Neural Control and Coordination Chapter Notes | Biology Class 11 - NEET PDF Download
Introduction
Coordination of organ systems is essential for maintaining homeostasis in the body. When we engage in physical activities, the demand for energy and oxygen increases, requiring a coordinated response from various organs such as muscles, lungs, heart, and kidneys. The neural and endocrine systems work together to ensure this coordination, with the neural system providing quick, point-to-point connections and the endocrine system offering chemical regulation through hormones. This chapter will focus on the neural system in humans and how nerve impulses are transmitted and conducted across synapses.

Neural System
The neural system in animals consists of specialized cells known as neurons. These neurons are responsible for detecting, receiving, and transmitting various types of stimuli.
- Lower Invertebrates: In simple organisms like Hydra, the neural organization is basic, consisting of a network of neurons.
- Insects: Insects have a more advanced neural system, featuring a brain along with several ganglia and neural tissues.
- Vertebrates: Vertebrates possess a highly developed neural system, which is more complex and organized compared to that of lower invertebrates and insects.
Human Neural System
The human neural system is categorized into two main parts:
(i) Central Neural System (CNS)
- The CNS comprises the brain and the spinal cord.
- It is responsible for processing information and controlling various functions of the body.
(ii) Peripheral Neural System (PNS)
- The PNS includes all the nerves that are associated with the CNS.
- It connects the CNS to the rest of the body.
The nerve fibers in the PNS are of two types:
- (a) Afferent Fibers: These fibers transmit impulses from tissues and organs to the CNS.
- (b) Efferent Fibers: These fibers transmit regulatory impulses from the CNS to peripheral tissues and organs.
Divisions of the PNS
- (i) Somatic Neural System: This system relays impulses from the CNS to skeletal muscles, allowing for voluntary movements.
- (ii) Autonomic Neural System: This system transmits impulses from the CNS to involuntary organs and smooth muscles.
The autonomic neural system is further divided into:
- (a) Sympathetic Neural System: This part prepares the body for stressful situations (fight or flight response).
- (b) Parasympathetic Neural System: This part promotes relaxation and recovery (rest and digest).
Visceral Nervous System: This system is part of the PNS and includes the nerves, fibers, ganglia, and plexuses that transmit impulses between the CNS and the viscera (internal organs).
Neuron as Structural and Functional Unit of Neural System
Neuron: Basic Structure
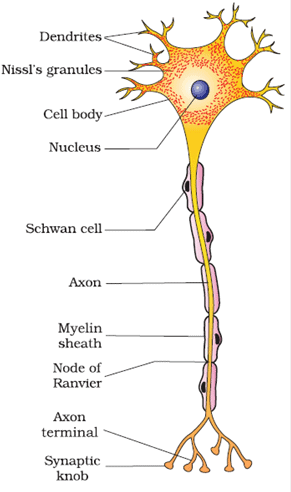 Structure of Neuron
Structure of Neuron
- A neuron is a tiny structure made up of three main parts: the cell body, dendrites, and axon.
- The cell body contains cytoplasm with usual cell organelles and special granular bodies called Nissl’s granules.
- Dendrites are short fibers that branch out from the cell body. They also contain Nissl’s granules and transmit impulses towards the cell body.
- The axon is a long fiber with a branched distal end. Each branch ends in a bulb-like structure called the synaptic knob, which contains synaptic vesicles filled with chemicals called neurotransmitters. Axons transmit nerve impulses away from the cell body to a synapse or a neuro-muscular junction.
Types of Neurons
Neurons are classified based on the number of axons and dendrites into:
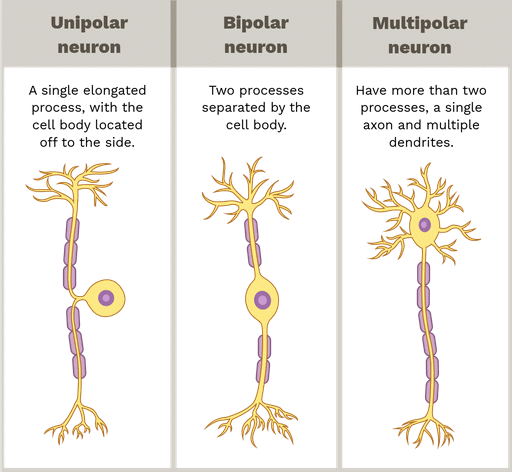 Types of Neuron
Types of Neuron
- Multipolar Neurons. These have one axon and two or more dendrites. They are found in the cerebral cortex.
- Bipolar Neurons. These have one axon and one dendrite and are found in the retina of the eye.
- Unipolar Neurons. These have one axon only and are usually found in the embryonic stage.
Types of Axons
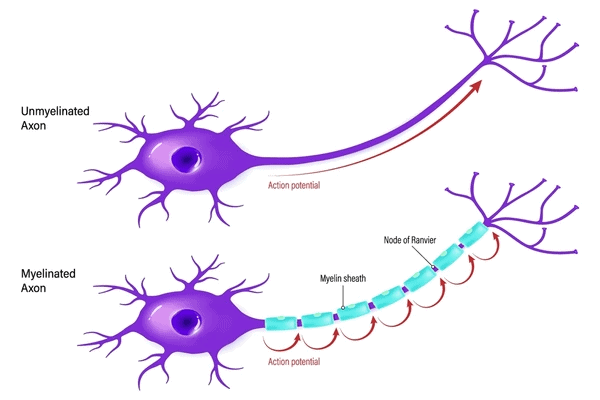 Types of Axons
Types of Axons
- Myelinated Axons. These are covered with Schwann cells that form a myelin sheath around the axon. The gaps between two adjacent myelin sheaths are called nodes of Ranvier. Myelinated nerve fibers are found in spinal and cranial nerves.
- Non-Myelinated Axons. In these axons, Schwann cells enclose the axon but do not form a myelin sheath. Non-myelinated axons are commonly found in the autonomous and somatic neural systems.
Generation and Conduction of Nerve Impulse
Neurons are specialized cells responsible for transmitting signals in the body. They are called "excitable" because their membranes are polarized, meaning there is a difference in charge between the inside and outside of the membrane. This polarization is maintained by different types of ion channels on the neural membrane, which allow specific ions to pass through and create a concentration gradient.
Resting Potential
- When a neuron is at rest, its membrane is more permeable to potassium ions (K+) and less permeable to sodium ions (Na+). This means that K+ can move in and out of the cell more easily than Na+. Additionally, the membrane is impermeable to negatively charged proteins found in the axoplasm, the fluid inside the axon. As a result, the axoplasm contains a high concentration of K+ and negatively charged proteins, while the concentration of Na+ is low. In contrast, the fluid outside the axon has a low concentration of K+ and a high concentration of Na+.
- The difference in ion concentration is maintained by the sodium-potassium pump, which actively transports 3 Na+ ions out of the cell and 2 K+ ions into the cell. This process creates a positive charge on the outer surface of the axonal membrane and a negative charge on the inner surface, resulting in a polarized membrane. The difference in electrical potential across the resting plasma membrane is called the resting potential.
(i) Generation of Nerve Impulse
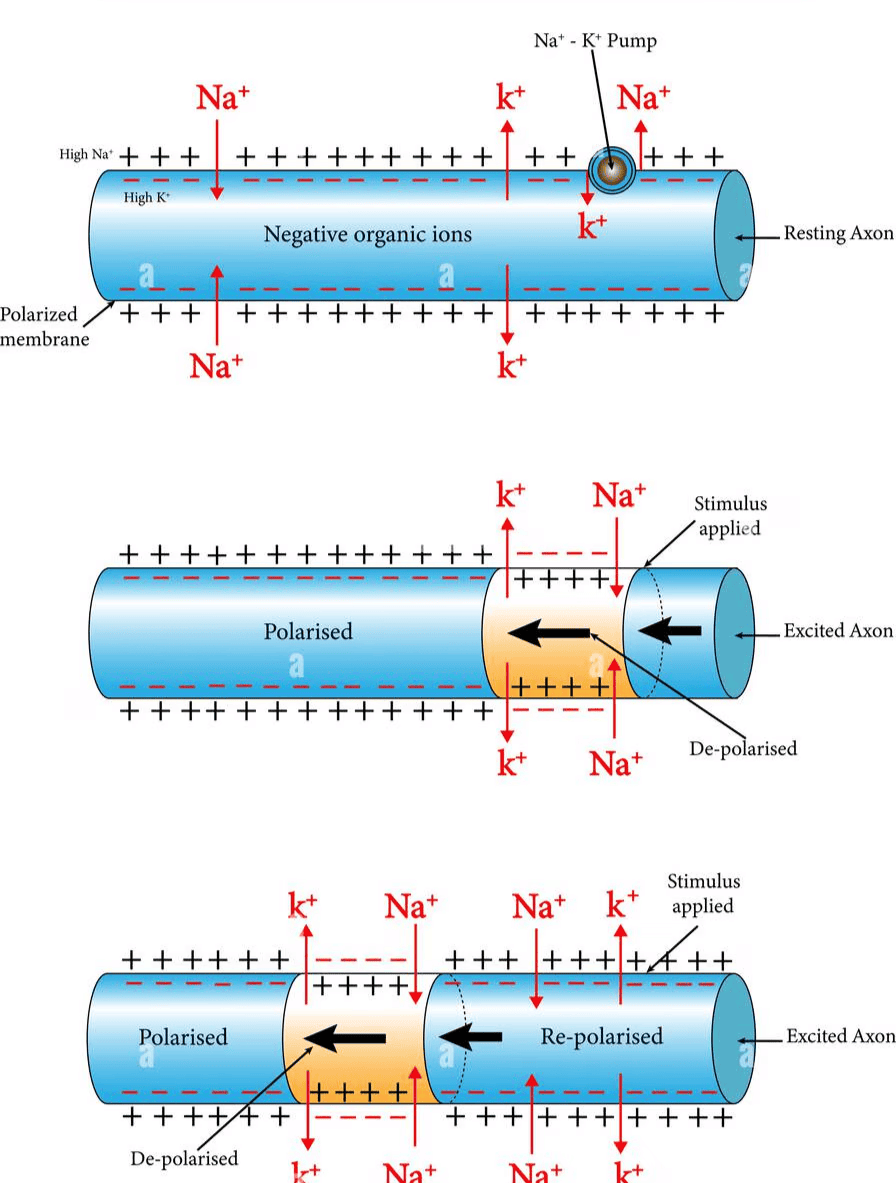
When a stimulus is applied to a polarized membrane at a specific site, such as point A, the membrane becomes permeable to Na+ ions at that site. This leads to a rapid influx of Na+ ions, causing the polarity of the membrane to reverse. The outer surface of the membrane becomes negatively charged, and the inner surface becomes positively charged. This change in polarity at site A is called depolarization, and the electrical potential difference at this site is known as the action potential, which represents a nerve impulse.
(ii) Conduction of Nerve Impulse
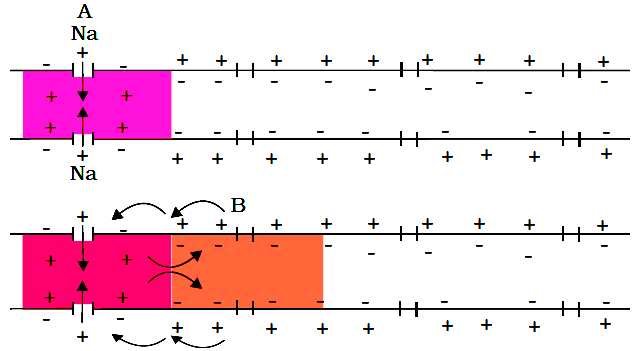 Conduction of Nerve Impulse
Conduction of Nerve Impulse
(a) As the action potential occurs at site A, the sites immediately ahead on the axon, such as site B, have a positive charge on the outer surface and a negative charge on the inner surface. This creates a current that flows from site A to site B on the inner surface of the membrane, and a current that flows from site B to site A on the outer surface, completing the circuit of current flow. As a result, the polarity at site B is reversed, and an action potential is generated at that site.
(b) This process is repeated along the length of the axon, with the action potential moving from one site to the next. The increase in Na+ permeability is temporary and is quickly followed by an increase in K+ permeability. K+ ions diffuse out of the membrane, restoring the resting potential at the site of excitation. This restoration allows the fiber to become responsive to further stimulation.
Transmission of Impulses
A nerve impulse is passed from one neuron to another at a junction called a synapse. A synapse consists of the membranes of a pre-synaptic neuron and a post-synaptic neuron, which may be separated by a small gap called the synaptic cleft. There are two main types of synapses: electrical and chemical synapses.
Electrical Synapses:
- In electrical synapses, the membranes of the pre- and post-synaptic neurons are very close together. This allows electrical current to flow directly from one neuron to the other.
- The transmission of an impulse across electrical synapses is similar to the conduction of an impulse along a single axon.
- Electrical synapses are faster than chemical synapses and are relatively rare in the human body.
Chemical Synapses:
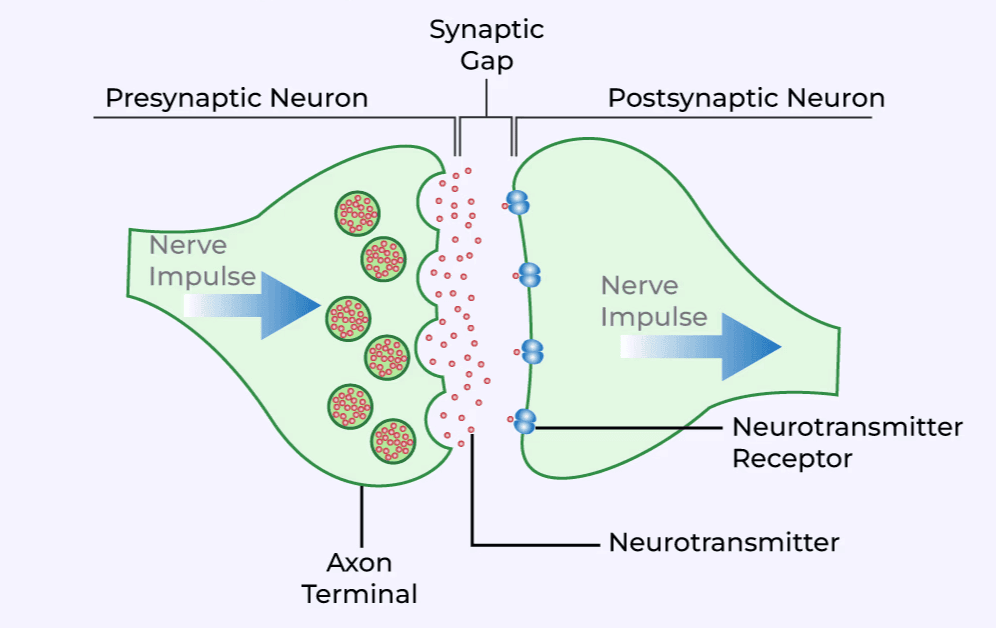 Chemical Synapse
Chemical Synapse
- At chemical synapses, the membranes of the pre- and post-synaptic neurons are separated by the synaptic cleft, a fluid-filled space.
- When an impulse (action potential) reaches the axon terminal of the pre-synaptic neuron, it triggers the release of chemicals called neurotransmitters from vesicles in the axon terminals.
- These neurotransmitters are released into the synaptic cleft, where they bind to specific receptors on the post-synaptic membrane.
- The binding of neurotransmitters to their receptors opens ion channels in the post-synaptic membrane, allowing ions to enter the post-synaptic neuron. This can generate a new electrical potential in the post-synaptic neuron, which may be either excitatory or inhibitory, depending on the type of neurotransmitter and receptor involved.
Central Neural System
Brain
- The brain is the main organ for processing information in the body. It acts as the control center, managing both voluntary actions like moving your arms and involuntary functions such as breathing, heartbeat, and kidney activity.
- It also helps keep the body in balance, regulates temperature, and controls feelings of hunger and thirst. The brain plays a key role in setting internal body clocks and coordinating hormones that affect growth, metabolism, and mood.
- Moreover, it processes sensory information from our eyes, ears, and mouth, and is responsible for memory, intelligence, emotions, and thoughts.
- To keep the brain safe, it is surrounded by the skull. Within the skull, the brain is protected by three layers of tissue called the cranial meninges. the tough outer layer (dura mater), the middle layer (arachnoid), and the inner layer (pia mater) that is in direct contact with the brain.
- The brain can be divided into three parts: Forebrain, Midbrain, and Hindbrain.
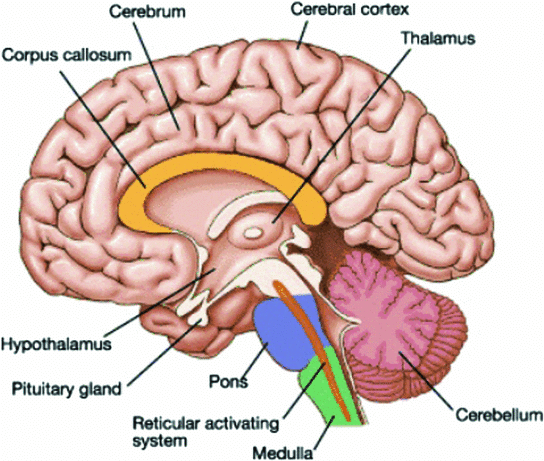 Structure of Brain
Structure of Brain
1. Forebrain (The Largest Part of the Brain)
- The forebrain includes the cerebrum, thalamus, and hypothalamus.
- The cerebrum is the biggest part of the brain and is split into two halves called the left and right cerebral hemispheres, which are connected by a bundle of nerve fibers known as the corpus callosum.
- The outer layer of the cerebrum is called the cerebral cortex, which has many folds and is grey in color because it is made up of a lot of nerve cell bodies. This area has motor and sensory regions, as well as large sections called association areas that are responsible for complex tasks like memory and communication.
- The inner part of the cerebral hemispheres contains white matter, which is made up of nerve fibers covered in a fatty layer called the myelin sheath, giving it a white appearance. The cerebrum surrounds the thalamus, which is a key hub for processing sensory and motor signals.
- Below the thalamus is the hypothalamus, which helps regulate body temperature, hunger, and thirst, and produces hormones that control various bodily functions. The inner parts of the cerebral hemispheres, along with deep structures like the amygdala and hippocampus, make up the limbic lobe or limbic system. This system works with the hypothalamus to control emotions, sexual behavior, and motivation.
2. Midbrain
The midbrain is situated between the thalamus and hypothalamus of the forebrain and the pons of the hindbrain. Within the midbrain, there is a canal known as the cerebral aqueduct. The dorsal part of the midbrain is primarily composed of four rounded swellings called the corpora quadrigemina.
3. Hindbrain
The hindbrain consists of the pons, cerebellum, and medulla oblongata. The pons contains fiber tracts that connect various regions of the brain. The cerebellum has a highly convoluted surface, allowing for additional space for a greater number of neurons. The medulla is directly linked to the spinal cord and houses centers that regulate respiration, cardiovascular reflexes, and gastric secretions.
The brain stem is made up of three main parts: the midbrain, pons, and medulla oblongata. It serves as a crucial connection between the brain and spinal cord.
|
150 videos|401 docs|136 tests
|
FAQs on Neural Control and Coordination Chapter Notes - Biology Class 11 - NEET
| 1. What is the role of neurons in the human neural system? |  |
| 2. How is a nerve impulse generated and conducted? |  |
| 3. What are the main functions of the central nervous system (CNS)? |  |
| 4. What are the key structures of the midbrain and their functions? |  |
| 5. What is the significance of the hindbrain in the neural system? |  |
















