Year 7 Exam > Year 7 Notes > Types of Industry
Types of Industry - Year 7 PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Introduction |

|
| Types of industry |

|
| Phases of Industry |

|
| The effects of industry |

|
Introduction
- There are four main types of industry: primary, secondary, tertiary, and quaternary.
- The type of industry a country specializes in changes over time.
- There are social, environmental, and economic impacts of industry.
Types of industry
Industry involves any economic activity that creates jobs and generates income.
There are four main types of industry:
- Primary sector
- Secondary sector
- Tertiary sector
- Quaternary sector
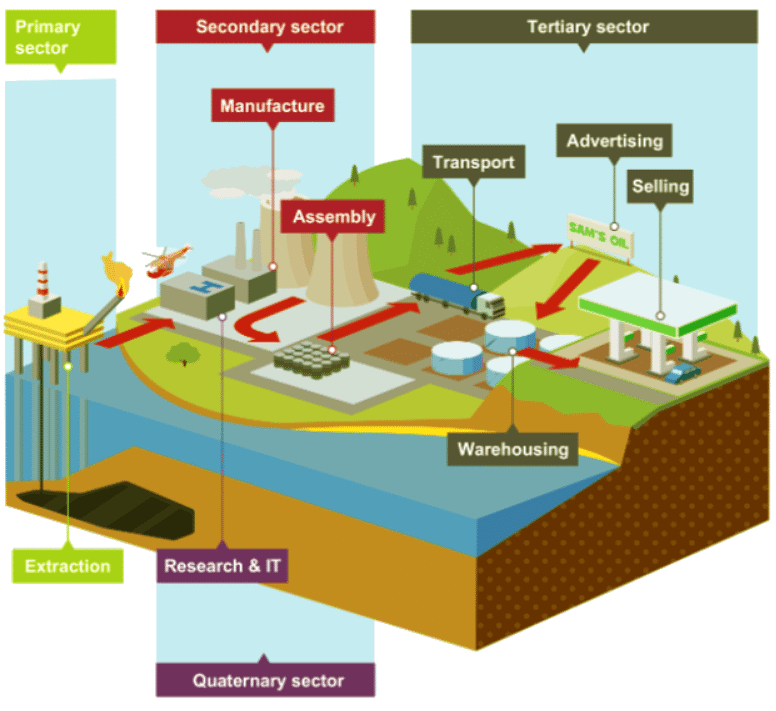 There are four main types of industry: primary, secondary, tertiary, quaternary
There are four main types of industry: primary, secondary, tertiary, quaternary
Primary sector
- Primary industry involves the production or extraction of raw materials, such as forestry, farming, fishing, and mining.
Secondary sector
- Secondary industry involves the manufacturing of goods.
- For instance, textile production in the north west of England, electronic manufacturing in China, and car manufacturing in Germany are notable examples.
Tertiary sector
- The tertiary industry revolves around offering services to people, such as cleaning or medical care.
Quaternary sector
- The quaternary industry, the newest sector, concentrates on knowledge-based or high-tech industries like ICT (information and communication technologies) and research and development.
Question for Types of IndustryTry yourself: Which sector of industry involves the manufacturing of goods?View Solution
Phases of Industry
What industry or industries a country focuses on changes over time and can be shown using the Clark Fisher model.
Clark Fisher Model
The model is split into three phases:
- The Pre-Industrial Phase:
- This phase represents a time before there were machines to produce goods on a large scale. During this phase, a country is primarily focused on the primary sector, with agriculture being the main activity.
- Example: In cities like Manchester and later Liège in Belgium during the Industrial Revolution, which occurred in the 18th and 19th centuries, the primary sector activities started to decline.
- The Industrial Phase:
- In this phase, both the secondary and tertiary sectors increase in importance. Activities in the primary sector begin to decrease. This phase is characterized by the use of machines to produce goods on a large scale.
- Example: The Industrial Revolution marked a significant shift in production methods in European countries and the United States.
- The Post-Industrial Phase:
- During the post-industrial phase, manufacturing declines as service industries take over. The tertiary sector becomes the most crucial, and quaternary industries, such as those providing information services like computing and research and development, start to emerge.
- In this phase, only a small percentage of the population is engaged in primary industries.
- Example: The shift towards a post-industrial economy is evident in many developed nations today, where services dominate the economic landscape.
 The Clark Fisher model shows how a country changes its focus.
The Clark Fisher model shows how a country changes its focus.
The effects of industry
- Different countries globally are in varying stages of industrial development with regional disparities.
- Countries depend on each other for manufacturing and selling goods, fostering international cooperation through trade.
- International trade can both strengthen relationships between nations and be a source of conflict.
- As countries progress, they transition through the Clark Fisher model, where a shift from manufacturing to services occurs, termed de-industrialization.

Economic effects
- The transition in phases as per the Clark Fisher model can occur due to various factors, such as offshoring - relocating a business to a foreign country for reduced costs.
- An illustration of this is the relocation of aeroplane engine production from the UK to Singapore to capitalize on financial advantages.
Offshoring
- Offshoring involves relocating a business to a foreign country to benefit from lower taxes or reduced costs.
- Companies often offshore to increase profits by taking advantage of lower labor costs, achieved by paying lower wages.
- Another reason for offshoring is to exploit less stringent regulations, such as fewer environmental or safety laws.
Labor Cost Advantage
- Offshoring allows companies to exploit the lower cost of labor in foreign countries, thereby increasing their profit margins.
- This is achieved by leveraging the lower wages paid to workers in these countries.
- For example, a manufacturing company may move its production to a country with lower labor costs to reduce expenses.
Regulatory Arbitrage
- Companies engage in offshoring to take advantage of lax regulations in foreign countries.
- By operating in regions with fewer environmental or safety laws, companies can reduce compliance costs and increase profitability.
- For instance, a company might choose to offshore its operations to a country with minimal labor regulations to cut costs.
Social effects
- When older industries are replaced by new ones, conflicts can arise within a country.
- Example: The United Kingdom transitioned from secondary industries to post-industrialism in the 1980s, causing social unrest.
- The decline of primary and secondary industries often leads to unemployment and various social problems.
- Example: Job loss in traditional industries can result in health and well-being issues for the population.
- Newly emerging economies benefit from the decline of old industries by utilizing funds for development.
- Example: Nigeria's shift to industrialization creates opportunities to enhance infrastructure, education, healthcare, and employment.
Newly Emerging Economies (NEEs)
- Countries classified as newly emerging economies are those that experience rapid industrialization and economic growth.
- These nations witness a significant transformation in their industrial sectors alongside overall economic development.
Environmental Effects
- Industrial activities in NEEs can have adverse effects on the environment, such as pollution.
- For instance, the leather manufacturing industry in India significantly pollutes the River Ganges through the release of wastewater and harmful chemicals.
- There is a growing global push for a 'Green Industrial Revolution' to promote environmentally friendly manufacturing practices.
- Countries like the UK are implementing strategies like a ten-point plan to transition towards a zero-carbon economy, emphasizing green technologies like wind turbines.
Zero Carbon Economy

- A zero carbon economy is centered on utilizing low-carbon energy sources to significantly reduce the emission of carbon dioxide and other greenhouse gases into the atmosphere.
Political Effects
- Low-income countries (LICs) often depend on exporting raw materials like cocoa beans to developed nations, which then process these into goods like chocolate.
- This dynamic can result in the exploitation of less affluent nations by wealthier ones, further entrenching the dominance of already powerful countries.
FAQs on Types of Industry - Year 7
| 1. What are the different types of industries? |  |
Ans. The different types of industries include primary industries (such as agriculture and mining), secondary industries (such as manufacturing and construction), and tertiary industries (such as services and tourism).
| 2. What are the phases of industry? |  |
Ans. The phases of industry include the pre-industrial phase (characterized by manual labor and basic tools), the industrial phase (marked by the use of machinery and mass production), and the post-industrial phase (focused on technology and information).
| 3. How do industries affect the environment? |  |
Ans. Industries can have negative effects on the environment through pollution, deforestation, habitat destruction, and resource depletion. However, advances in technology and sustainability practices have led to efforts to minimize these impacts.
| 4. How do industries contribute to the economy? |  |
Ans. Industries contribute to the economy by creating jobs, generating income, driving innovation, and supporting other sectors through the production of goods and services. They play a crucial role in economic development and growth.
| 5. What role do industries play in society? |  |
Ans. Industries play a significant role in society by meeting the needs and wants of consumers, providing opportunities for employment and economic growth, driving technological advancements, and shaping the overall quality of life for individuals within a community.
Related Searches

















