Class 10 Exam > Class 10 Notes > Business Studies for GCSE/IGCSE > Motivational Theories
Motivational Theories | Business Studies for GCSE/IGCSE - Class 10 PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| An Introduction to Motivational Theories |

|
| Maslow's Hierarchy of Human Needs |

|
| Taylor's Scientific Management Theory |

|
| Herzberg's Motivation Theory |

|
An Introduction to Motivational Theories
- Motivation theories present diverse views on the significance of monetary incentives in inspiring employees, as well as how non-monetary factors can influence workers to enhance their performance and productivity.
- Key Motivational Theories
- Maslow's Hierarchy of Needs Theory: This theory suggests that individuals are motivated by a hierarchy of needs, progressing from basic physiological requirements to higher-level psychological needs. Once a need is fulfilled, it no longer serves as a motivator.
- Taylor's Scientific Management Theory: According to this theory, workers are primarily motivated by monetary rewards and require well-defined tasks and close supervision to perform efficiently.
- Herzberg's Two-Factor Theory: Herzberg posited that money is not a direct motivator, but its absence can lead to dissatisfaction. Instead, factors such as skill development opportunities and job enrichment are key motivators for employees.
Maslow's Hierarchy of Human Needs
- Maslow's Hierarchy of Needs presents five levels of human needs essential for individuals to achieve their maximum potential. Once a particular level of need is satisfied, it ceases to act as a motivator.
- When a need level is fulfilled, it typically loses its motivational power. For instance, after employees receive adequate compensation to meet their safety needs, they will start seeking the fulfillment of their love and belonging needs.
Maslow's Hierarchy of Needs
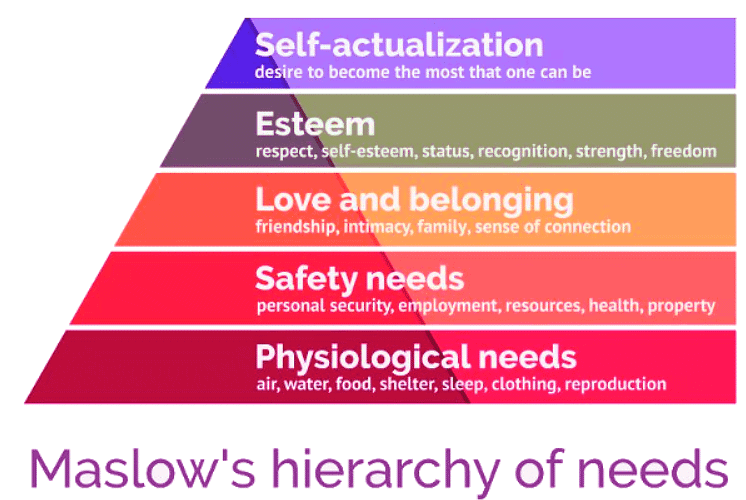
- Meeting Physiological Needs: Companies can ensure employees have essential amenities like a comfortable workspace, access to clean water and food, and sufficient breaks for rest.
- Addressing Safety Needs: Employers can offer job stability, fair compensation, benefits, and a safe work environment to fulfill employees' safety requirements.
- Fostering Love and Belonging: Businesses can promote teamwork and foster a sense of community and belonging among their workforce.
- Recognizing Esteem: Companies can acknowledge employees' achievements and cultivate a positive workplace culture that values individual contributions.
- Fulfilling Self-Actualization:
- Employers can support employees' pursuit of self-actualization by providing opportunities for them to explore their passions and interests.
- For instance, Barclays Bank exemplifies this by enabling elite athletes to balance work and training, emphasizing task completion over strict attendance.
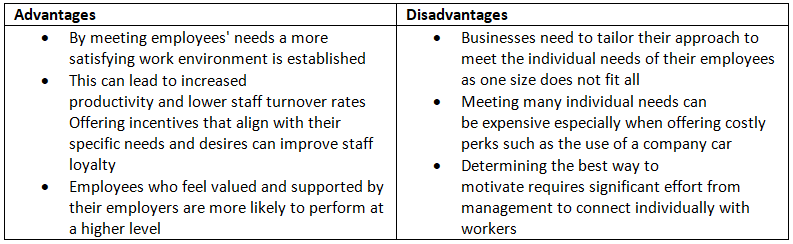
The Advantages & Disadvantages to Business of Applying Maslow's Hierarchy
Question for Motivational TheoriesTry yourself: According to Maslow's Hierarchy of Needs Theory, what happens once a need is fulfilled?View Solution
Taylor's Scientific Management Theory
- Developed by Frederick Taylor in the early 20th century, this theory emphasizes the division of complex tasks into simpler components.
- Standardizing work processes and providing workers with explicit instructions and training are key aspects of this approach, aimed at maximizing efficiency.
- Many manufacturing firms adopt Taylor's principles to structure their employee benefits.
- Piece rate pay systems, which tie compensation to output, are commonly used to incentivize productivity.
- Production lines that incorporate human labor often follow these principles to enhance operational efficiency.
Taylor's Theory of Motivation
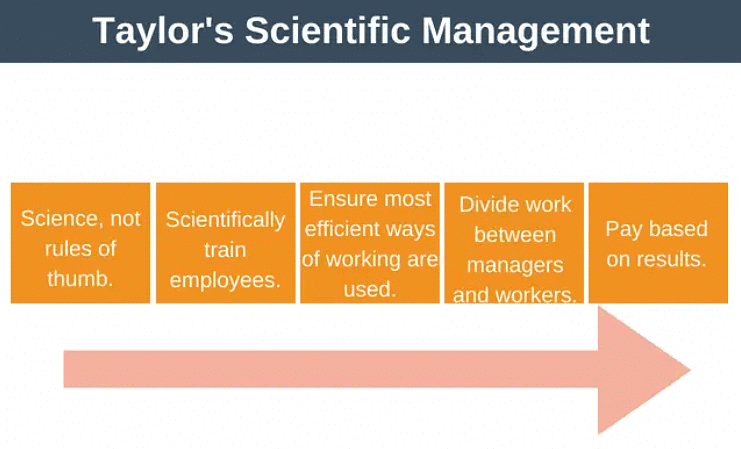
- Study and analyse the work process:
- Thoroughly examine each stage of the work process.
- Simplify complex tasks into more manageable ones and determine the most optimal methods for task execution.
- Standardise the work process:
- Develop detailed guidelines and protocols for every task to ensure consistency in execution among workers.
- Select and train workers
- Carefully select employees based on their aptitudes and capabilities.
- Provide comprehensive training to equip workers with the necessary skills and attitudes required for task performance, encompassing both technical competencies and appropriate behavioral attributes like patience.
- Provide incentives for performance
- Embrace the principle of scientific management by utilizing incentives to motivate employees.
- Incentives may include bonuses or piece-rate pay schemes designed to reward performance and productivity.
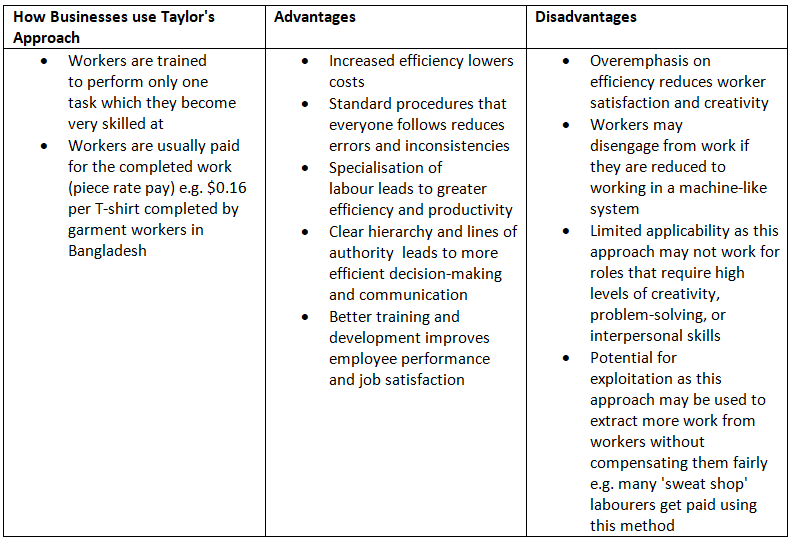
An Evaluation of Taylor's Motivation Theory
Herzberg's Motivation Theory
Herzberg's theory proposes that employee motivation and job satisfaction are influenced by two main factors: hygiene factors and motivators.
- Hygiene factors are aspects that, when lacking, can lead to dissatisfaction but do not directly result in satisfaction. For instance, poor teamwork in the workplace can be a hygiene factor.
- Motivators are elements that directly contribute to job satisfaction and motivation, such as increased responsibilities.
Herzberg's Two-factor Theory
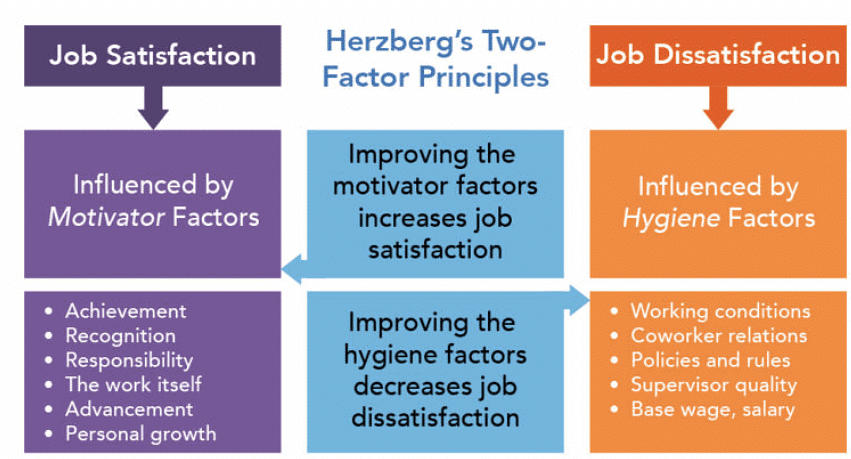
Managing Dissatisfaction with Hygiene Factors
- Ensuring Fair Compensation: When employees are not fairly compensated, they may feel demotivated and dissatisfied with their work.
- Providing Optimal Work Environment: Dirty, unsafe, or uncomfortable workplaces can lead to employee dissatisfaction and demotivation. For example, Google offers exceptional workspaces with amenities like gourmet restaurants, laundry services, and dog care facilities.
- Offering Job Security: Employees need to feel secure in their roles to perform effectively. If job security is lacking, employees may experience anxiety and reduced motivation, impacting organizational goals.
Using Motivating Factors to Increase Satisfaction
Building a Recognition and Rewards Culture
- When employees are acknowledged and rewarded for their efforts, it boosts their motivation to maintain high performance levels.
- Examples of this approach include honoring the 'Salesperson of the Month' and organizing regular staff social events.
Offering Opportunities for Growth and Development
- Providing avenues for employees to acquire new skills and progress in their careers serves as a strong motivator for them to stay committed to the organization.
- For instance, personalized growth plans can assist employees in reaching their professional aspirations, while sabbaticals enable them to pursue personal interests intermittently.
Providing Challenging Work Requiring Problem-Solving
- Assigning challenging tasks that leverage employees' skills and capabilities encourages them to sustain high performance levels.
- Examples of such tasks include job rotation and job enlargement through delegation.
Question for Motivational TheoriesTry yourself: Which theory emphasizes the division of complex tasks into simpler components and aims to maximize efficiency?View Solution
The document Motivational Theories | Business Studies for GCSE/IGCSE - Class 10 is a part of the Class 10 Course Business Studies for GCSE/IGCSE.
All you need of Class 10 at this link: Class 10
|
70 videos|93 docs|26 tests
|
FAQs on Motivational Theories - Business Studies for GCSE/IGCSE - Class 10
| 1. What is Maslow's Hierarchy of Human Needs? |  |
Ans. Maslow's Hierarchy of Human Needs is a theory proposed by psychologist Abraham Maslow, which suggests that individuals are motivated to fulfill certain needs in a hierarchical order. These needs range from basic physiological needs such as food and water to higher-level needs such as self-actualization.
| 2. How does Taylor's Scientific Management Theory impact motivation in the workplace? |  |
Ans. Taylor's Scientific Management Theory focuses on optimizing efficiency and productivity in the workplace through task specialization and standardization. This can impact motivation by providing clear guidelines and expectations for employees, leading to increased job satisfaction and performance.
| 3. What is Herzberg's Motivation Theory and how does it differ from Maslow's theory? |  |
Ans. Herzberg's Motivation Theory, also known as the Two-Factor Theory, suggests that there are two types of factors that influence motivation in the workplace: hygiene factors and motivators. Unlike Maslow's theory, which focuses on a hierarchy of needs, Herzberg's theory emphasizes the importance of intrinsic motivators in driving employee satisfaction and performance.
| 4. How can organizations apply motivational theories such as Maslow's Hierarchy of Human Needs in practice? |  |
Ans. Organizations can apply Maslow's Hierarchy of Human Needs by understanding the different levels of needs that employees have and tailoring their strategies to meet those needs. For example, providing competitive salaries and benefits can address employees' physiological and safety needs, while offering opportunities for growth and development can fulfill their higher-level needs for esteem and self-actualization.
| 5. What are some practical examples of how companies have successfully implemented motivational theories in their workplaces? |  |
Ans. Companies like Google and Zappos have implemented motivational theories by creating innovative work environments that prioritize employee well-being and job satisfaction. Google, for example, offers perks such as free meals and on-site fitness facilities to meet employees' physiological needs, while Zappos focuses on building strong company culture and providing opportunities for personal growth to fulfill higher-level needs.
Related Searches














