Class 10 Exam > Class 10 Notes > Computer for GCSE/IGCSE > Number Systems
Number Systems | Computer for GCSE/IGCSE - Class 10 PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Introduction |

|
| The Denary Number System |

|
| The Binary Number System |

|
| The Hexadecimal Number System |

|
Introduction
- In the realm of Computer Science, data can be represented using three primary numbering systems: Denary, Binary, and Hexadecimal.
The Denary Number System
- The denary, or decimal, system operates on a base-10 model, employing ten digits from 0 to 9.
- Denary numbers are versatile, capable of representing integers, fractions, and decimal figures.
- In denary notation, each digit's position denotes a power of 10, starting from the rightmost digit representing 100, the next 101, and so forth.
- Converting data between different numerical systems, such as denary to binary or denary to hexadecimal, is a common requirement.
- Conversion processes are greatly facilitated with the aid of a conversion table, streamlining operations. For instance, the number 3268 can be transcribed as follows:
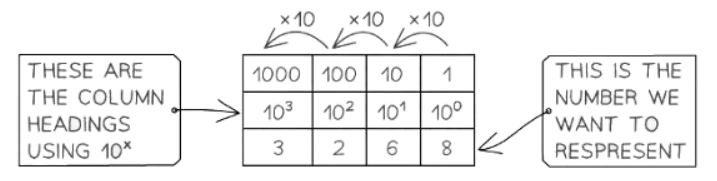
- (3 x 1000) + (2 x 100) + (6 x 10) + (8 x 1) = 3268
Question for Number SystemsTry yourself: Which numbering system operates on a base-10 model and employs ten digits from 0 to 9?View Solution
The Binary Number System
- Binary, a base-2 numbering system, employs just two digits: 0 and 1.
- In binary notation, every digit symbolizes a power of 2, starting from the rightmost digit representing 20, followed by 21, and so forth.
- For instance, the decimal number 12 is represented as 1100 in binary:
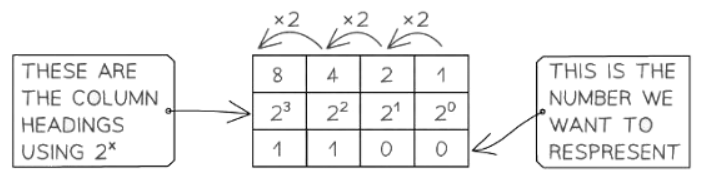
- We know this as (1 x 8) + (1 x 4) + (0 x 2) + (0 x 1) =12
The Hexadecimal Number System
- Hexadecimal, a base-16 numbering system, incorporates 16 digits: 0 to 9 and A to F, where A represents 10, B represents 11, and so forth up to F, representing 15.
- In hexadecimal notation, each digit signifies a power of 16, with the rightmost digit representing 160, followed by 161, and so forth.
- For example, the decimal number 146 is represented as 92 in hexadecimal:
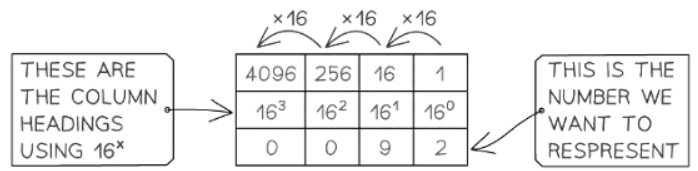
The document Number Systems | Computer for GCSE/IGCSE - Class 10 is a part of the Class 10 Course Computer for GCSE/IGCSE.
All you need of Class 10 at this link: Class 10
|
99 docs|31 tests
|
FAQs on Number Systems - Computer for GCSE/IGCSE - Class 10
| 1. What is the Denary Number System? |  |
Ans. The Denary Number System, also known as the Decimal Number System, is a base-10 numeral system that uses 10 digits (0-9) to represent numbers. Each digit's place value is a power of 10, making it the most commonly used number system in everyday life.
| 2. What is the Binary Number System? |  |
Ans. The Binary Number System is a base-2 numeral system that uses only two digits, 0 and 1, to represent numbers. It is commonly used in computer science and digital electronics, where each digit's place value corresponds to a power of 2.
| 3. What is the Hexadecimal Number System? |  |
Ans. The Hexadecimal Number System is a base-16 numeral system that uses 16 symbols (0-9 and A-F) to represent numbers. It is often used in computer programming and digital communications due to its concise representation of binary data.
| 4. How do you convert a Denary number to a Binary number? |  |
Ans. To convert a Denary number to a Binary number, divide the Denary number by 2 and record the remainder. Continue this process until the quotient is 0, then write the remainders in reverse order to get the Binary equivalent.
| 5. Why is the Binary Number System important in computing? |  |
Ans. The Binary Number System is important in computing because computers use electrical circuits that can be in one of two states (0 or 1). By representing data and instructions in Binary form, computers can process and store information efficiently, making it the foundation of digital technology.
Related Searches















