GST Exemption: List of Goods & Services Exempt Under GST | Taxation for CA Intermediate PDF Download
What are GST Exemptions?
GST exemptions refer to specific goods or services that are not subject to GST. In simple terms, these are items that do not have GST applied to them. These exemptions can change and are different in various countries. Governments may grant exemptions to reduce taxes on essential items or to support certain industries.
Types of GST Exemptions
In India, there are three types of GST exemptions:
- Absolute Exemptions: These exemptions apply to the full amount without any conditions. An example is the exemption on services provided by the RBI.
- Conditional Exemptions: These exemptions have specific limits or conditions. For instance, hotel services are partially exempt up to a certain point.
- Partial Exemptions: Unregistered individuals supplying goods to registered persons within a state are exempt from GST under reverse charge if the total daily supply value does not exceed Rs. 5000.
List of GST Exemptions
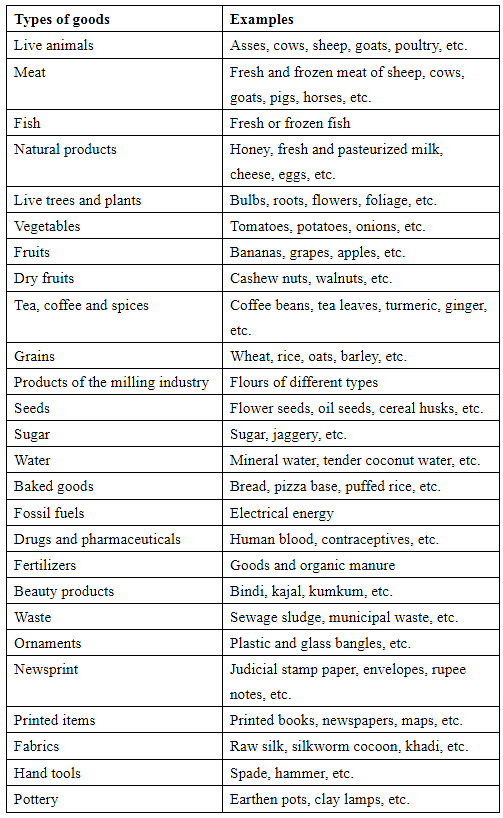
List of GST Exemption on Goods
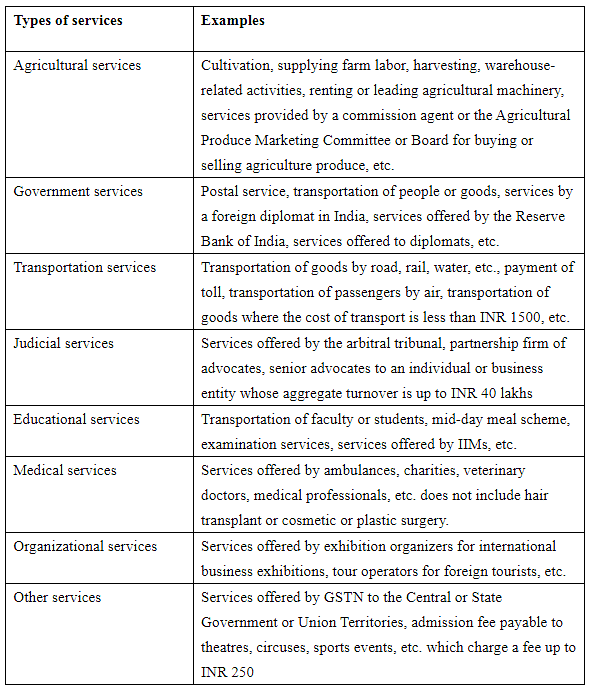
List of GST Exemption on Services
Though GST is applicable for all businesses and on the supply of goods and services, the above-mentioned exemptions are available. These exemptions reduce the GST burden and help in the socio-economic development of the country.
Exempt supply under GST
- Supplies considered exempt under GST do not incur goods and service tax. No GST is levied on these supplies, and input tax credits from them cannot be utilized. There are three main types of exempt supplies:
- Supplies taxed at nil rates.
- Supplies either partially or entirely exempt from GST due to specific notifications modifying section 11 of CGST and section 6 of IGST.
- Supplies falling under section 2(78) of the Act, encompassing items not taxable under the Act such as alcoholic beverages for human consumption.
GST Exemption from Registration
- Agriculturists
- Individuals falling within specified turnover limits for goods and services
- Those engaged in NIL Rated and exempt supply of goods and services like fresh milk, honey, cheese, and agricultural services
- Individuals involved in activities not covered under regular supply, such as funeral services and petroleum products
- Suppliers of goods subject to reverse charge, like tobacco leaves and unshelled cashew nuts
In simpler terms: - Farmers are exempt. - People within certain turnover limits for goods and services are exempt. - Those dealing with certain goods and services like milk, honey, and agriculture services are exempt. - Those in activities such as funeral services and petroleum products are exempt. - Suppliers of specific goods like tobacco leaves and unshelled cashew nuts are exempt under reverse charge.
GST Exemption for Businesses
Small and medium-scale businesses can enjoy GST exemptions if their aggregate turnover is up to a specified limit. These limits are as follows:
- Businesses and individuals supplying goods can claim GST exemption if their turnover is less than INR 40 lakhs annually.
- For hilly and north-eastern States, the limit is INR 20 lakhs.
- Businesses and individuals supplying services can claim exemption up to INR 20 lakhs.
- In hilly and north-eastern States, businesses with turnover up to INR 10 lakhs can claim exemptions for services.
Hilly and North-Eastern States:
States include Arunachal Pradesh, Jammu and Kashmir, Himachal Pradesh, Uttarakhand, Tripura, Nagaland, Sikkim, Meghalaya, Mizoram, Assam, and Manipur.
Aggregate turnover, as defined by the GST Act, includes the total value of taxable supplies, inter-state supplies, exempt supplies, and exports. Certain deductions are allowed from the aggregate turnover.
- CGST, SGST, or IGST already paid by the investor
- Taxes which are payable on the basis of reverse charge mechanism
- Value of the inward supply of goods and services
- Value of non-taxable goods and services
GST exemptions for goods
There is a list of goods which do not attract GST as recommended by the GST Council. The reasons for granting exemption on goods might include any of the following:
- In the interest of the public
- The exemption is as per the GST Council's recommendation
- The exemption is granted by the Government through a special order
- The exemption is allowed on specific goods through an official notification
Moreover, there are two types of GST exemptions on goods. These are as follows:
- Absolute exemption: This exemption means that certain goods are not taxed under GST, regardless of who supplies or receives them and whether they are supplied within or outside the State.
- Conditional exemption: This exemption means that certain goods are exempt from GST only if they meet specific terms and conditions outlined in the GST Act or related notifications.
GST Exemption on services
Similar to goods, certain services are also exempt from GST. There are three types of service supplies that qualify for GST exemption:
- Supplies with a 0% tax rate
- Supplies not subject to CGST or IGST as per specific provisions in relevant notifications
- Supplies defined under Section 2(78) of the GST Act as non-taxable
For these exempt supplies, Input Tax Credit cannot be used to offset GST liability. Additionally, there are two types of GST exemptions for service supplies:
- Absolute exemption: Service exempted from GST without any conditions.
- Conditional exemption: Exemption granted based on a condition. If the service is supplied intra-State or by a registered person to an unregistered one, GST is exempted if the total value of such supplies received by a registered person does not exceed INR 5000/day.
Reasons for exemption under GST
- Goods, services, and transactions exempt from GST in India are not subject to GST taxation.
- Exemptions under GST are granted based on policy objectives, socio-economic considerations, and administrative simplicity.
- Common reasons for granting exemptions include:
- Policy goals and objectives
- Socio-economic factors
- Administrative ease and simplicity
- Social Welfare and Public Interest: Certain important goods and services needed for society's well-being may not have GST applied. This includes basic food items like rice, wheat, and milk, along with healthcare and education services.
- Small Businesses: To make things easier for small businesses and encourage business activities, there could be exceptions or lower tax rates for businesses with lower earnings. For instance, the Composition Scheme offers reduced GST rates for small businesses within specific turnover limits.
- Export of Goods and Services: Goods and services meant for export are usually taxed at a 0% rate under GST. This helps keep exports competitive globally and avoids burdening them with GST taxes.
- Interstate Supplies: Goods and services moving between states might be either exempt from taxes or taxed at reduced rates to support the smooth flow of goods across state borders.
- Agriculture: Many agricultural products and related services are not subject to GST. This exemption is to aid the agricultural sector, a vital part of India's economy.
- Government Services: Some services provided by the government or local authorities might be free from GST to prevent double taxation and simplify accounting processes.
- Financial Services: Specific financial services such as banking, loan interests, and insurance might be exempt from GST or have unique rules to determine their tax liabilities.
- Cultural and Religious Significance: Goods and services utilized for cultural, religious, or charitable purposes could be exempt to honor the cultural and social values of the community.
- Administrative Simplicity: Some goods or services might be exempted from GST to make the tax system less complex, decrease compliance costs, and make it simpler for businesses and taxpayers to follow GST regulations.
- Transitional Provisions: During the shift to GST, there could be special exemptions or lower rates to help businesses transition smoothly and reduce the impact of the new tax system.
Difference between Exempt, Nil Rated, Zero Rated and Non-GST supplies
In the realm of India's Goods and Services Tax (GST) system, various categories delineate distinct tax treatments for supplies, encompassing goods and services. These categories are "Exempt," "Nil Rated," "Zero Rated," and "Non-GST Supplies." Each category carries unique implications concerning GST applicability. Below is an analysis of the disparities among these categories:
Exempt Supplies:
- GST Applicability: Exempt supplies are exempt from GST, meaning no GST is imposed on their value, and suppliers cannot claim input tax credit (ITC) for the GST paid on inputs and services used for such supplies.
- Examples: Essential goods and services like fresh produce, milk, and healthcare services from clinical establishments are typically exempt from GST.
Nil Rated Supplies:
- GST Applicability: Nil rated supplies are also free from GST but are specifically taxed at a 0% GST rate. Suppliers can claim input tax credit on GST paid for inputs and services.
- Examples: Exported goods and services, such as pharmaceuticals and certain agricultural products, fall under this category.
Zero Rated Supplies:
- GST Applicability: Zero-rated supplies share similarities with nil-rated supplies as they are taxed at a 0% GST rate. However, zero-rated supplies pertain exclusively to exports of goods and services, allowing suppliers to claim input tax credit on GST paid for inputs and services.
- Examples: Goods and services exported to foreign countries are classified as zero-rated supplies under GST.
Non-GST Supplies:
- GST Applicability: Non-GST supplies are beyond the GST scope, exempt from GST levy or collection, and do not qualify for input tax credit.
- Examples: Items such as petroleum products (subject to separate state taxes), alcohol for human consumption, and specific goods like stamps and currency are considered non-GST supplies.
In essence, the primary differentiators among these categories lie in the tax rate and the eligibility for claiming input tax credit:
- Exempt supplies are GST-free, and ITC cannot be claimed.
- Nil rated supplies are taxed at a 0% GST rate, with ITC claimable.
- Zero-rated supplies specifically apply to exports, taxed at a 0% GST rate, with ITC claimable.
- Non-GST supplies are completely outside GST's purview, without GST levy or ITC eligibility.
|
42 videos|98 docs|12 tests
|
FAQs on GST Exemption: List of Goods & Services Exempt Under GST - Taxation for CA Intermediate
| 1. What is an exempt supply in GST? |  |
| 2. How is Input Tax Credit (ITC) treated in case of exempt supplies? |  |
| 3. What is a non-taxable supply under GST? |  |
| 4. What are some exemptions of services under GST for CA Intermediate students to be aware of? |  |
| 5. What are some frequently asked questions (FAQs) related to exempt supplies and ITC in GST? |  |

|
Explore Courses for CA Intermediate exam
|

|

















