Short Answer Questions: Business Services | Business Studies (BST) Class 11 - Commerce PDF Download
Q1: State the five I's of services?
Ans: The five I’s of services are:
- Intangibility
- Inconsistency
- Inseparability
- Inventory
- Involvement.
Q2: What is the meaning of Banking?
Ans: Banking companies transact the business of banking for the aim of lending and investing public money deposits repayable on demand or otherwise, and withdrawable by checks, drafts, orders, or some other means. In simple terms, a bank accepts money on deposit that is repayable on demand, as well as lending money to generate a profit margin.
Q3: It is the prime responsibility of the insured to take reasonable steps to minimize loss/damage to the insured property. Name the principle of insurance.
Ans: Principle of Mitigation of Loss.
This principle states, as the owner of an insurance policy, the insured has an obligation to take the required actions to limit the loss of his/her insured property. The insured can't be careless or irresponsible just because he’s insured. The insured shall treat the insured thing with the same care as he or she would if the insurance were not present.
Q4: Define Insurance.
Ans: Insurance is a device that spreads the risk of a loss produced by an unpredictable event among a group of people who are exposed to it and who prepare to protect themselves against it. It's a contract or agreement in which one party agrees to pay an agreed amount of money to another party in the event of a loss, damage, or injury to something of value in which the insured has a pecuniary interest as a result of an uncertain event in exchange for a consideration.
Q5: Rahul's father wants to save Rs. 100,000 so that he can gift the money to Rahul on his graduation day. Which type of deposit should he open with the bank?
Ans: Fixed Deposit should be opened with the bank. Fixed accounts are time deposits with higher rates of interest as compared to savings accounts.
Q6: Name two companies that offer DTH service in our country?
Ans: Airtel, Tatasky offers DTH services in our country.
Q7: A company insures its stock against fire for Rs. 15 Lakh. A fire broke down and the total stock was lost. At the time of the fire, there was stock worth Rs. 25 Lakh. What is the value of compensation the company would be entitled to?
Ans: The contract for fire insurance is a rigorous indemnity contract. An insurance contract's objective is to make you whole in the case of a loss, not to allow you to profit. Hence in case of insurance other than life insurance, one can only be compensated for the amount of loss or the amount assured, whichever is lower.
As a result, the value of compensation the company would be entitled to is Rs 15 lakh.
Q8: Mr. Satish gets his house insured against fire of Rs. 20 Lakh with insurer A and for Rs. 10 Lakh with insurer B. A loss of Rs. 3 Lakh occurred.
(a) How much compensation can be claimed from A and B separately and Why?
Ans: According to this principle, the insurer can only seek compensation from all insurers or from a single insurer to the extent of the real damage. If one insurer provides the full compensation, the other insurers must pay a proportionate share of the claim.
Total value of insurance: Rs. 20,00,000 + Rs. 10,00,000 = Rs. 30,00,000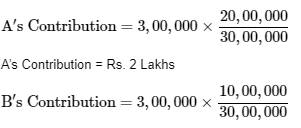
B’s Contribution =1 Lakh
(b) Name the principle of Insurance in the above case.
Ans: Principle of Contribution is followed. If an individual purchases many insurance policies for the same item, the insurers will pool their resources to reimburse the insured for the real loss. The insured can only claim reimbursement to the extent of actual loss from all insurers or from any one insurer, according to this concept.
It applies when:
- Different policies cover the same subject matter;
- The policies cover the same period that generated the loss;
- All the policies are in force at the time of loss; and
- One of the insurers has paid the insured more than his share of the loss, the right of contribution arises.
Q9: Explain the function of Insurance
Ans: Insurance's Functions are as follows:
Certainty: Insurance tends to reduce the level of risks, and the insured receives the payment for loss. The insurer charges for providing the certainty, in terms of premium.
Protection: Insurance provides protection from probable chances of loss, such as loss due to fire, theft etc. Insurance may not prevent a risk or event from occurring, but it can compensate for losses incurred as a result of it.
Risk sharing: All those who have been affected by the loss, share it. Every insured member pays a premium to acquire their share.
Capital formation: The assets accumulated by insurers as a result of premium payments made by the insured are invested in a variety of income-generating schemes.
Promote effectiveness and motivation: Insurance has made significant contributions to the progress of industry and commerce. Insurance businesses provide a variety of services that have resulted in today's large-scale industrial and commercial enterprises.
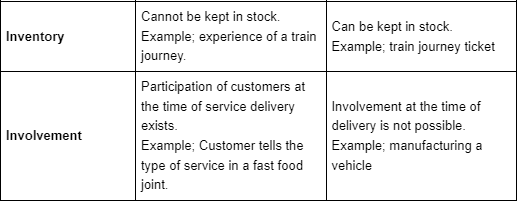
Q10: Explain the Difference between Goods and services based on its nature.
Ans: On the basis of nature, the following differences exist between services and goods: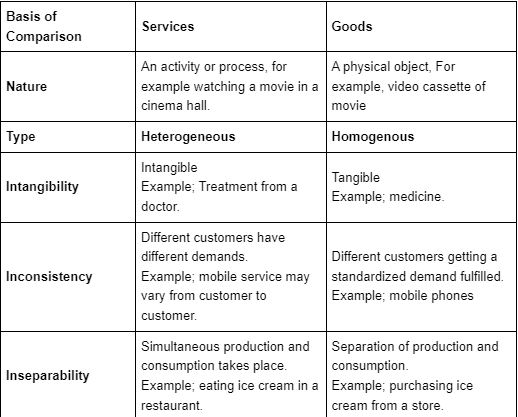
Q11: Name the principle of insurance for each of the following statements:
(a) The insured is expected to disclose all the important facts related to the property insured.
Ans: Principle of Utmost Good Faith.
(b) Insured must have some economic interest in the subject matter of Insurance contract.
Ans: Principle of Insurable Interest.
(c) To claim for insurance the insured must take reasonable steps to minimize the loss.
Ans: Principle of Mitigation of loss.
(d) Insured is entitled to recover the loss suffered by him, up to the limit of the policy amount.
Ans: Principle of Indemnity.
Q12: Explain the types of Life Insurance Policies?
Ans: Different types of life insurance policies include:
- Whole Life Policy: In this type of policy, the sum due to the insured is not paid until the assured passes away. The money is then solely due to the deceased's beneficiaries or heirs.
- Endowment Life Assurance Policy: The insurer agrees to pay a set amount when the insured reaches a certain age or dies, whichever comes first. In the event of the assured's death, the payment is payable to his legal heirs or nominee stated therein. Otherwise, the payment will be paid to the assured when a certain amount of time has passed.
- Joint Life Insurance: This coverage is purchased by two or more people. The premium is paid jointly or by either of them in installments, or in a lump sum assured sum or policy money is due to the other survivor or survivors upon the death of any one of them.
- Policy on Annuities: After the person reaches a particular age, the promised sum or policy money is paid out in monthly, quarterly, or annual installments.
- Policy on Children's Endowment: A person purchases this policy for his or her children in order to cover the costs of their education or marriage. The agreement specifies that the insurer will pay a certain amount when the children reach a certain age.
Q13: Explain electronic banking and state its three benefits?
Ans: Online banking, often known as internet banking, e-banking, or virtual banking, is an electronic payment system that allows bank or other financial institution customers to execute a variety of financial transactions via the financial institution's website. The word "internet banking" refers to the process of a client doing banking transactions over the internet. This sort of banking makes use of the internet as the primary mode of delivery for all banking transactions.
The following are some of the advantages:
- Availability 24x7: E-banking is available 24 hours a day, 365 days a year. At any moment, a client can log into his or her own bank account and execute financial activities online. Customers benefit from increased flexibility and comfort because they do not have to visit their banks in person.
- Convenient access: Transactions may be done on mobile phones and PCs as needed.
- E-banking decreases bank workload: E-banking reduces bank workload by allowing a substantial part of tasks to be performed electronically.
Q14: Explain the Functions of Warehousing?
Ans: The functions of warehousing are:
- Storage: Warehouses make it easier to store products and raw materials that aren't needed right away for sale or manufacture, while also protecting them from rotting and damage.
- Value-added services: They provide producers with value-added services such as product grading, packaging, and labelling.
- Financing: The warehouse receipt can be used as collateral to borrow money from banks or other financial organisations by the owner of the products or raw materials kept in the warehouse.
- Break the bulk: Warehouses are responsible for dividing large quantities of items received from manufacturing companies into smaller quantities. The smaller quantities are then transported according to the requirements of clients to their places of business
- Consolidation: The warehouses gather and consolidate material/goods from various manufacturing units before dispatching them to a specific consumer via a single transportation package.
- Stockpiling: The seasonal storing of commodities for certain businesses is the next role of warehousing. Raw materials, which are not required immediately for sale or manufacturing, are stored in warehouses. They are made available to enterprises according to the number of consumers they have.
- Price stabilisation: Warehousing provides the role of price stabilisation by adapting the supply of products to the demand condition.
Q15: Explain the three important insurances involved in Marine Insurance?
Ans: A marine insurance contract is an arrangement in which the insurer agrees to indemnify the insured against marine losses in the way and to the extent agreed upon. Marine insurance protects against losses caused by marine perils, often known as sea perils.
There are three important insurances under this:
- Ship or Hull Insurance: Because the ship is exposed to several dangers at sea, this insurance policy is designed to compensate the insured for losses incurred as a result of ship damage.
- Cargo insurance: Cargo or the goods in the ship is exposed to numerous dangers while being transported by ship, this insurance covers the risk of voyage.
- Freight insurance: If the cargo is damaged or lost in transit, the shipping business is not reimbursed for the freight payments, hence to avoid this scenario, the shipping company takes up this insurance policy.
|
39 videos|272 docs|28 tests
|





















