Respiratory Balance Sheet and Quotient | Biology for EmSAT Achieve PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| What is Respiratory Balance Sheet? |

|
| Aerobic respiration vs Fermentation |

|
| Amphibolic Pathway |

|
| Respiratory Quotient |

|
Cellular respiration is a vital biological process through which living organisms extract energy from organic molecules, primarily glucose, to fuel various cellular activities. This process involves the sequential breakdown of glucose molecules in a series of metabolic pathways to generate adenosine triphosphate (ATP), the universal energy currency of cells. While theoretical calculations provide insights into energy production, the reality of cellular metabolism is far more complex, with pathways operating simultaneously and dynamically adapting to the organism's metabolic needs.
What is Respiratory Balance Sheet?
The respiratory balance sheet refers to the theoretical calculation of the net gain of ATP molecules during aerobic respiration of one molecule of glucose.
The net gain in ATP per glucose molecule is calculated theoretically using the respiration balance sheet. One mole of glucose is converted into 38 ATP during the entire process.
In glycolysis; 1 ATP + 2 NADH2 (=6 ATP) = 8 ATPs
In Oxidative decarboxylation; 2 NADH2 = 6 ATPs
In Krebs Cycle; 2 GTP (2 ATP) + 6 NADH2 (=18 ATP) + 2 FADH2 (= 4ATP) = 24 ATPs
Total ATPs generated during aerobic respiration = 38 ATPs – 2 ATPs utilized during glycolysis = 36 ATPs
Total ATPs generated during anaerobic respiration = 2 ATPs
- According to traditional calculations, aerobic respiration yields a net gain of 38 ATP molecules per glucose molecule. This estimation is based on the assumption of a sequential and orderly pathway, where glycolysis, the citric acid cycle (TCA cycle), and the electron transport chain (ETC) occur consecutively.
- Additionally, it assumes that NADH generated during glycolysis is shuttled into the mitochondria for oxidative phosphorylation. However, in living systems, metabolic pathways operate concurrently, and substrates enter and exit as needed, reflecting the dynamic nature of cellular metabolism and regulatory mechanisms.
Aerobic respiration vs Fermentation
Fermentation represents an alternative pathway for ATP production, particularly under anaerobic conditions. Unlike aerobic respiration, which fully oxidizes glucose to carbon dioxide and water, fermentation results in the partial breakdown of glucose, typically yielding two ATP molecules per glucose molecule.
Furthermore, the rate of NADH oxidation differs between fermentation and aerobic respiration, with aerobic respiration exhibiting a more vigorous reaction. This comparison highlights the efficiency and energy yield differences between aerobic respiration and fermentation, underscoring the importance of oxygen availability in cellular energy metabolism.
Amphibolic Pathway
The concept of an amphibolic pathway emphasizes the dual role of the respiratory pathway in both catabolic (breakdown) and anabolic (synthesis) processes.
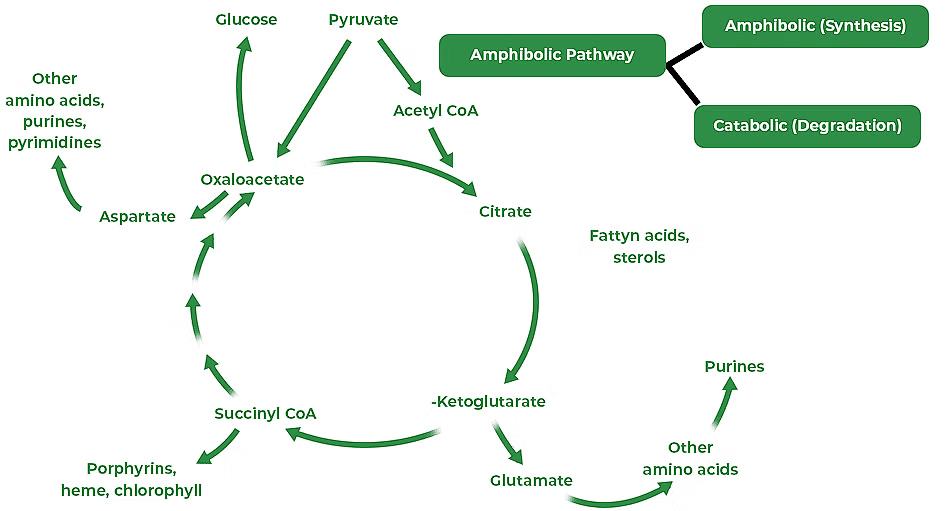
- Glucose is the preferred substrate for respiration, other carbohydrates, fats, and proteins can also be utilized. However, these substrates undergo prior conversion steps before entering the respiratory pathway.
- For example, fats must be broken down into glycerol and fatty acids, while proteins are degraded into amino acids before entering the pathway.
- Additionally, intermediates of the respiratory pathway are essential for the synthesis of various biomolecules, such as fatty acids and proteins. This dual functionality highlights the versatility and integrative nature of cellular metabolism.
Respiratory Quotient
The respiratory quotient or respiratory ratio is the proportion of oxygen consumed to the carbon dioxide exhaled during breathing. RQ value is influenced by the oxidation of respiratory substrates.
RQ = (Volume OF CO2 Eliminated)/(Volume of O2 Consumed)
- Respiratory Ratio sometimes referred to as Respiratory Quotient, is abbreviated as RQ. It is defined as the proportion of carbon dioxide released during respiration to oxygen received over the same period and weight at a constant temperature and pressure.
- In the respiration process, the respiratory substrate is broken down to liberate energy.
- The two basic forms of respiration that take place in the presence or absence of molecular oxygen are aerobic and anaerobic respiration.
|
157 videos|173 docs|136 tests
|
FAQs on Respiratory Balance Sheet and Quotient - Biology for EmSAT Achieve
| 1. What is the difference between aerobic respiration and fermentation? |  |
| 2. What is meant by an amphibolic pathway in the context of a respiratory balance sheet? |  |
| 3. How is the respiratory quotient calculated in a respiratory balance sheet? |  |
| 4. How does the respiratory balance sheet help in understanding the overall energy metabolism of an organism? |  |
| 5. Why is the concept of respiratory balance sheet and quotient important in NEET exams? |  |




















