Year 11 Exam > Year 11 Notes > Economics for GCSE/IGCSE > Causes & Consequences of Growth
Causes & Consequences of Growth | Economics for GCSE/IGCSE - Year 11 PDF Download
Causes of Economic Growth
Growth Caused by a Change in Total Demand
Actual economic growth refers to a rise in the volume of goods and services produced within an economy over a specific period.
- Typically quantified by the percentage alteration in real Gross Domestic Product (GDP).
- Any elevation in the components of real GDP—be it consumption, investment, government spending, or net exports—will result in a surge in total demand.
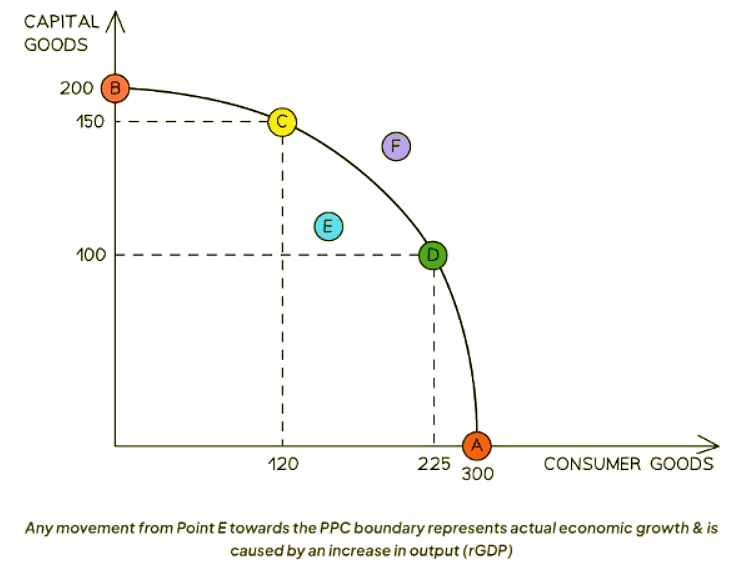
Diagram Explanation:
- Previously untapped resources or factors of production are now being utilized.
- This shift is exemplified by a movement from a position within the production possibilities curve (PPC), like Point E, towards the boundary of the PPC.
- At any given moment, actual economic growth might fall short of the potential growth that the economy could achieve.
Growth Caused by a Change in the Quantity/Quality of Factors of Production
- Potential growth signifies the expansion in the productive capacity of an economy.
- This expansion occurs through increases in the quantity or quality of the factors of production available within an economy.
- For instance, improving the quality of a factor of production, such as through training and education, enhances workforce productivity, consequently broadening production possibilities.
- Similarly, augmenting the quantity of a factor of production, like through changes in migration policies to allow more foreign workers, can expand production possibilities.
- Enhancing the quality of capital is achieved by investing in new capital machinery.
- Adoption of new technology leads to increased productivity, representing an advancement in production capabilities.

Diagram Explanation:
- Economic growth signifies an expansion in the productive capacity of an economy, illustrated by an outward shift of the entire curve denoted by 'A'.
- This shift enables the production of more consumer goods and capital goods utilizing all available resources.
Question for Causes & Consequences of GrowthTry yourself: What does actual economic growth refer to?View Solution
The Consequences of Economic Growth
- Economic growth plays a pivotal role in enhancing living standards within a society.
- There is ongoing debate regarding the downsides of economic growth, leading to questions about its continued prioritization in macroeconomics. Alternatively, there is a growing advocacy for emphasizing overall societal welfare.
A Table Summarising the Benefits & Costs of Economic Growth

The document Causes & Consequences of Growth | Economics for GCSE/IGCSE - Year 11 is a part of the Year 11 Course Economics for GCSE/IGCSE.
All you need of Year 11 at this link: Year 11
|
71 videos|82 docs|39 tests
|
FAQs on Causes & Consequences of Growth - Economics for GCSE/IGCSE - Year 11
| 1. What are some common causes of economic growth? |  |
Ans. Some common causes of economic growth include increased productivity, technological advancements, investment in physical and human capital, improved infrastructure, and favorable government policies.
| 2. How does economic growth impact employment rates? |  |
Ans. Economic growth typically leads to an increase in employment rates as businesses expand and create more job opportunities to meet the growing demand for goods and services.
| 3. What are some consequences of sustained economic growth? |  |
Ans. Some consequences of sustained economic growth include higher living standards, increased income levels, reduced poverty rates, improved infrastructure, and greater access to education and healthcare.
| 4. How do government policies influence economic growth? |  |
Ans. Government policies can influence economic growth by promoting investment, encouraging innovation, reducing regulatory burdens, fostering competition, and maintaining macroeconomic stability through measures such as monetary and fiscal policies.
| 5. How does economic growth impact income inequality? |  |
Ans. Economic growth can either exacerbate or reduce income inequality depending on various factors such as the distribution of wealth, access to education and opportunities, and government policies aimed at addressing inequality.
|
Explore Courses for Year 11 exam
|

|
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.
Related Searches
















