Year 11 Exam > Year 11 Notes > Computer for GCSE/IGCSE > MAC address
MAC address | Computer for GCSE/IGCSE - Year 11 PDF Download
MAC Addresses
- A Media Access Control (MAC) address serves to identify a device within a network.
- This distinct identifier comprises six pairs of hexadecimal codes separated by colons.
- Each pair of hexadecimal digits represents a byte of data, resulting in a total length of 6 bytes or 48 bits for a MAC address.
- For instance, a MAC address could appear as b4:71:ac:f3:21:a2.
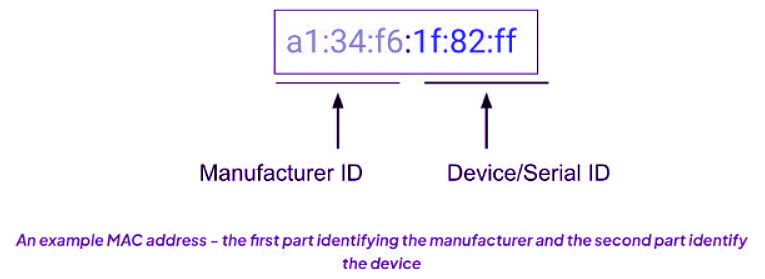
- Manufacturers assign MAC addresses to Network Interface Cards (NICs).
- The first three pairs denote the manufacturer's identification number, while the last three pairs represent the NIC's serial number, enabling device identification on the network.
- A MAC address remains static and cannot be altered.
Differences between an IP address and a MAC address

Question for MAC addressTry yourself: What is the purpose of a MAC address?View Solution
The document MAC address | Computer for GCSE/IGCSE - Year 11 is a part of the Year 11 Course Computer for GCSE/IGCSE.
All you need of Year 11 at this link: Year 11
|
92 docs|30 tests
|
FAQs on MAC address - Computer for GCSE/IGCSE - Year 11
| 1. What is a MAC address and how is it different from an IP address? |  |
Ans. A MAC address, also known as a physical address, is a unique identifier assigned to network interfaces for communications on a network segment. It is hardcoded onto the network interface card and is used for local communication within a network. An IP address, on the other hand, is a logical address assigned to devices for communication over a network and is used for identifying devices on a larger scale, such as the internet.
| 2. Can a MAC address change? |  |
Ans. Typically, a MAC address is hardcoded onto the network interface card by the manufacturer and does not change. However, there are certain methods that allow for MAC address spoofing, where the MAC address can be temporarily changed for specific purposes.
| 3. How many characters are in a MAC address? |  |
Ans. A MAC address is usually represented as a string of 12 hexadecimal characters (0-9, A-F), separated by colons or dashes. For example, 00:1A:2B:3C:4D:5E.
| 4. Can two devices have the same MAC address? |  |
Ans. No, MAC addresses are globally unique identifiers assigned to network interfaces, ensuring that no two devices have the same MAC address. This uniqueness is crucial for proper functioning of network communication.
| 5. Can a MAC address be used to track a device's physical location? |  |
Ans. While MAC addresses can provide information about the manufacturer and type of device, they do not contain specific location data. MAC addresses are primarily used for network communication and are not designed to track physical locations of devices.

|
Explore Courses for Year 11 exam
|

|
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.
Related Searches
















