AS 11 The Effects of Changes in Foreign Exchange Rates | Advanced Accounting for CA Intermediate PDF Download
Applicability of AS 11 The Effects of Changes in Foreign Exchange Rates
The significance of AS 11 lies in its treatment of accounting for foreign operations and foreign currency transactions. It offers guidance on selecting the appropriate exchange rate and recognizing the financial impact of exchange rate fluctuations in financial statements.
Additionally, AS 11 addresses transactions in foreign currency, specifically those involving forward exchange contracts.
Representation of Books of Accounts
- Companies are not bound by AS 11 to use a specific currency for their accounts, although they typically opt for their country's currency. If a different currency is chosen, disclosure of the reasons is mandatory. Moreover, any alteration in the reporting currency must be justified.
Restatement of Financial Statements
- AS 11 does not cover the restatement of financial statements from one reporting currency to another. This exclusion extends to aiding users accustomed to specific currencies or similar purposes.
Cash Flow Statement Presentation
- The standard does not address the presentation of cash flows resulting from foreign currency transactions or the translation of cash flows from foreign operations.
Exchange Differences on Borrowings
- AS 11 does not encompass exchange differences arising from borrowings in foreign currency to the extent that they are treated as adjustments to interest costs.
Foreign Currency Transactions
Initial Recognition
A foreign currency transaction refers to any transaction conducted in or requiring settlement in a foreign currency. When initially recording such transactions in the reporting currency, the exchange rate between the foreign currency and the reporting currency at the transaction date is applied to the foreign currency amount.
Reporting at Subsequent Balance Sheet Dates
- Foreign currency monetary items are to be reported at the closing rate during each balance sheet date. However, in certain situations, the closing rate may not accurately reflect the amount expected to be realized in the reporting currency. In such cases, monetary items should be reported in the reporting currency at the anticipated realization value on the balance sheet date.
- Non-monetary items held at historical cost in a foreign currency are to be reported using the exchange rate at the transaction date.
- Non-monetary items valued at fair value or similar valuations in a foreign currency should be reported at the exchange rates prevailing during the determination of those values.
Recognition of Exchange Differences
- Exchange differences that occur when an enterprise reports its monetary items at rates different from their initial recording should be acknowledged either as income or as an expense.
X Ltd. bought fixed assets worth 3,000 lakh on 1.1.2006 and was financed by a foreign currency (US Dollar) loan which is payable in 3 equal annual installments. The exchange rates were 1 Dollar = INR 40.00 and INR 42.50 as on 1.1.2006 and 31.12.2006 respectively. The initial installment was rendered on 31.12.2006. The total difference in the foreign exchange is capitalized. Here, these transactions would be accounted as follows:
According to para 13, any exchange differences which arises on reporting the enterprise’s monetary items or settlement of monetary items at the rates different from the ones at which they’re recorded initially during the period, or reported in the previous financial statements, must be recognized as an income or an expense in the period in which it arises.
Computation of the Exchange Difference:
Foreign currency (US Dollar) loan = `3,000 lakh ÷ 40 (Exchange rate on 1/1/2006) = USD 75 lakhs
Exchange difference = USD 75 lakhs × (42.50 – 40.00) = INR 187.50 lakhs. Hence, the entire loss arising due to the exchange differences of INR 187.50 lakhs must be charged to the profit and loss account for the respective year.
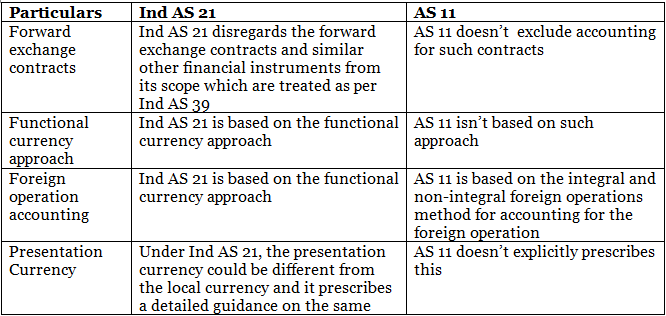
AS 11 vs Ind AS 21
Para 46 and 46A
The general principle is that exchange differences should be recorded in the profit or loss statement, regardless of whether they arise from revenue or capital accounts. However, the Government of India, through a notification issued on March 31st, 2009, amended AS 11 "The Effects of Changes in Foreign Exchange Rates" to include specific provisions.
Exchange differences related to a depreciable asset do not need to be charged to the profit or loss statement; instead, they may be added to or subtracted from the asset's cost. This adjusted cost should then be depreciated over the asset's useful life.
The conditions are that the asset must be a depreciable capital asset, represented in the balance sheet in foreign currency terms, and designated as a “Long-term Foreign Currency Monetary Item.”
Tax Implications of Exchange Differences
Profits and losses from foreign currency transactions and exchange differences arising from the translation of financial statements of a foreign operation may have related tax effects, which are accounted for in accordance with AS 22, Accounting for Taxes on Income.
|
53 videos|134 docs|6 tests
|
FAQs on AS 11 The Effects of Changes in Foreign Exchange Rates - Advanced Accounting for CA Intermediate
| 1. What is the purpose of AS 11 The Effects of Changes in Foreign Exchange Rates? |  |
| 2. How should foreign currency transactions be recognized under AS 11? |  |
| 3. When should exchange differences be recognized in the financial statements as per AS 11? |  |
| 4. Can you provide an example of how exchange differences are recognized under AS 11? |  |
| 5. How does AS 11 impact the reporting of foreign exchange gains or losses in subsequent balance sheet dates? |  |
















