Short Notes: Nutrition in plants | Science Class 7 (Old NCERT) PDF Download
All living organisms such as plants and animals require food. So food is essential for all living organisms.
What is Nutrition in plants ?
Nutrition in plants is a fundamental process that sustains their growth, development, and overall functioning. Unlike animals, plants possess the remarkable ability to produce their own food through a process known as photosynthesis.
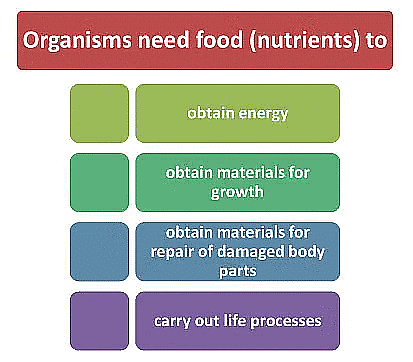 Function of Nutrients
Function of Nutrients
All living organisms require food. The food gives energy to the organisms for growth and maintenance of their body functions. Carbohydrates, proteins, fats, vitamins and minerals are the components of food. These components of food are necessary for our body and are called nutrients.
Mode of nutrition in plants
Plants prepare their food by using raw materials like water, carbon dioxide and minerals and the process of utilization of food by a living organism to obtain energy is called nutrition.
There are two modes of nutrition as shown below in the figure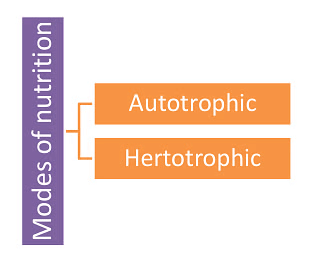 Modes of Nutrition
Modes of Nutrition
(i) Autotrophs
Autotrophs, such as plants possessing chlorophyll, harness solar energy to synthesize their own sustenance through a process known as photosynthesis. This self-sustaining mode of nutrition is termed autotrophic nutrition, with organisms capable of this feat referred to as autotrophs. Essentially, autotrophs derive nourishment independently (auto meaning self and trophos meaning nourishment).(ii) Heterotrophs
Heterotrophs rely on external sources for nutrition, often consuming other organisms for sustenance. Animals and non-photosynthetic organisms like fungi fall into this category, known as heterotrophs.Photosynthesis
Photosynthesis is the biological process by which green plants, algae, and some bacteria convert light energy into chemical energy stored in glucose molecules. This process occurs in the chloroplasts of plant cells and involves the absorption of sunlight by chlorophyll, a pigment found in chloroplasts and Oxygen is released during photosynthesis.
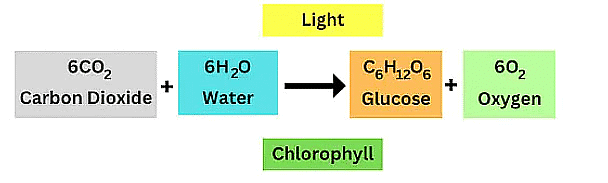
The process of photosynthesis can be represented as:
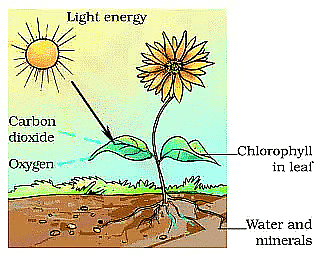 Photosynthesis
Photosynthesis
- The process of photosynthesis takes place in the green leaves of a plant.
- The food is prepared by the green leaves of a plant in the form of a simple sugar called glucose.
- The extra glucose is changed into another food called starch. This starch is stored in the leaves of the plant.
- The green plants convert sunlight energy into chemical energy by making carbohydrates.
The photosynthesis takes place in the following three steps:
- Absorption of sunlight energy by chlorophyll.
- Conversion of light energy into chemical energy, and splitting of water into hydrogen and oxygen by light energy.
- Reduction of carbon dioxide by hydrogen to form carbohydrate like glucose by utilizing the chemical energy.
Conditions necessary for photosynthesis
The conditions necessary for photosynthesis to take place are:
- Sunlight
- Chlorophyll
- Carbon dioxide
- Water
Raw materials for photosynthesis
The raw materials for photosynthesis are:
- Carbon dioxide
- Water
How the plants obtain carbon dioxide?
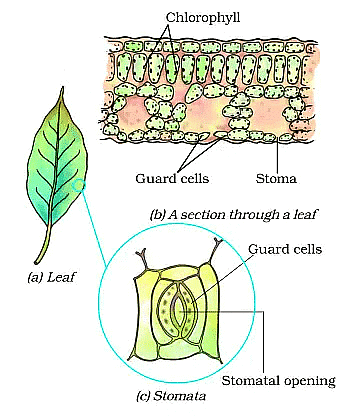 Function of Stomata
Function of Stomata
- There are a large number of tiny pores called stomata on the surface of the leaves of plants.
- The carbon dioxide gas enters the leaves of the plant through the stomata present on their surface.
- Each stomatal pore is surrounded by a pair of guard cells. The opening and closing of stomatal pores is controlled by the guard cells.
How the plants obtain water for photosynthesis
- The water required by the plants for photosynthesis is absorbed by the root of the plants from the soil through the process of osmosis.
- The water absorbed by the roots of the plants is transported upward through the xylem vessels to the leaves where it reaches the photosynthetic cells.
- The plants also need other raw materials such as nitrogen, phosphorus, iron and magnesium, etc., for building their body.
- The plants take these materials from the soil.
- Nitrogen is essential element used by the plants to make proteins and other compound.
Site of photosynthesis: Chloroplasts
- Photosynthesis takes place in the leaves of the plants.
- Leaves have green pigment called chlorophyll
- It helps leaves capture the energy of the sunlight which is then used to prepare food from carbon di oxide and water.
- Here, you see that solar energy is captured by the leaves and is stored in the plant in the form of food.
- So, we can say that Sun is ultimate source of energy for all living organisms.
Other Modes of Nutrition in Plants
Most of the plants have green pigment called chlorophyll and can make their own food. Some plants do not have chlorophyll and cannot synthesize their own food and are known as Heterotrophic plants
This type of nutrition can be categorized into
- parasitic mode of nutrition
- Insectivorous mode
- saprophytic mode of nutrition
- Symbiotic mode of nutrition
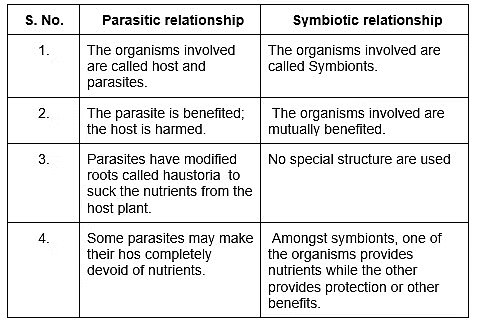
Parasites
In parasitic mode of nutrition, plants depend on other plants or animals for their nourishment. Such dependent plants are called as parasites and the ones on which parasites depend are called as hosts.
- A parasite plant climbs on the host plant from which they get all the food.
- The host does not get any benefit from the parasite.
- Some examples of parasites are Cuscuta (akash-bel), Cassytha (amar-bel), hookworms, tapeworms, leeches, etc.
Insectivorous Plants
The insectivorous mode of nutrition is observed in plants like pitcher plant and the Venus fly trap. These types of plants purely depend on other insects and small animals for their nutrition.
- Pitcher plants trap small insects inside the pitcher and insects are digested by the digestive juices secreted in the pitcher.
- Insectivorous plants grow in those soils which do not contain sufficient nitrogen mineral.
- These types of plants are green and carry out photosynthesis to obtain a part of food.
Saprotrophs
Mode of nutrition in which organisms or plants that obtain their nutrition from dead and decaying organic matter is called Saprophytic mode
- The plants which exhibit saprotrophic mode of nutrition are called as saprotrophs
- Saprotrophs secrete digestive juices onto dead and decaying matter to dissolve it and then absorb nutrients from it.
- Examples of saprotrophs are moulds, mushrooms, yeasts and some bacteria.
How Nutrients are replenished in soil?
In this mode of nutrition there is a close association between two different plants of different categories. In such type of association both the plants get benefited.
Example:
1: Fungi live in the roots of the trees. In this case tree provides nutrients to fungi and in return receives help from it to take up water and nutrients from the soil.
2: The bacterium called Rhizobium can take atmospheric nitrogen and convert it into a soluble form but Rhizobium cannot make its own food. So it lives in the roots of gram, peas, moong, beans and other legumes and provides them with nitrogen. In return plants provide food and shelter to the bacteria. plants and bacteria have a symbiotic relationship here.
Differences between a parasitic and a symbiotic relationship
|
112 videos|286 docs|28 tests
|
FAQs on Short Notes: Nutrition in plants - Science Class 7 (Old NCERT)
| 1. What is the primary mode of nutrition in plants? |  |
| 2. Where does photosynthesis occur in plants? |  |
| 3. What are the other modes of nutrition in plants aside from photosynthesis? |  |
| 4. How are nutrients replenished in the soil for plants? |  |
| 5. Why is chlorophyll important for plant nutrition? |  |