Year 11 Exam > Year 11 Notes > Physics for GCSE/IGCSE > Thermal Expansion
Thermal Expansion | Physics for GCSE/IGCSE - Year 11 PDF Download
Thermal Expansion
- When substances are heated, they undergo expansion.
- This expansion occurs due to the acceleration of molecular movement or vibration.
- Consequently, molecules collide more frequently, exerting force on each other, and thus pushing each other farther apart.
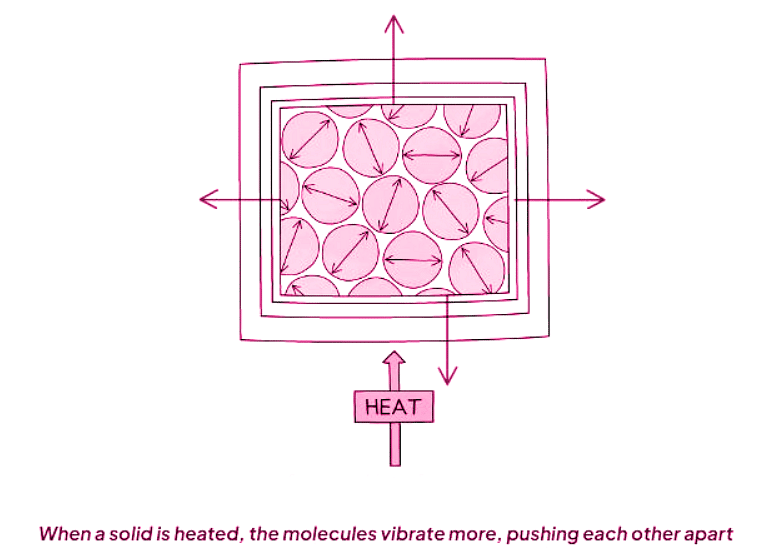
- It's important to note that during this process, it's the volume occupied by the molecules that expands, while the molecules themselves maintain their original size.
- Thermal expansion is evident across solids, liquids, and gases.
- When temperature rises (while keeping pressure constant):
- Solids exhibit the least expansion.
- Gases demonstrate the most significant expansion.
- Liquids experience expansion levels falling between those of solids and gases.
Thermal Expansion in Terms of Particles
- Molecules themselves do not undergo expansion, but rather the space between them increases.
- Heating solids, liquids, and gases results in:
- Expansion occurring primarily in the space between molecules.
- Solids, liquids, and gases all experiencing thermal expansion.

Question for Thermal ExpansionTry yourself: Which state of matter experiences the least expansion when heated?View Solution
Uses & Consequences of Thermal Expansion
The thermal expansion of materials can lead to beneficial uses as well as undesirable outcomes.
Applications
- Thermometers utilize the expansion of liquids to gauge temperature.
- Temperature-activated switches operate based on the bending of a bimetallic strip, composed of two metals expanding at different rates, at specific temperatures.
 The bimetallic strip will bend upwards when heated, closing the circuit
The bimetallic strip will bend upwards when heated, closing the circuit
Consequences
- When solid materials heat up, they have a tendency to expand, potentially leading to buckling under extreme heat stress.
- Examples of materials susceptible to buckling due to thermal expansion are metal railway tracks, road surfaces, and bridges.
- To mitigate the risk of damage from expansion, structures prone to buckling are designed with intentional gaps to accommodate the expansion without causing harm.
The document Thermal Expansion | Physics for GCSE/IGCSE - Year 11 is a part of the Year 11 Course Physics for GCSE/IGCSE.
All you need of Year 11 at this link: Year 11
|
127 videos|148 docs|35 tests
|
FAQs on Thermal Expansion - Physics for GCSE/IGCSE - Year 11
| 1. What is thermal expansion and how does it occur? |  |
Ans. Thermal expansion is the tendency of matter to change its shape, area, and volume in response to a change in temperature. It occurs because particles in a substance have more kinetic energy when heated, causing them to move more and take up more space.
| 2. How do particles contribute to thermal expansion? |  |
Ans. When a substance is heated, the particles within it gain kinetic energy and move more vigorously, causing them to push against each other and take up more space. This leads to an increase in the substance's volume.
| 3. What are the uses of thermal expansion in everyday life? |  |
Ans. Thermal expansion is used in various applications such as in the design of bridges, railways, and buildings to account for changes in temperature. It is also utilized in thermometers, thermostats, and bimetallic strips for temperature sensing and control.
| 4. What are the consequences of thermal expansion in materials? |  |
Ans. The consequences of thermal expansion in materials include the risk of structural damage due to expansion and contraction with temperature changes. This can lead to cracks, warping, and other forms of deformation in structures and components.
| 5. How can thermal expansion be minimized or controlled in engineering applications? |  |
Ans. Thermal expansion can be minimized or controlled in engineering applications by using materials with low coefficients of thermal expansion, incorporating expansion joints in structures to allow for movement, and designing components with proper allowances for thermal expansion and contraction.
|
Explore Courses for Year 11 exam
|

|
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.
Related Searches
















