Grade 11 Exam > Grade 11 Notes > Chemistry for Grade 11 (IGCSE) > Experimental Design
Experimental Design | Chemistry for Grade 11 (IGCSE) PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Time |

|
| Temperature |

|
| Mass |

|
| Volume - Liquids |

|
| Volume-gases |

|
| Advantages & Disadvantages of Methods & Apparatus |

|
Time
- Time can be gauged using either a stopwatch or a stopclock, typically accurate to one or two decimal places.
- Common time units include seconds or minutes, though different units may be utilized for very slow reactions, such as rusting.
- 1 minute is equivalent to 60 seconds.
Temperature
- Temperature is determined using a thermometer or a digital probe.
- Laboratory thermometers usually offer a precision of half or one degree.
- Digital temperature probes, more accurate than traditional thermometers, often provide readings to 0.1 degrees Celsius.
- Traditional thermometers function based on the uniform expansion and contraction of a liquid substance with temperature, while digital probes can be equally or more precise.
- The standard unit of temperature is degrees Celsius (ºC).
Question for Experimental DesignTry yourself: Which instrument is typically used to measure time accurately to one or two decimal places?View Solution
Mass
- Mass is assessed using a digital balance, typically providing measurements to two decimal places.
- Balances need to be zeroed (tared) prior to usage.
- The primary unit of mass is kilograms (kg), although grams (g) are predominantly used in chemistry.
- 1 kilogram equals 1000 grams.
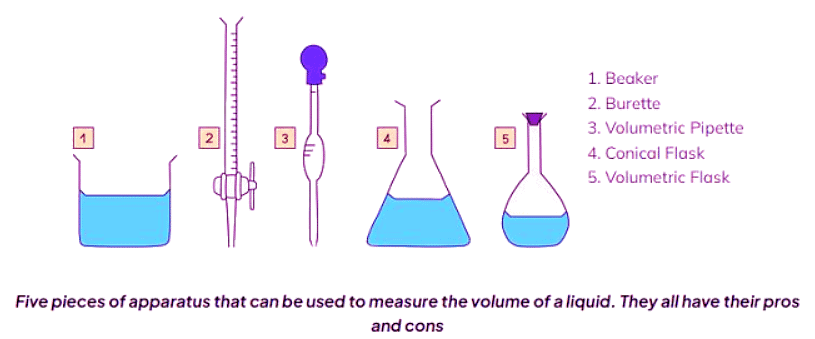
Volume - Liquids
- Determining the volume of a liquid depends on the required level of accuracy, and various apparatus are available for this purpose.
- For approximate volumes where high accuracy isn't crucial, measuring cylinders are employed.
- These cylinders are graduated, featuring a scale for measurement, and are typically offered in sizes ranging from 10 cm3 to 1 liter (1 dm3).
- Volumetric pipettes offer the most precise method for measuring a fixed liquid volume, usually 10 cm3 or 25 cm3.
- They include a scratch mark on the neck, aligned with the bottom of the meniscus for measurement.
- Burettes provide the most precise means of measuring a variable liquid volume between 0 cm3 and 50 cm3, commonly used in titrations.
- When using burettes, it's important to read the scale from top to bottom, with 0.00 cm3 positioned at the top of the column.
- Regardless of the apparatus used, markings may appear in milliliters (ml), equivalent to cubic centimeters (cm3).
- Diagram of a burette with conical flask and pipette with filler:

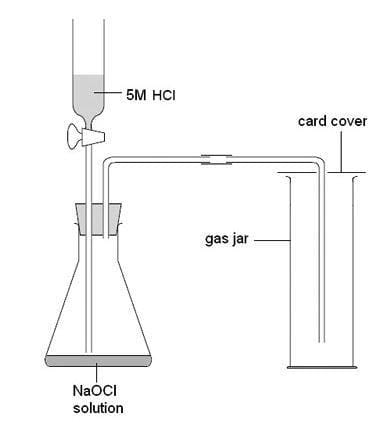
Volume-gases
- Gas volume measurement often requires collecting the gas in a graduated measuring device.
- Typically, a gas syringe serves as the primary apparatus for this purpose.
- Alternatively, an inverted graduated cylinder submerged in water may suffice, as long as the gas is not water-soluble.
- In instances where the gas is heavier than air and has coloration, the cylinder may be used in an upright position.
- Diagram of the set-up for an experiment involving gas collection:

Question for Experimental DesignTry yourself: What is the primary unit of mass used in chemistry?View Solution
Advantages & Disadvantages of Methods & Apparatus
- In laboratory settings, there are often various options for performing a particular task.
- Selecting the most suitable apparatus is essential for effective experimental planning and design.
- This involves understanding the advantages and disadvantages associated with different laboratory equipment.

Planning your method
- Effective experimental design involves addressing key questions such as:
- Have I selected the right equipment for the measurement I intend to make?
- Will the chosen equipment provide results within a reasonable timeframe?
- Will it yield sufficient data for analysis and drawing conclusions?
- Does it allow for repeated trials to assess result reliability?
- Does my experimental plan encompass a suitable range of outcomes?
- How can I ensure the accuracy of my results?
- Have I opted for appropriate quantities without being wasteful or compromising safety?
- Exam questions may inquire about experimental methodologies, and your familiarity with practical chemistry techniques can help identify errors and propose enhancements.
The document Experimental Design | Chemistry for Grade 11 (IGCSE) is a part of the Grade 11 Course Chemistry for Grade 11 (IGCSE).
All you need of Grade 11 at this link: Grade 11
|
103 docs|53 tests
|
FAQs on Experimental Design - Chemistry for Grade 11 (IGCSE)
| 1. What are the advantages of using a thermometer to measure temperature? |  |
Ans. Thermometers provide a quick and accurate measurement of temperature, making it easy to monitor changes in temperature over time. They are also portable and can be used in various settings, making them a versatile tool for temperature measurement.
| 2. How does measuring mass differ from measuring volume for liquids? |  |
Ans. Measuring mass involves using a balance or scale to determine the amount of matter in an object, while measuring volume for liquids typically involves using a graduated cylinder or beaker to measure the amount of space the liquid occupies.
| 3. What are the advantages of using a syringe to measure the volume of gases? |  |
Ans. Syringes provide a precise and controlled way to measure the volume of gases, as the plunger can be moved to accurately capture the gas. They are also easy to read and have markings for accurate measurements.
| 4. What experimental design considerations should be taken into account when measuring temperature? |  |
Ans. When designing an experiment to measure temperature, factors such as the type of thermometer used, the placement of the thermometer, and the calibration of the thermometer should be carefully considered to ensure accurate and reliable results.
| 5. What are the disadvantages of using a balance to measure mass compared to a scale? |  |
Ans. Balances can be more sensitive to external factors such as air currents or vibrations, which can affect the accuracy of the measurement. Scales are often more stable and less prone to these external influences, making them a more reliable option for measuring mass.

|
Explore Courses for Grade 11 exam
|

|
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.
Related Searches