Difference Between ejusdem generis and noscitur a sociis | Important Acts and Laws for Judiciary Exams PDF Download
Introduction
Laws and regulations often incorporate terms that may seem unclear, leading to various interpretations. Legal scholars and practitioners have established principles like Ejusdem Generis and Noscitur a Sociis to guide the interpretation of statutes, contracts, and legal documents.
Understanding Noscitur a Sociis
- Noscitur a Sociis, a Latin legal maxim, signifies "it is known by its associates" or "it is known from its companions." In legal interpretation, this principle aids in determining the meaning of a word or phrase in a statute or legal document based on its surrounding words or phrases.
- Contextual Interpretation: When a legal provision uses multiple words or phrases together and one is unclear, Noscitur a Sociis dictates that the meaning of the unclear word should be inferred from the context provided by the other words in the same provision.
- Restriction or Clarification: This principle helps in clarifying or restricting the meaning of an ambiguous word by considering it in connection with the surrounding words. Essentially, the unclear word's meaning is shaped by its associations.
- Avoiding Ambiguity: The primary aim of applying Noscitur a Sociis is to eliminate ambiguity in legal texts by interpreting words in a manner consistent with the overall context of the statute or document.
For instance, if a legal text mentions vehicles, including cars, trucks, and other vehicles, with the term "other vehicles" being ambiguous, Noscitur a Sociis would suggest interpreting it in the context of the specific examples provided (cars and trucks) without encompassing unrelated items like bicycles or boats.
Understanding Ejusdem Generis
- Definition: Ejusdem generis is a legal principle that signifies items of the same kind or nature.
- Application in Legal Interpretation: In legal contexts, when specific terms are followed by a general or ambiguous term, ejusdem generis dictates that the general term should be interpreted to be of the same kind as the specific terms.
- Restriction and Clarification: This principle helps to limit or clarify the meaning of the ambiguous term by relating it to the specific examples provided earlier. Essentially, the general term inherits the characteristics of the specific terms preceding it.
- Preventing Broad Interpretations: The purpose of applying ejusdem generis is to avoid broad interpretations of the general term that could result in unintended consequences or legal loopholes.
For instance, consider a scenario where a contract prohibits bringing animals, including dogs, cats, and other animals into the workplace. If the term "other animals" is unclear, ejusdem generis would suggest interpreting it to include only similar types of animals like pets, excluding farm animals or exotic wildlife.
Key Differences Between Ejusdem generis and noscitur a sociis
Meaning and Purpose
- Ejusdem Generis: This term refers to interpreting general or ambiguous words in a legal document by connecting them with specific words preceding them, restricting the general term's meaning.
- Noscitur a Sociis: This phrase suggests understanding a word's meaning by looking at the context provided by other words or phrases in the same legal provision.
Application
- Ejusdem Generis: Applied when specific words precede a general term, indicating that the general term should be interpreted to be of the same kind as the specific words listed.
- Noscitur a Sociis: Utilized when words within a legal text have related meanings due to their association, advising interpretation in this contextual framework.
Focus
- Ejusdem Generis: Focuses on limiting the scope of general terms to match specific terms to avoid broad interpretations.
- Noscitur a Sociis: Emphasizes understanding a word's meaning based on its companions in the text to prevent ambiguity.
Specific vs. General
- Ejusdem Generis: Deals with the relationship between specific and general terms within a list.
- Noscitur a Sociis: Applies to any words or phrases that appear together and may have related meanings without focusing on specific vs. general distinctions.
Nature of Ambiguity
- Ejusdem Generis: Invoked when there is ambiguity in the meaning of a general term within a list.
- Noscitur a Sociis: Used when ambiguity in the meaning of a word or phrase in a broader context requires interpretation based on surrounding words.
Examples
- Ejusdem Generis Example: In a statement prohibiting vehicles, including cars, trucks, and others, ejusdem generis would limit 'other vehicles' to those similar to cars and trucks.
- Noscitur a Sociis Example: In a provision mandating attendance at meetings, conferences, and related events, noscitur a sociis would interpret 'related events' in the context of meetings and conferences.
Here’s a table summarising the key differences between Ejusdem Generis and Noscitur a Sociis in statutory interpretation: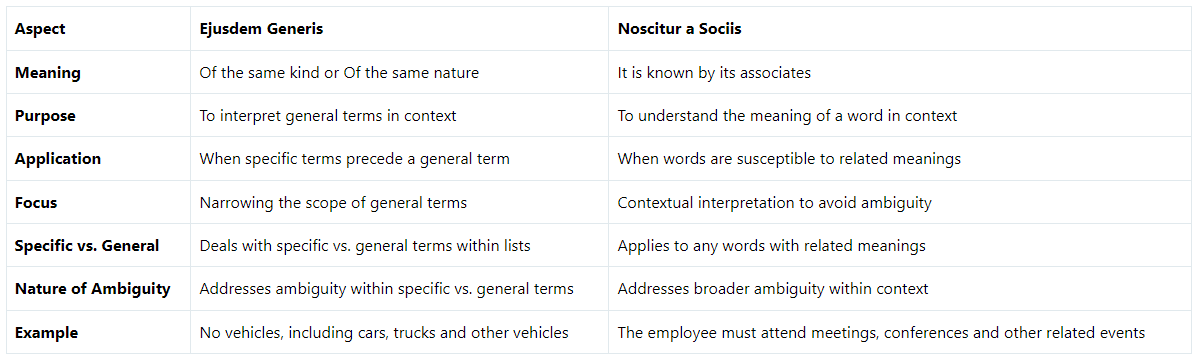
In the case of Kavalappara Kottarathil Kochuni v. State of Madras, the legal principle of ejusdem generis was established and clarified. This principle dictates that it should only be applied when general terms in a law or statute follow specific words, and all those specific words belong to the same general category or class. However, it’s important to note that this rule is not an absolute and inflexible law; rather, it is a permissible inference that can be drawn in the absence of any clear indication to the contrary within the law.
Similarly, in the case of Powell v. Kempton Park Racecourse Co., the ejusdem generis doctrine was applied. The court ruled that other items mentioned in the statute were related to indoor places, while Tattersall’s enclosure was located outdoors. Therefore, the court concluded that no offense had been committed in this instance. This decision underscored the importance of interpreting the law in a manner that aligns with the specific context and details of the statute in question.
Ejusdem generis: A Facet of noscitur a sociis
- Noscitur a sociis and ejusdem generis are legal concepts closely related to each other. Noscitur a sociis means that the meaning of a word in law is determined by the words surrounding it. Ejusdem generis is a specific application of this concept, used when general words are accompanied by specific words in a law or rule.
- In essence, when general words appear alongside specific ones, ejusdem generis instructs us to interpret the general words in light of the specific ones and their context. For instance, if a law mentions "vehicles" including "cars" and "trucks," ejusdem generis implies that other vehicles must be similar to cars and trucks.
- Court cases like Maharashtra University of Health and others Vs. Satchikitsa Prasarak Mandal & Others and Attorney General v. Prince Ernest Augustus of Hanover have highlighted the importance of considering specific words alongside general ones to understand their meaning within a legal framework. Ejusdem generis aids in deciphering the meaning of general words when they are used in conjunction with specific terms in laws or rules.
Conclusion
- While both ejusdem generis and noscitur a sociis are principles used for interpreting ambiguous terms in legal documents, there is a difference between them in terms of focus, application, and purpose.
- Ejusdem Generis specifically deals with the relationship between specific and general terms within a list, while Noscitur a Sociis applies more broadly to any words or phrases that appear together and may share related meanings, emphasizing the context provided by surrounding words.
- Both ejusdem generis and noscitur a sociis help ensure clarity and consistency in legal interpretation.
|
233 docs|219 tests
|
FAQs on Difference Between ejusdem generis and noscitur a sociis - Important Acts and Laws for Judiciary Exams
| 1. What is the difference between Ejusdem Generis and Noscitur a Sociis? |  |
| 2. How do Ejusdem Generis and Noscitur a Sociis affect statutory interpretation? |  |
| 3. Can Ejusdem Generis and Noscitur a Sociis be applied together in statutory interpretation? |  |
| 4. How do courts determine whether to apply Ejusdem Generis or Noscitur a Sociis in a particular case? |  |
| 5. Can Ejusdem Generis and Noscitur a Sociis lead to different interpretations of the same statutory provision? |  |




















