Past Perfect Tense | English Language & Comprehension for SSC CGL PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Introduction |

|
| How to make the Past Perfect tense? |

|
| Contraction with Past Perfect |

|
| How to use the Past Perfect tense? |

|
Introduction
The Past Perfect tense is relatively straightforward in both comprehension and application. It pertains to the "past within the past."
How to make the Past Perfect tense?
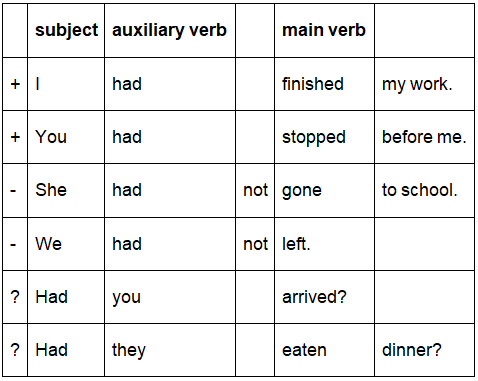
The structure of the Past Perfect tense is:

The auxiliary verb (have) is conjugated in the Past Simple: had
The main verb is invariable in past participle form: -ed (or irregular)
For negative sentences we insert not between the auxiliary verb and the main verb.
For question sentences, we exchange the subject and the auxiliary verb.
Look at these example sentences with the Past Perfect tense:
Contraction with Past Perfect
In spoken language, it's common to contract the subject and auxiliary verb when using the Past Perfect tense. This contraction is also occasionally employed in informal writing.
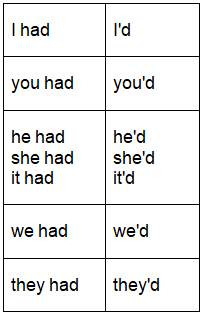
- I'd eaten already.
- They'd gone home.
In negative sentences, we may contract the auxiliary verb and "not":
- I hadn't finished my meal.
- Anthony hadn't had a day off for months.
How to use the Past Perfect tense?
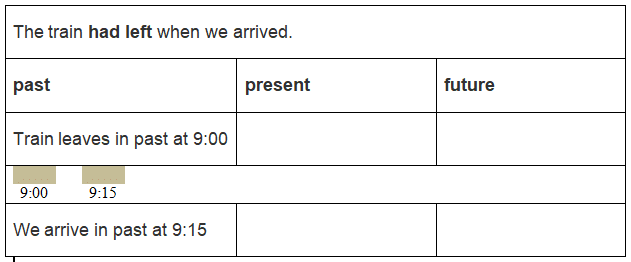
The Past Perfect tense expresses action in the past before another action in the past. This is the past in the past. For example:
- The train left at 9am. We arrived at 9:15am. When we arrived, the train had left.
Look at some more examples:
- I wasn't hungry. I had just eaten.
- They were hungry. They had not eaten for five hours.
- I didn't know who he was. I had never seen him before.
- "Mary wasn't at home when I arrived." / "Really? Where had she gone?"
You can sometimes think of the Past Perfect tense like the Present Perfect tense, but instead of the time being now the time is before.
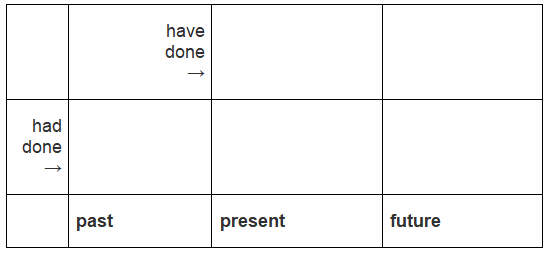
For example, imagine that you arrive at the station at 9:15am. The stationmaster says to you:
- "You are too late. The train has left."
Later, you tell your friends:
- "We were too late. The train had left."
We often use the Past Perfect in reported speech after verbs like: said, told, asked, thought, wondered
Look at these examples:
- He told us that the train had left.
- I thought I had met her before, but I was wrong.
- He explained that he had closed the window because of the rain.
- I wondered if I had been there before.
- I asked them why they had not finished.
|
137 videos|209 docs|152 tests
|















