Year 11 Exam > Year 11 Notes > Physics for GCSE/IGCSE > Force on a Current-Carrying Conductor
Force on a Current-Carrying Conductor | Physics for GCSE/IGCSE - Year 11 PDF Download
Force on a Current-Carrying Conductor
- A conductor with electric current generates its magnetic field.
- Consequently, when it encounters an external magnetic field, it undergoes a force.
- The conductor experiences this force only when the current flowing through it is perpendicular to the magnetic field lines' direction.
- An example scenario is a copper rod situated in a uniform magnetic field.
- When current flows through the copper rod, it encounters a force, causing its motion.
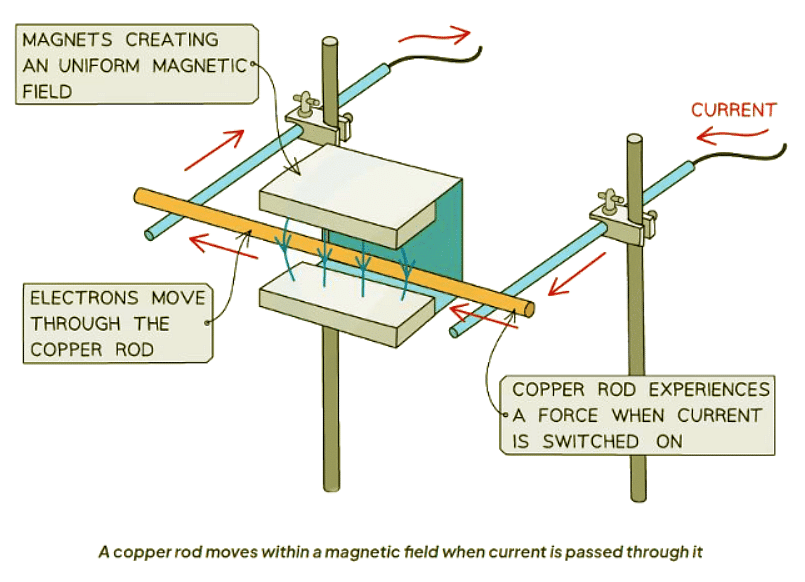
- Two methods to alter the force's direction (and consequently, the copper rod) include:
- Inverting the current's direction.
- Reversing the magnetic field's direction.
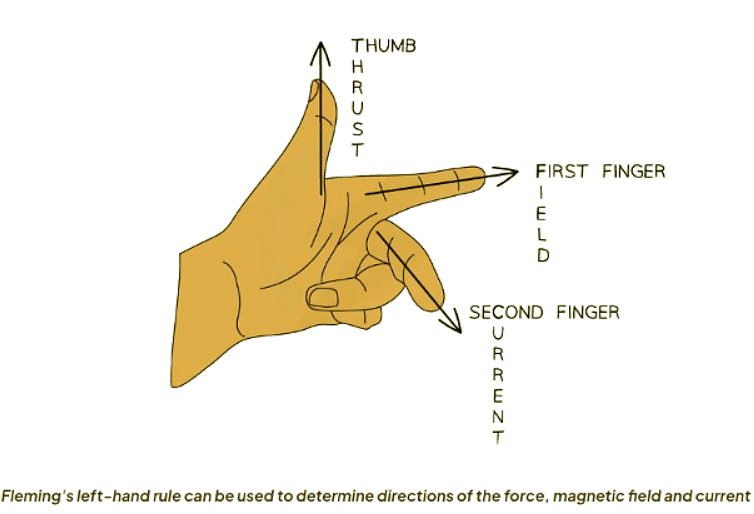
Left Hand Rule
- The force (also known as thrust) acting on a current-carrying wire is determined by the directions of the current and magnetic field, which are all perpendicular to each other. This perpendicularity sometimes makes the force seem like it is either entering or exiting the page.
- To find the direction of the force, Fleming's left-hand rule can be applied. This rule helps in determining the relationships among the force, magnetic field, and current.
Question for Force on a Current-Carrying ConductorTry yourself: Which of the following conditions is necessary for a conductor to experience a force when placed in an external magnetic field?View Solution
Charged Particles in a Magnetic Field
- When a current-carrying wire is placed in a magnetic field, it experiences a force if the wire is perpendicular. This occurs because the magnetic field exerts a force on each individual electron flowing through the wire.
- Therefore, when a charged particle moves through a magnetic field, it can experience a force that causes it to deflect. This force always acts at a 90-degree angle to both the particle's direction of travel and the magnetic field lines. To determine the direction of this force, one can utilize Fleming's left-hand rule.
Understanding the Interaction
- The magnetic field exerts a force on individual electrons within a current-carrying wire when placed in a magnetic field.
- As a charged particle passes through a magnetic field, the field can apply a force on it, leading to deflection. This force is perpendicular to both the particle's motion and the magnetic field lines.
- Fleming's left-hand rule is a useful tool for determining the direction of the force experienced by a charged particle in a magnetic field.
Force on a Charged Particle in a Magnetic Field
- The force acting on a charged particle in a magnetic field is always perpendicular to both the particle's direction of motion and the magnetic field lines.
- To determine the direction of this force, Fleming's left-hand rule can be employed.
Mechanism of Force Calculation
- The force's orientation is consistently at a right angle (90 degrees) concerning the particle's movement and the magnetic field.
- Fleming's left-hand rule aids in establishing the precise direction of this force.
Application to Electron Motion
- For an electron traversing a magnetic field, its path is bent in a direction opposite to its motion.
- Conventional current, often opposite to the electron flow, is indicative of the force's direction.
- Using the right hand can also assist in determining directions for charged particles.
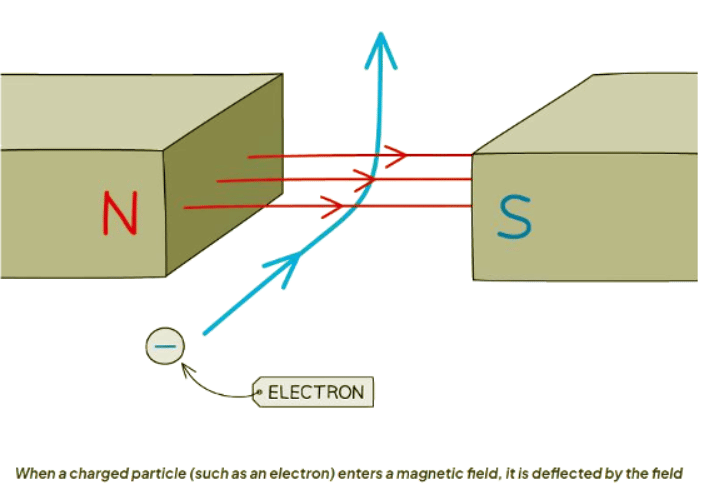
- When a particle moves perpendicular to the field lines, it encounters the highest force.
- When a particle moves parallel to the field lines, it undergoes no force.
- When a particle moves at an angle to the field lines, it experiences a minimal force.
The document Force on a Current-Carrying Conductor | Physics for GCSE/IGCSE - Year 11 is a part of the Year 11 Course Physics for GCSE/IGCSE.
All you need of Year 11 at this link: Year 11
|
127 videos|148 docs|35 tests
|
FAQs on Force on a Current-Carrying Conductor - Physics for GCSE/IGCSE - Year 11
| 1. How does the left hand rule help determine the direction of the force on a current-carrying conductor in a magnetic field? |  |
Ans. The left hand rule states that if the forefinger points in the direction of the magnetic field, the thumb in the direction of the current, then the middle finger represents the direction of the force acting on the conductor.
| 2. What factors affect the force experienced by a current-carrying conductor in a magnetic field? |  |
Ans. The force on a current-carrying conductor in a magnetic field is influenced by the strength of the magnetic field, the current flowing through the conductor, and the angle between the direction of the current and the magnetic field.
| 3. How can the magnitude of the force on a current-carrying conductor be calculated using the formula? |  |
Ans. The formula to calculate the force on a current-carrying conductor in a magnetic field is F = BILsinθ, where F is the force, B is the magnetic field strength, I is the current, L is the length of the conductor in the magnetic field, and θ is the angle between the current and the magnetic field.
| 4. What is the significance of the force on a current-carrying conductor in practical applications? |  |
Ans. The force on a current-carrying conductor in a magnetic field is utilized in devices such as electric motors, generators, and transformers, where the interaction between the magnetic field and the current generates motion, electricity, or voltage.
| 5. How does the force on a current-carrying conductor affect the efficiency of electrical devices? |  |
Ans. The force on a current-carrying conductor plays a crucial role in the efficiency of electrical devices, as it determines the movement of components within the device, the generation of electricity, and the overall performance of the system.

|
Explore Courses for Year 11 exam
|

|
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.
Related Searches
















