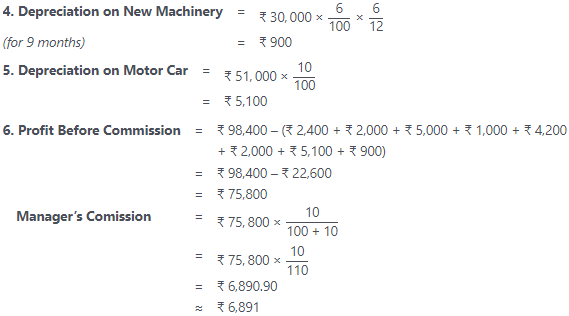
Note:
- The manager is entitled for the 10% commission of the net profit after charging such commission. So we need to take (100 + 10) = 110 in the denominator. If the net profit is computed before charging the manager’s commission then it would have simply be 100. But our case falls under first option.
- In this problem, the old provision is more than the sum of bad debts and provision for doubtful debtors. So, it is considered on the Revenues/Gains side instead of the Expenses/Losses side.
|
61 videos|154 docs|35 tests
|
FAQs on Worksheet Solutions: Financial Statements - II - Accountancy Class 11 - Commerce
| 1. What are the main components of financial statements? |  |
| 2. How do financial statements help in decision-making? |  |
| 3. What is the difference between cash basis and accrual basis accounting in financial statements? |  |
| 4. Why is the income statement important for businesses? |  |
| 5. How often should a company prepare financial statements? |  |
















