Important Formula: Mixtures & Alligations | Quantitative Aptitude for SSC CGL PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| What is an Alligation? |

|
| What is a Mixture? |

|
| What is a Mean Price? |

|
| Formulas to Solve Mixture and Alligations |

|
What is an Alligation?
When blending two ingredients, X and Y, with prices p and q respectively, to form a mixture with a mean price M, the ratio (R) in which the ingredients are combined is determined by the alligation rule.
(Cheaper quantity) : (Dearer quantity) = (d – m) : (m – c)
What is a Mixture?
In a mixture, two or more ingredients are mixed together to get a desired quantity. The quantity can be expressed as ratio or percentage.
For example: When two varieties of sugar are mixed to form a new variety of sugar then it is called as a mixture.
What is a Mean Price?
The cost of a unit quantity of the mixture is called the mean price.
Formulas to Solve Mixture and Alligations
Alligation and Mixture Formulas 1
When two commodities are mixed then ,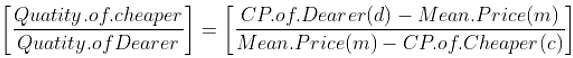
Alligation and Mixture Formulas 2
Imagine a container holding x units of liquid A, from which y units are withdrawn and replaced with water. If this process is repeated n times, the formula to calculate the quantity of pure liquid is as follows: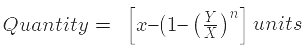
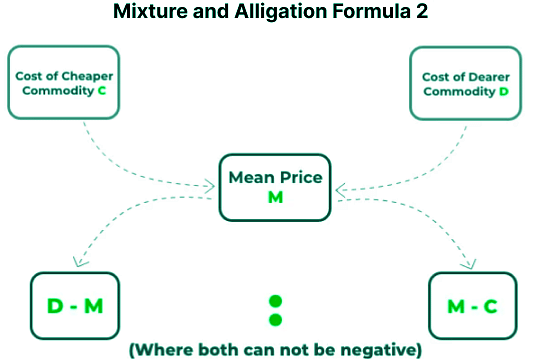
Therefore, (Cheaper Commodity) : (Dearer Commodity) = (d – m) : (m-c)
Alligation and Mixture Formulas 3
Calculate quantity of pure Liquid after ‘n’ successive operations,
If a container contains ‘x’ units of pure liquid , and we replace the liquid with ‘y’ units of water ,
Then after ‘n’ successive operations, the units of pure liquid left is ,
After n operations, the quantity of pure liquid 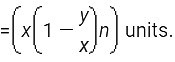
Criss-Cross Method
Some aspirants use the above method in different format, which we call criss-cross method. Below is the format: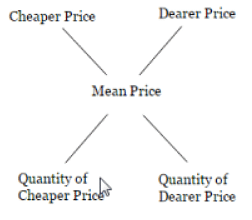
The procedure involves calculating the positive difference between the mean price and the lower price, then assigning this difference to the quantity of the higher-priced item. Similarly, the positive difference between the mean price and the higher price is calculated and assigned to the quantity of the lower-priced item.
Rule of Constant
Another category of questions related to mixtures and alligation involves scenarios where the quantity of one element in the mixture remains constant while introducing another element. In such cases, I suggest employing an alternative approach using the constant rule to arrive at the solution. This concept is based on a straightforward understanding of percentages.
Method 1: School textbook approach
We assume that the quantity of water added to be x litres. The quantity of milk in the existing solution is 30% of 40 = 12 litres, with the addition of water, the quantity of new solution becomes (40 + x) litres. As per the problem, the percentage of milk in new solution should be 15 %. we will get x = 40.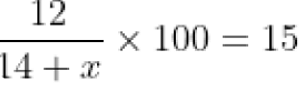
Method 2: Rule of Alligation.
We assume that the two solutions of milk and water are added to get the new solution and apply the approach we used in Example 3.
Taking milk as the common element in both the solutions, we have 30% milk in first and 0% milk in the second solution (i.e. pure water). On mixing them, we got 15% milk in the final solution. Therefore,
Or the ratio of the quantity of first and second solution should be 15:15 = 1:1
Hence, 40 litres of pure water should be mixed to get the desired new solution.
Method 3: Rule of Constant
In this principle, we focus on the component in the mixture whose quantity remains constant, but its percentage alters due to the variation in the overall amount of the mixture.
As calculated earlier, the quantity of milk in the initial solution is 12 liters, and this quantity remains unchanged in the new solution. That is,
12 liters = 30% of the first solution =15% of the new solution
Examples
Example1: A and B are two alloys of iron and silver prepared by mixing metals in the ratio 4 : 5 and 7 : 5 respectively. If equal quantities of alloys are melted to form a third alloy C, the ratio of iron to silver in C is
Sol: In alloy A, the ratio of iron to Silver=4:5, 5+4=9
In alloy B, the ratio of iron to Silver=7:5, 7+5=12, as the amount to be mixed.
So take the LCM of 9 and 12. hence, we mix 36 gm of A and 36 gm of B.
(the reason for choosing LCM as the amount is to simplify calculations.)
For a: amount of iron 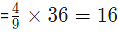 and amount of silver
and amount of silver 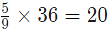
For B: amount of iron 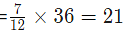 and amount of silver
and amount of silver 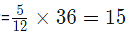
Hence, Total amount of iron=16+21=37
Total amount of silver=20+15=35
Hence, Final ratio of iron to Silver in the mix of two alloys= 37:35
Example 2: Two containers of equal volume contains milk and water in the ratio 3: 5 and 5: 3, respectively. If the contents of both containers are emptied into a third one, what would be the ratio of milk to water in that container?
Sol: Let the volume of both the container b x units each. Thus, the first container would contain 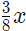 units of milk and
units of milk and 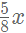 units of water, whereas the second container would contain
units of water, whereas the second container would contain 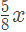 units of milk and
units of milk and 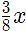 units of water. When the content of both are empty into a third one it would have,
units of water. When the content of both are empty into a third one it would have,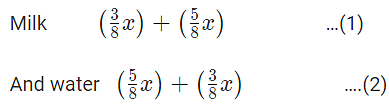
Thus, the required ratio. x:x = 1 : 1
Example 3: A sum of money is sufficient to pay Sachin’s salary of 45 days and kale’s salary for 60 days. For how many days can the sum pay the salary of both?
Sol: Sachin’s salary for one day = 1/45th of the sum of money.
For kale’s salary for one day = 1/60 of the sum of money.
⇒ (Sachin + kale)’s salary for one day= 1/45+1/60=7/180th of the sum.
Hence, when they both work together, the sun will last for 180/7 days.
Example 4: Mixture of alcohol and water contains 35% of alcohol by volume. Then, 40 ml of water is added to such a mixture of 100 ml. The percentage of alcohol in the new mixture is?
Sol: Here percentage alcohol in the mixture is to be found out. So, the quantity of alcoholis kept as numerator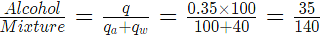
(since 40 ml water is added Quantity of mixture=100+40).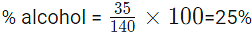
the mixture contains 20% alcohol.
Example 5: From two ornament Weighing 18 gram and 24 gram containing gold and silver in the ratio of 2: 1 and 5: 1 respectively, a new ornament is made. What is the amount of gold in the new ornament?
Sol: From the first ornament, gold 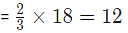
From the second ornament gold 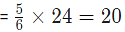
Thus, total gold=32 gm.
|
314 videos|170 docs|185 tests
|
|
314 videos|170 docs|185 tests
|

|
Explore Courses for SSC CGL exam
|

|

















