Year 11 Exam > Year 11 Notes > Biology for GCSE/IGCSE > Enzyme Action & Specificity
Enzyme Action & Specificity | Biology for GCSE/IGCSE - Year 11 PDF Download
Enzyme Action & Specificity: Extended
- Enzymes exhibit specificity to particular substrates due to the complementarity between the active site of the enzyme, where the substrate binds, and the substrate itself.
- The unique three-dimensional structure of enzymes, being proteins, underpins their specificity.
- This concept is encapsulated in the lock and key hypothesis.
- Upon the substrate binding to the active site, it forms an enzyme-substrate complex.
- Following the reaction, the products disengage from the active site, facilitated by their altered shape, rendering the enzyme available to bind another substrate.
How Enzymes Work
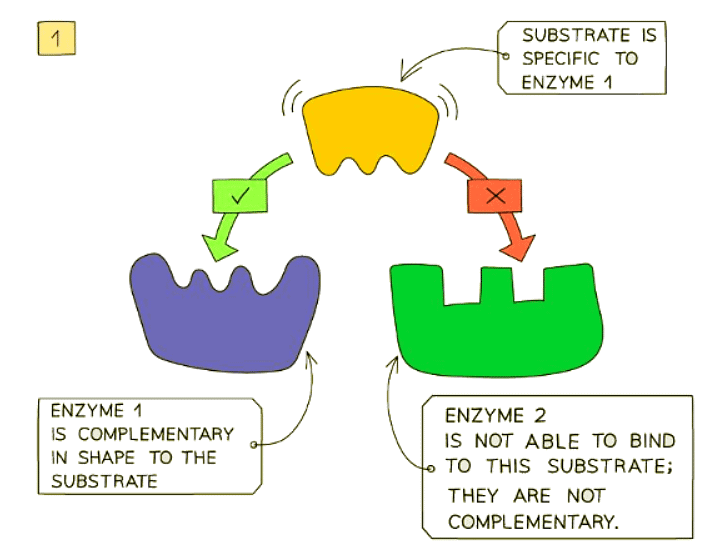
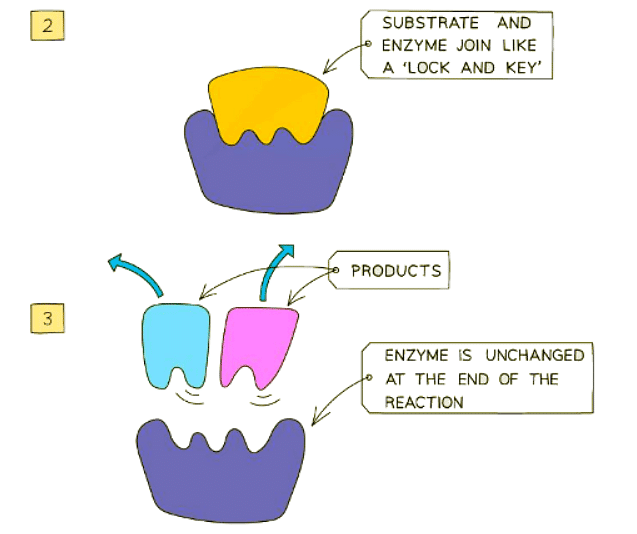
Enzymes Work Process:
- Enzymes and substrates exhibit random movement within a solution.
- When an enzyme and its corresponding substrate collide randomly, and the substrate fits into the enzyme's active site, an enzyme-substrate complex is generated, initiating the reaction.
- Subsequently, products emerge from the substrates within the active site, and upon release, the enzyme remains unaltered, available to catalyze subsequent reactions.
Question for Enzyme Action & SpecificityTry yourself: What is the main reason for the specificity of enzymes to particular substrates?View Solution
The document Enzyme Action & Specificity | Biology for GCSE/IGCSE - Year 11 is a part of the Year 11 Course Biology for GCSE/IGCSE.
All you need of Year 11 at this link: Year 11
|
110 videos|158 docs|34 tests
|
FAQs on Enzyme Action & Specificity - Biology for GCSE/IGCSE - Year 11
| 1. How do enzymes work in the body? |  |
Ans. Enzymes work by speeding up chemical reactions in the body. They bind to specific molecules, called substrates, and lower the activation energy needed for the reaction to occur, making the process more efficient.
| 2. What is enzyme specificity? |  |
Ans. Enzyme specificity refers to the ability of an enzyme to only catalyze a specific reaction with a specific substrate. Each enzyme has a unique active site that fits only one specific substrate, ensuring precise and efficient reactions.
| 3. How does enzyme action impact biological processes? |  |
Ans. Enzyme action is crucial for various biological processes such as metabolism, digestion, and cellular signaling. Without enzymes, these processes would be too slow to sustain life, highlighting the importance of enzyme specificity in maintaining cellular functions.
| 4. Can enzymes work on any type of substrate? |  |
Ans. Enzymes are highly specific and can only work on substrates that fit into their unique active sites. While some enzymes may have flexibility in recognizing similar substrates, they generally cannot catalyze reactions with completely different molecules.
| 5. How can enzyme specificity be affected by factors such as pH and temperature? |  |
Ans. Enzyme specificity can be influenced by pH and temperature changes. Extreme pH levels or temperatures can alter the enzyme's structure, affecting its active site and overall function. This can lead to a decrease in enzyme activity and specificity.

|
Explore Courses for Year 11 exam
|

|
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.
Related Searches
















