Class 10 Exam > Class 10 Notes > Biology for GCSE/IGCSE > Emulsification of Fats & Oils
Emulsification of Fats & Oils | Biology for GCSE/IGCSE - Class 10 PDF Download
Emulsification of Fats & Oils: Extended
- Liver cells produce bile, which is then stored in the gallbladder.
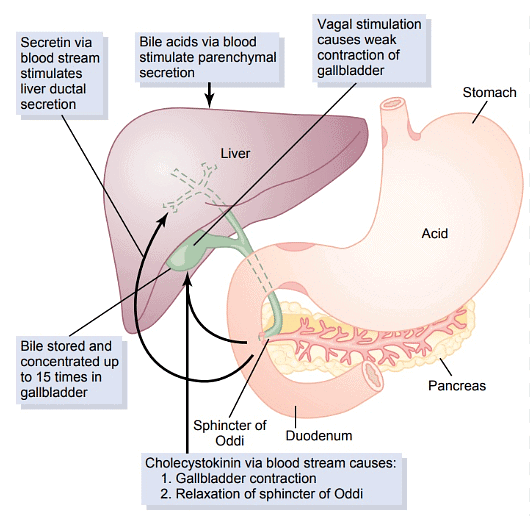 Bile production and secretion
Bile production and secretion
Bile has two main roles
- Bile is alkaline to neutralize the hydrochloric acid from the stomach.
- Enzymes in the small intestine function best at a higher (more alkaline) pH than those in the stomach.
- Bile breaks down large fat droplets into smaller ones, a process called emulsification. The increased surface area allows lipase to break down lipids into glycerol and fatty acids more quickly.
Question for Emulsification of Fats & OilsTry yourself: What is the main role of bile in the digestive process?View Solution
The document Emulsification of Fats & Oils | Biology for GCSE/IGCSE - Class 10 is a part of the Class 10 Course Biology for GCSE/IGCSE.
All you need of Class 10 at this link: Class 10
|
101 videos|193 docs|33 tests
|
FAQs on Emulsification of Fats & Oils - Biology for GCSE/IGCSE - Class 10
| 1. What is emulsification and why is it important in the food industry? |  |
Ans. Emulsification is the process of mixing two immiscible liquids, such as fats and water, to form a stable emulsion. This process is important in the food industry as it helps to create products with desirable textures, appearances, and mouthfeels.
| 2. How does emulsification of fats and oils work on a molecular level? |  |
Ans. Emulsification of fats and oils works by breaking down the large fat molecules into smaller droplets, which are then dispersed in water with the help of an emulsifier. The emulsifier helps to stabilize the emulsion by forming a protective layer around the fat droplets, preventing them from coalescing.
| 3. What are some common emulsifiers used in the food industry for emulsification of fats and oils? |  |
Ans. Some common emulsifiers used in the food industry for emulsification of fats and oils include lecithin, mono- and diglycerides, and polysorbate.
| 4. How can emulsification of fats and oils affect the nutritional value of a food product? |  |
Ans. Emulsification of fats and oils can affect the nutritional value of a food product by increasing the bioavailability of fat-soluble vitamins and nutrients. It can also help to reduce the amount of fat needed in a product, leading to a lower calorie content.
| 5. What are some challenges faced in the emulsification of fats and oils in food production? |  |
Ans. Some challenges faced in the emulsification of fats and oils in food production include achieving a stable emulsion, preventing phase separation, and maintaining the desired texture and mouthfeel of the final product.
Related Searches




















