Year 11 Exam > Year 11 Notes > Economics for GCSE/IGCSE > Fiscal Policy Measures
Fiscal Policy Measures | Economics for GCSE/IGCSE - Year 11 PDF Download
Fiscal Policy Defined
- Fiscal Policy utilizes government spending and taxation to impact total demand within the economy.
- Expansionary fiscal policies aim to stimulate further economic growth, achieved through tax reduction or increased government spending.
- Contractionary fiscal policies aim to decelerate economic growth or curb inflation, achieved through tax hikes or reduced government spending.
- Fiscal Policy is typically outlined annually by the Government through the Government Budget.
- A balanced budget indicates that government revenue equals government expenditure.
- A budget deficit indicates that government revenue is less than government expenditure.
- A budget surplus indicates that government revenue exceeds government expenditure.
- Financing a budget deficit necessitates public sector borrowing, which adds to the public debt.
The Effects of Fiscal Policy on Government Macroeconomic Aims
- Understanding Total Demand Calculation: To comprehend the impact of fiscal policy on an economy, it's essential to grasp how total demand (Gross Domestic Product) is computed.
- Components of Total Demand: Total demand equals household consumption (C), firms' investment (I), government spending (G), and exports (X) minus imports (M). It can be represented as: Total demand = C + I + G + (X - M).
- Influence of Fiscal Policy Changes: Changes in fiscal policy can affect any of these components individually and often have simultaneous impacts on multiple components.
Examples of the Impact of Contractionary Fiscal Policy
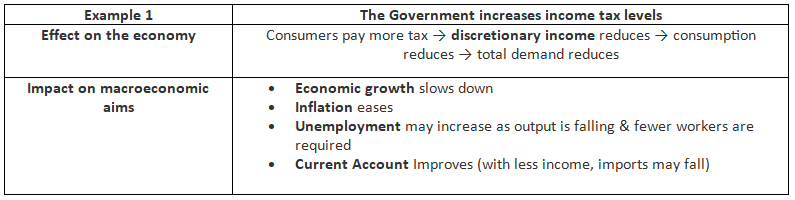
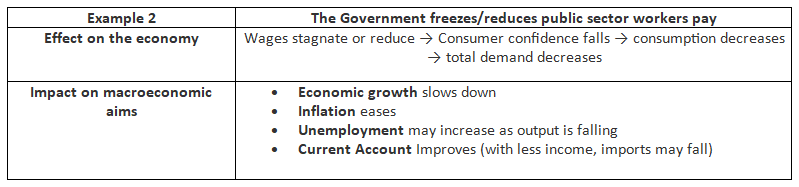
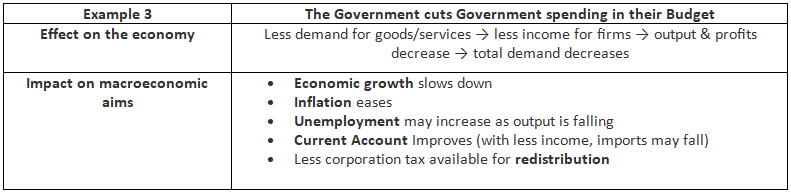
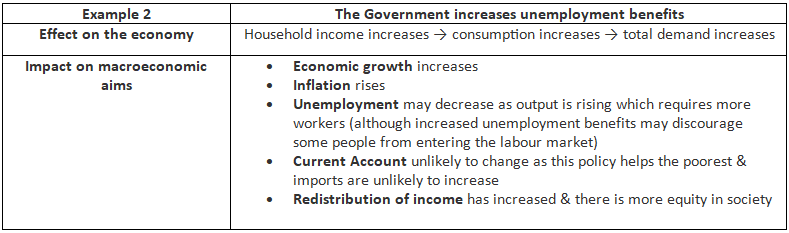
Examples of The Impact of Expansionary Fiscal Policy
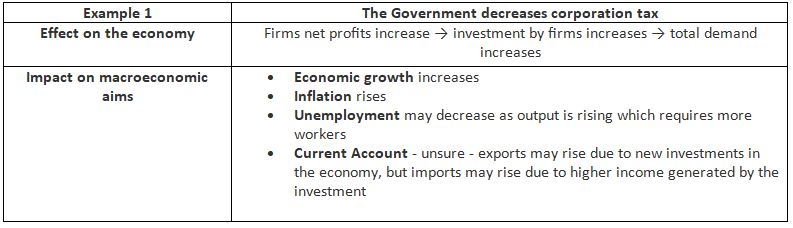
Effects of Fiscal Policy
- Targeted Spending: Targeted spending involves directing financial resources towards specific sectors or industries to spur their development. For instance, investing in renewable energy projects can help reduce carbon emissions and promote sustainability.
- Shorter Impact Timeframe: Compared to monetary policy adjustments, fiscal policy changes take effect more rapidly. For example, a government decision to increase infrastructure spending can create jobs and stimulate economic growth almost immediately.
- Income Redistribution: Through taxation measures, fiscal policy aims to redistribute wealth by collecting taxes from the affluent and using them to fund social programs that benefit the less privileged. This helps create a more equitable society.
- Addressing Negative Externalities: Fiscal policy can be used to discourage activities that have harmful effects on society or the environment. By imposing taxes on products like tobacco or carbon emissions, the government can mitigate these negative impacts.
- Promoting Merit and Public Goods Consumption: Government intervention through fiscal policy can encourage the consumption of goods and services that bring positive externalities to society. For example, subsidizing education can lead to a more knowledgeable workforce and boost economic productivity.
- Boosting Total Supply: Immediate government spending on infrastructure projects, such as building airports or roads, not only creates jobs in the short term but also enhances the economy's total productive capacity in the long run. This leads to sustained economic growth and development.
Weaknesses of Fiscal Policy
- Policies and Government Transitions
- Policies often undergo significant changes with the election of new governments.
- Newly implemented policies may lack continuity, especially in long-term infrastructure projects.
- Long-Term Effects of Government Spending
- Increased government spending can result in budget deficits.
- The need to repay this debt may impose austerity measures on future generations.
- Conflicting Objectives
- Conflicts can arise when pursuing different objectives simultaneously.
- For example, reducing taxes to boost economic growth may trigger inflation.
Question for Fiscal Policy MeasuresTry yourself: What is the purpose of expansionary fiscal policies?View Solution
The document Fiscal Policy Measures | Economics for GCSE/IGCSE - Year 11 is a part of the Year 11 Course Economics for GCSE/IGCSE.
All you need of Year 11 at this link: Year 11
|
71 videos|104 docs|48 tests
|
FAQs on Fiscal Policy Measures - Economics for GCSE/IGCSE - Year 11
| 1. What is fiscal policy and how does it impact the economy? |  |
Ans. Fiscal policy refers to the government's use of taxation and spending to influence the economy. By adjusting tax rates and government spending levels, policymakers can stimulate or slow down economic growth, control inflation, and reduce unemployment.
| 2. How does fiscal policy differ from monetary policy? |  |
Ans. Fiscal policy involves government actions related to taxation and spending, while monetary policy involves actions taken by central banks to control the money supply and interest rates. Fiscal policy is determined by the government, while monetary policy is determined by the central bank.
| 3. How does fiscal policy impact government macroeconomic aims? |  |
Ans. Fiscal policy can impact government macroeconomic aims such as economic growth, inflation, and unemployment. For example, increasing government spending can stimulate economic growth, but may also lead to inflation if not carefully managed.
| 4. What are some examples of fiscal policy measures that can be implemented? |  |
Ans. Some examples of fiscal policy measures include changes in tax rates, increased government spending on infrastructure projects, and the implementation of targeted tax credits to stimulate specific industries.
| 5. How do budget concepts play a role in fiscal policy decisions? |  |
Ans. Budget concepts such as deficit spending, surplus, and debt-to-GDP ratio play a crucial role in fiscal policy decisions. Policymakers must consider the long-term implications of their fiscal policy decisions on the government's budget and overall economic stability.
Related Searches















