Year 11 Exam > Year 11 Notes > Biology for GCSE/IGCSE > Photosynthesis Chemical Equation
Photosynthesis Chemical Equation | Biology for GCSE/IGCSE - Year 11 PDF Download
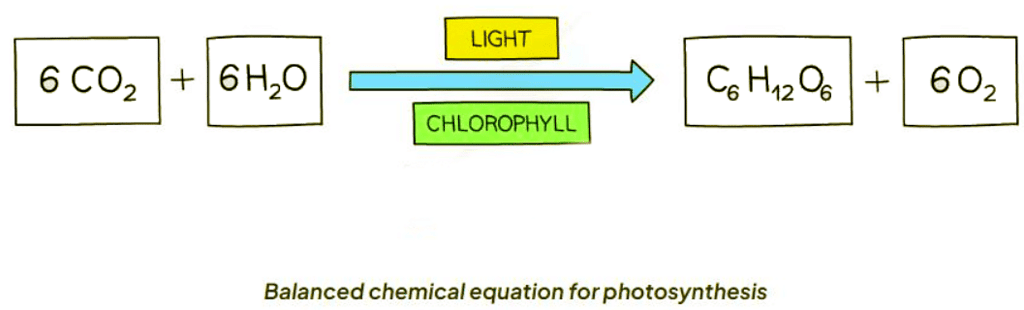
Balanced Photosynthesis Chemical Equation: Extended
- The balanced chemical equation for photosynthesis is:

- The light energy is converted into chemical energy in the bonds that hold the atoms in the glucose molecules together.
- In the process of photosynthesis, light energy is absorbed by chlorophyll molecules in the chloroplasts of plant cells.
- This energy is then used to power a series of chemical reactions that convert carbon dioxide and water into glucose and oxygen.
- Specifically, during the light-dependent reactions of photosynthesis, light energy is used to split water molecules into oxygen, protons, and electrons.
- These electrons are then used to generate ATP (adenosine triphosphate) and NADPH (nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate), which are energy-rich molecules used in the subsequent light-independent reactions (Calvin cycle).
- In the Calvin cycle, ATP and NADPH are utilized to convert carbon dioxide into glucose.
- Thus, the light energy is ultimately stored in the chemical bonds of glucose molecules, representing a form of chemical energy that can be used by the plant for various metabolic processes.
Question for Photosynthesis Chemical EquationTry yourself: What is the purpose of the light-dependent reactions in photosynthesis?View Solution
The document Photosynthesis Chemical Equation | Biology for GCSE/IGCSE - Year 11 is a part of the Year 11 Course Biology for GCSE/IGCSE.
All you need of Year 11 at this link: Year 11
|
110 videos|158 docs|34 tests
|
FAQs on Photosynthesis Chemical Equation - Biology for GCSE/IGCSE - Year 11
| 1. What is the chemical equation for photosynthesis? |  |
Ans. The chemical equation for photosynthesis is 6CO2 + 6H2O + light energy → C6H12O6 + 6O2.
| 2. What are the reactants and products of photosynthesis? |  |
Ans. The reactants of photosynthesis are carbon dioxide (CO2) and water (H2O), while the products are glucose (C6H12O6) and oxygen (O2).
| 3. Why is light energy necessary for photosynthesis to occur? |  |
Ans. Light energy is necessary for photosynthesis to occur because it is used to power the process of converting carbon dioxide and water into glucose and oxygen.
| 4. How does photosynthesis contribute to the environment? |  |
Ans. Photosynthesis contributes to the environment by producing oxygen as a byproduct, which is essential for the survival of most living organisms, and by removing carbon dioxide from the atmosphere, helping to regulate the Earth's climate.
| 5. What are the factors that can affect the rate of photosynthesis? |  |
Ans. Factors that can affect the rate of photosynthesis include light intensity, carbon dioxide concentration, temperature, and the availability of water and nutrients.

|
Explore Courses for Year 11 exam
|

|
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.
Related Searches