Year 11 Exam > Year 11 Notes > Accounting for GCSE/IGCSE > Business Documents for Credit Transactions
Business Documents for Credit Transactions | Accounting for GCSE/IGCSE - Year 11 PDF Download
What is an invoice?
- An invoice serves as a documentation of a credit sale or purchase transaction.
- The supplier issues the invoice to the credit customer, who may recognize it as a purchases invoice. A copy is retained by the supplier, often referred to as a sales invoice.
- Accounting entries are recorded in the books of prime entry upon issuance or receipt of an invoice:
- The customer records the value in the purchases journal.
- The supplier records the value in the sales journal.
What information is contained in an invoice?
Name and Address- Name and address
- The details of the customer Name and address
Details of Goods or Services
- The details of the goods or services
- The quantity
- The price of each item
- Trade discount - This is deducted before the total amount is stated
Financial Information
- The total amount owed
- Terms for eligibility of cash discount
- Date payment is required by - It might also state any interest or charges that will be applied after this date
Example of an Invoice
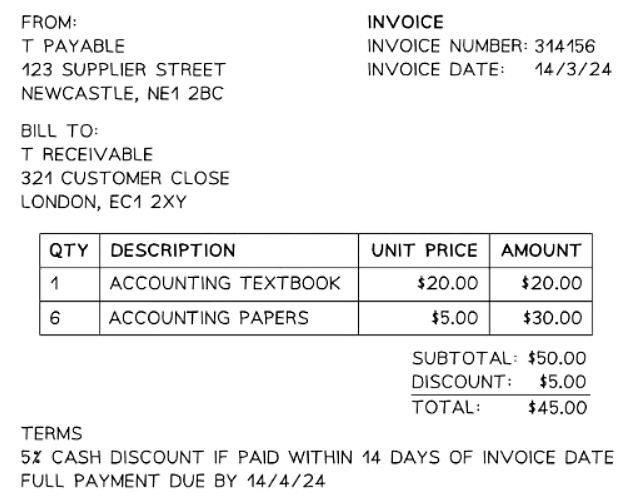
Debit Notes & Credit Notes
What is a debit note?
- A debit note is a document issued by a customer to a supplier to request a decrease in the invoice balance.
- Customers typically send debit notes in scenarios such as:
- The goods received are damaged or faulty.
- Incorrect items were shipped to the customer.
- Items are missing from the received order.
- During the initial stages, these adjustments are not recorded in the primary accounting records because the supplier has yet to approve them.
- Authorization for these adjustments is granted when the supplier issues a credit note to the customer.
- The goods may be damaged or faulty, indicating a defect or impairment in their quality or condition.
- Customers might receive incorrect items, implying that the products sent do not match what was ordered.
- There could be instances where items are missing from a customer's order, leading to incomplete deliveries.
- When no entries are documented in the books of prime entry initially, it is typically due to the supplier not yet approving the deduction.
- This action is typically taken when a customer receives a credit note from the supplier as acknowledgment of the reduction.
What information is contained in a debit note?
- The details of the supplier
- Name and address
- The details of the customer
- Name and address
- The reason for the request for a reduction
- Details of the goods that are being returned
- Details of the goods that were missing
- The total reduction that is being requested
What is a credit note?
- A supplier issues a credit note to a credit customer to reduce the balance on an invoice.
- The customer utilizes the credit note to document returns, aligning it with the respective invoice and debit note.
- The supplier retains a copy of the credit note for recording returns and matches it with the corresponding invoice.
- Entries are made in the books of prime entry when issuing or receiving a credit note.
- Customers record the value of returned purchases in the purchases returns journal.
- Conversely, suppliers record the value of returned sales in the sales returns journal.
Details in a Credit Note
- The credit note includes:
- The date of the reduction.
- Supplier's details like name and address.
- Customer's details such as name and address.
- Reason for the reduction.
- Details of returned goods and any missing items.
- Total amount of reduction provided.
- Including these details ensures clarity and transparency in the credit note process.
What is a statement of account?
- A statement of account serves to display all transactions occurring between a credit customer and a supplier within a specified timeframe.
- Issued periodically by the supplier, this document does not prompt any new entries in the primary records, as it reflects past transactions only.
- Customers utilize the statement to cross-reference their balance with the one in their purchases ledger account.
- Typically, a balance column is included, demonstrating the balance after each transaction.
- The statement is crafted from the supplier's viewpoint, denoting transactions that either increase (labeled as 'debit') or decrease (labeled as 'credit') the customer's balance.
What information is contained in a statement of account?
- The date that the statement is issued
- The details of the supplier (Name and address)
- The details of the customer (Name and address)
- The opening balance
- The date and amount of any purchases by the customer (corresponding to invoices)
- The date and amount of any returns by the customer (corresponding to credit notes)
- Payments made by the customer
- Cash discounts received by the customer
- The closing balance
Question for Business Documents for Credit TransactionsTry yourself: What is the purpose of an invoice?View Solution
The document Business Documents for Credit Transactions | Accounting for GCSE/IGCSE - Year 11 is a part of the Year 11 Course Accounting for GCSE/IGCSE.
All you need of Year 11 at this link: Year 11
|
22 videos|29 docs|12 tests
|
FAQs on Business Documents for Credit Transactions - Accounting for GCSE/IGCSE - Year 11
| 1. What is the purpose of an invoice? |  |
Ans. An invoice is a document that outlines the details of a transaction between a buyer and a seller, including the products or services purchased, the quantity, the price, and the payment terms. It serves as a request for payment from the buyer to the seller.
| 2. What is the difference between a debit note and a credit note? |  |
Ans. A debit note is issued by a seller to request additional payment from a buyer, usually due to an undercharge or additional charges. On the other hand, a credit note is issued to provide a refund or credit to the buyer, typically for overpayment, returned goods, or discounts.
| 3. How is a statement of account different from an invoice? |  |
Ans. A statement of account is a summary of all transactions between a buyer and a seller over a specific period, including invoices, payments, credits, and balances. It provides a complete overview of the financial relationship between the two parties, whereas an invoice is a specific document for a single transaction.
| 4. When should a business issue a credit note? |  |
Ans. A business should issue a credit note when a customer returns goods, receives a discount, or has been overcharged. This document serves as a record of the adjustment made to the original invoice and ensures that the customer is properly credited for any discrepancies.
| 5. How can businesses use documents for credit transactions effectively? |  |
Ans. Businesses can use documents such as invoices, debit notes, credit notes, and statements of account to maintain accurate records of their financial transactions, track payments, resolve discrepancies, and ensure smooth credit management processes. By utilizing these documents effectively, businesses can enhance their financial transparency and customer relationships.
Related Searches




















