Year 11 Exam > Year 11 Notes > Business Studies for GCSE/IGCSE > Classification Using the Economic Sector
Classification Using the Economic Sector | Business Studies for GCSE/IGCSE - Year 11 PDF Download
Primary, Secondary and Tertiary Sectors
The Three Main Business Sectors
- Businesses can be categorized based on the sector they operate in.
- This classification simplifies industry categorization:
- Allows for comparisons between companies within the same sector.
- Does not fully represent the intricate connections in the business world.
- Many businesses operate in multiple sectors or do not neatly fit into a single category.

- The primary sector focuses on extracting raw materials from various sources, including land, sea, or air, such as agriculture, mining, or fishing.
- The secondary sector involves the processing of raw materials, such as refining oil, and the manufacturing of goods like vehicles.
- The tertiary sector is dedicated to offering diverse services to consumers and businesses, encompassing areas such as entertainment, banking, or hospitality.
The chain of production
- The connection between the three sectors lies in the production chain, which constitutes a sequence of actions aimed at transforming raw materials into a finalized product ready for sale and marketing.

Changes in Sector Importance
- As economies expand and progress, many companies within these economies will transition their sector of operation (known as sectoral change).
- Typically, there are progressively higher levels of profits achievable in each successive sector. This progression is attributed to the fact that each sector generates more value than the one before it. Greater added value corresponds to increased profits.
Question for Classification Using the Economic SectorTry yourself: Which sector of the economy involves the extraction of raw materials?View Solution
Less Developed Economies
- Less developed economies typically center their focus on the primary sector, with a majority of the workforce engaged in agriculture and food production.
- Over the past twenty years, there has been a worldwide shift away from employment in primary sector activities.
- In the least developed countries, the proportion of the workforce employed in the primary sector remains consistently high.
- This trend is attributed partly to lower rates of participation in education and insufficient infrastructure to facilitate manufacturing or service delivery.
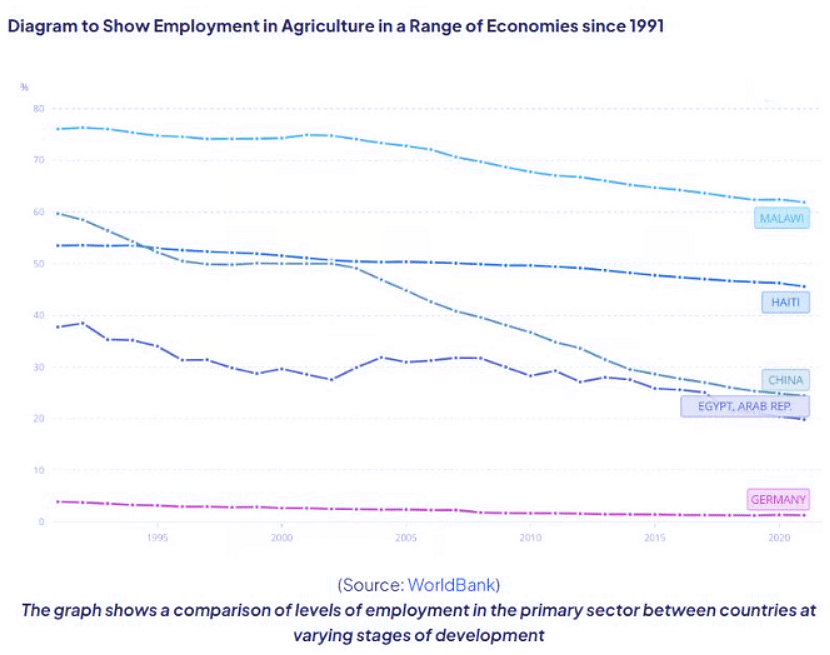
Diagram Analysis
- Malawi still maintains the highest percentage of employment in the primary sector.
- China has experienced a notable decline in primary sector activities.
- Germany has historically had minimal involvement in the primary sector and likely transitioned to manufacturing and services well before 1991.
Emerging Economies
- In emerging economies, advancements in technology have reduced the need for labor in the primary sector, leading to increased focus on manufacturing.
- The proportion of workers engaged in manufacturing has shown an upward trend over the past few decades.
- Many companies have moved their production facilities to capitalize on lower average wage levels in these economies.
- Emerging economies have witnessed growth in the tertiary and quaternary sectors, with a shift towards providing consumer services.

Diagram Analysis
- China leads with the highest proportion of secondary sector employment.
- Both Ghana and India have experienced substantial growth in this sector.
- Brazil and Turkey have maintained relatively stable secondary sectors from 1991 to 2019.
Developed Economies
- The most developed economies have a high percentage of the workforce engaged in the service sector, with a particular focus on the quaternary sector.
- Developed economies utilize their wealth to support advanced education and higher-level skills training, which in turn fosters the growth of these industries.
- Some exceptions like Australia (known for viticulture or wine production) and Norway (recognized for forestry and oil extraction) still maintain significant primary sectors.

Diagram Analysis
- The most developed nations exhibit a higher percentage of their workforce engaged in the service sector.
- Thailand's service industry has doubled its workforce from 1991 to 2019.
- Approximately half of Ecuador's labor force is currently employed in service-related roles.
The document Classification Using the Economic Sector | Business Studies for GCSE/IGCSE - Year 11 is a part of the Year 11 Course Business Studies for GCSE/IGCSE.
All you need of Year 11 at this link: Year 11
|
70 videos|94 docs|25 tests
|
FAQs on Classification Using the Economic Sector - Business Studies for GCSE/IGCSE - Year 11
| 1. What are the primary, secondary, and tertiary sectors in the economic classification system? |  |
Ans. The primary sector involves activities related to natural resources such as farming and mining. The secondary sector includes manufacturing and construction, while the tertiary sector comprises services like healthcare and education.
| 2. How have the importance of sectors changed over time in the economic sector classification? |  |
Ans. The importance of sectors has shifted over time due to factors such as technological advancements, globalization, and changes in consumer preferences. For example, the tertiary sector has grown in importance as societies become more service-oriented.
| 3. How does the economic sector classification impact a country's GDP? |  |
Ans. The sectoral composition of an economy can significantly impact its GDP. For example, a country with a strong tertiary sector may have a higher GDP compared to a country with a larger primary sector.
| 4. What are some examples of industries in each sector of the economic classification system? |  |
Ans. Examples of industries in the primary sector include agriculture and fishing, in the secondary sector include manufacturing and construction, and in the tertiary sector include healthcare and hospitality.
| 5. How do government policies and regulations affect the different sectors in the economic classification system? |  |
Ans. Government policies and regulations can have a significant impact on sectors by influencing factors such as investment, innovation, and competition. For example, subsidies for agriculture can support the primary sector, while regulations on emissions can affect the secondary sector.

|
Explore Courses for Year 11 exam
|

|
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.
Related Searches
















