Work, Force, Energy and Simple Machines - 2 Class 5 Worksheet Science
Q1: Short answer questions.
(i) You have to load your suitcase onto a truck. You are not able to lift the suitcase. Which simple machine can help you do this? Why?
Ans: We should use an inclined plane to load the suitcase onto the truck. An inclined plane allows us to move a heavy load with less effort, making it easier to lift objects that we cannot lift directly.

(ii) A single fixed pulley does not reduce the effort required to lift a load. How does it make our work easier?
Ans: A single fixed pulley makes our work easier by changing the direction of the force applied. Instead of lifting a load directly upwards, we can pull downwards. This method is generally easier because it allows us to use our body weight to assist in lifting.
(iii) How is wind energy more environment friendly than heat energy?
Ans: Using wind to produce energy has significantly fewer effects on the environment compared to many other energy sources, such as heat energy.
Wind turbines:
- Do not release emissions that can pollute the air or water, except in rare cases.
- Do not require water for cooling, unlike heat energy production.
(iv) What is the law of conservation of energy?
Ans: The law of conservation of energy states that energy can neither be created nor destroyed; it can only be converted from one form to another. This principle implies that a system always maintains the same total amount of energy unless energy is added from an external source.
(v) Does a screw join two pieces of wood better than a nail? How?
Ans: A screw is generally better than a nail for joining two pieces of wood. This is because screws have threading that grips the surrounding material tightly, providing a more secure hold. Additionally, screws are easier to control and can be removed with less difficulty compared to nails.
(vi) Name four different forms of energy.
Ans: Energy exists in many different forms. Examples of these are: light energy, heat energy, mechanical energy, gravitational energy, electrical energy, sound energy, and so on.
(vii) Why is geothermal energy referred to as a renewable source of energy? From where does most of the heat energy come?
Ans: Geothermal energy is a type of renewable energy taken from the Earth’s core which will never exhaust, that’s why it is renewable.
It comes from heat generated during the original formation of the planet and the radioactive decay of materials. This thermal energy is stored in rocks and fluids in the center of the earth.
(viii) Why are machines used?
Ans: A machine is a tool designed to make our work easier. It allows us to overcome a larger force, which is required to move a load, by applying a lesser force, known as effort.
(ix) What are the three main parts of a lever?
Ans: The three main parts of a lever are the fulcrum, load, and effort.
(x) Can you give an example of a class 2 lever and explain how it functions?
Ans: Yes, a bottle opener is an example of a class 2 lever. In this lever, the load (the cap of the bottle) is between the fulcrum (the point where the opener pivots) and the effort (the force applied by your hand). This arrangement allows for an increased force, making it easier to lift the cap.
 Bottle Opener
Bottle Opener
Q2: Long answer questions.
(i) Write a note on wind energy and solar energy.
Ans: Wind Energy
- The energy present in moving air or wind is called wind energy.
- Wind is used to produce electricity using wind turbines or wind energy conversion systems.
Solar Energy
- The energy that we get from sunlight is called solar energy.
- It can be used to carry out many functions on the Earth.
- Solar energy is abundant on Earth and is also non-polluting.
- When electricity is obtained from burning fuels, smoke and other polluting gases are formed. But when we use solar energy to get electricity, there is no pollution.
Examples:
- Solar panels convert solar energy into electrical energy, which is used to run machines.
- Solar cookers use sunlight to cook food.
(ii) Differentiate between renewable and non-renewable energy.
Ans: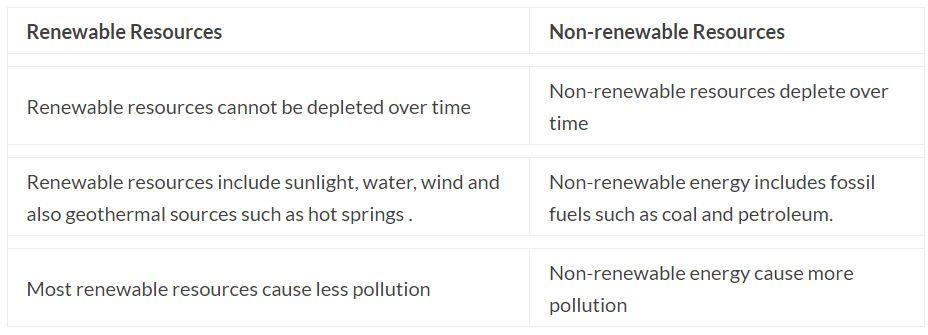
(iii) What is the difference between work and energy?
Ans: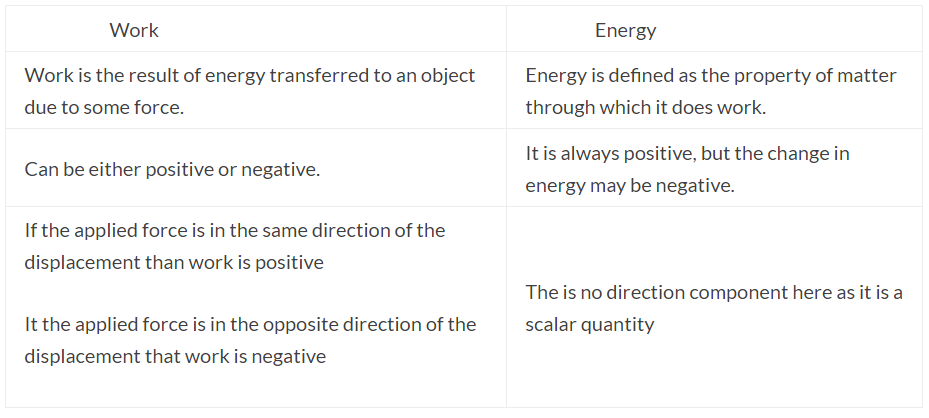

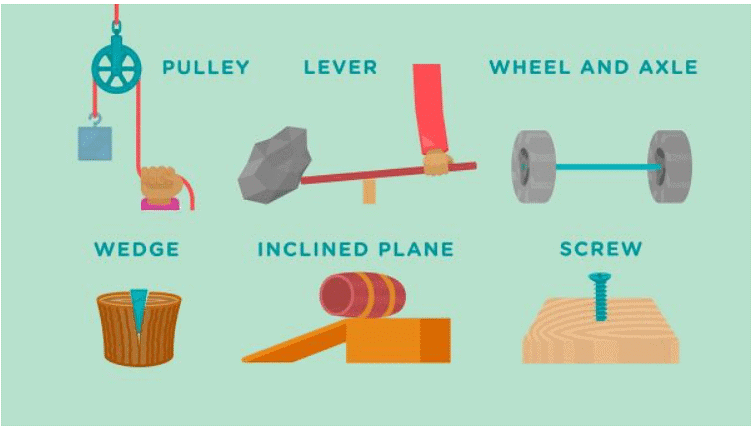
(iv) What is a simple machine? Name some simple machines and draw diagrams too.
Ans: A simple machine uses a single applied force to get the work done.
- A “simple” machine is one where both the input energy and the output energy are mechanical in nature .
- A simple machine has very few parts.
- A wheelbarrow is an example of a simple machine
Types of Simple Machines
There are mainly 6 types of simple machines.
- A lever
- pulley
- wheel and axle
- wedge
- screw
- and an inclined plane are some simple machines.
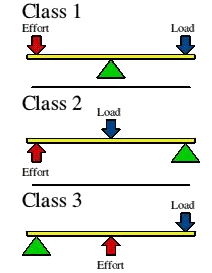
(v) Describe the characteristics and provide examples of each class of lever.
Ans:
- Class 1 Lever: In class 1 levers, the fulcrum is between the load and the effort. Examples include a pair of scissors, see-saw, crowbar, and pliers.
- Class 2 Lever: In class 2 levers, the load is between the fulcrum and effort. Examples include a bottle opener, wheelbarrow, and nut cracker. This class of lever always increases force.
- Class 3 Lever: In class 3 levers, the effort is between the fulcrum and load. Examples include a stapler, tweezers, fishing rods, and tongs. This class is used to decrease force for delicate work.
(vi) Explain the concept of a wheel and axle, providing examples of how it is used in everyday life.
Ans: A wheel and axle consist of a wheel attached to a rod called an axle. When the axle is turned, the wheel also moves. Examples of wheel and axle in everyday life include the steering wheel of a car, a screwdriver, a sewing machine, and a doorknob.
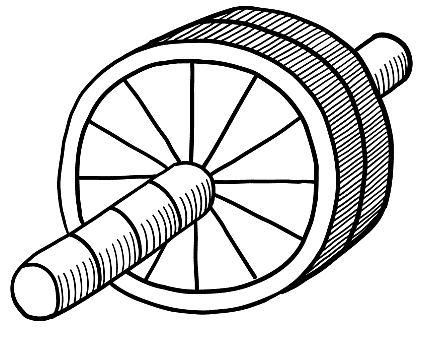 Wheel and Axle
Wheel and Axle
The interaction between the wheel and axle allows for efficient movement and transfer of force, making these devices essential in various applications.
|
42 videos|371 docs|45 tests
|
FAQs on Work, Force, Energy and Simple Machines - 2 Class 5 Worksheet Science
| 1. What is the relationship between work, force, and energy in physics? |  |
| 2. How do simple machines make work easier? |  |
| 3. What are the different types of energy associated with work? |  |
| 4. How do you calculate the mechanical advantage of a simple machine? |  |
| 5. What is the law of conservation of energy in the context of work and machines? |  |
















