Sport Injuries | Physical Education Class 12(XII) - Notes & Model Test Papers - Humanities/Arts PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Introduction |

|
| Causes of Injuries |

|
| Classification of Sports Injuries |

|
| Types of Injuries |

|
| Soft Tissue Injuries |

|
| First Aid |

|
| P.R.I.C.E. Protocol |

|
Introduction
Sports participation and exercise engagement often face interruptions due to injuries among athletes. These injuries can result from various causes such as incorrect movements, collisions with equipment, aggressive sporting actions like diving or sliding, overtraining, or inadequate conditioning. Understanding these injuries and their remedies is crucial to prevent them and ensure active participation.
- Athletic Injury: It refers to physical damage or insult to the body during athletic practice or competition, leading to a loss of capacity or impairing performance (Morris, 1984).
- Sports Injury: Damage to the body's tissues due to sports or exercise activities, causing pain or hindering performance (IOC manual of sports injuries, 2012).
- Sports Injury Classification: These injuries include cuts, tears, overstretching of tissues, bone breakage, or joint dislocation, which can occur during sports, athletic activities, or exercises.
Causes of Injuries
- Incorrect Movements: Improper techniques or movements can lead to injuries.
- Equipment Collisions: Contact with sports equipment can cause harm.
- Aggressive Actions: Diving, sliding, or aggressive sporting moves increase injury risks.
- Overtraining: Excessive exercise without adequate rest can result in injuries.
- Lack of Conditioning: Insufficient physical preparation increases vulnerability to injuries.
Risk Factors for Sports Injuries
- Inactive Lifestyle: Lack of regular physical activity increases injury risks.
- Overtraining: Excessive exercise without proper recovery can lead to injuries.
- Inadequate Warm-up: Skipping warm-up exercises before workouts can cause injuries.
- Improper Techniques: Incorrect execution of movements or exercises increases injury risks.
Understanding these factors and adopting preventive measures such as proper training techniques, warm-up routines, and adequate rest can significantly reduce the incidence of sports-related injuries and promote safe and enjoyable participation in sports and exercise activities.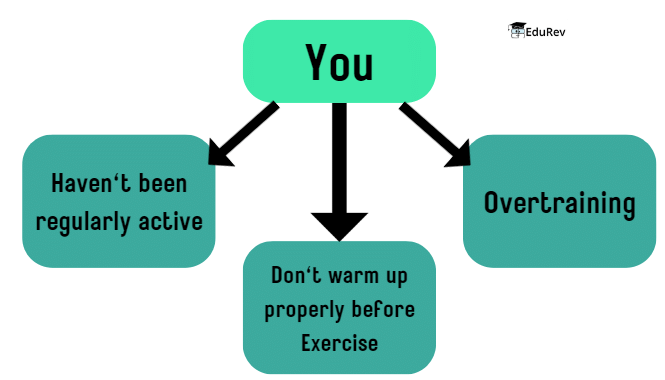
Classification of Sports Injuries
Classification of Sports Injuries
Sports injuries can be classified based on their causes:
- Direct Injuries: Result from external forces causing injury at a specific point of contact.
- Indirect Injuries: Involve damage to soft tissues (like ligaments, tendons, or muscles) through internal or external forces.
- Soft Tissue Injuries: Include injuries to the skin, muscles, or ligaments.
- Hard Tissue Injuries: Occur in bones and cartilages.
- Overuse Injuries: Result from continuous stress, repetitive actions, incorrect techniques, or excessive training.
Types of Injuries
1. Skin Injuries:
- Abrasion: Injury from falling on a rough surface.
- Laceration: Tears in the skin.
- Incision: Cut by a sharp object.
- Puncture Wound: Pierced by a pointed object.
- Avulsion: Tearing away of skin.
2. Soft Tissue Injuries (e.g., muscles, ligaments):
- Contusion: Bruise from a direct blow.
- Sprain: Ligament injury from violent overstretching or abnormal joint movement.
- Strain: Muscle or tendon injury, categorized as mild, moderate, or severe.
3. Joint Injuries:
- Dislocation: Displacement of contiguous bone surfaces in a joint due to external force, complete or partial.
4. Bone Injuries:
- Fractures: Break in bone continuity, classified as open/compound or closed/simple, ranging from mild cracks to severe shattering.
Understanding these classifications helps in recognizing and treating sports injuries effectively, ensuring athletes' well-being and timely recovery.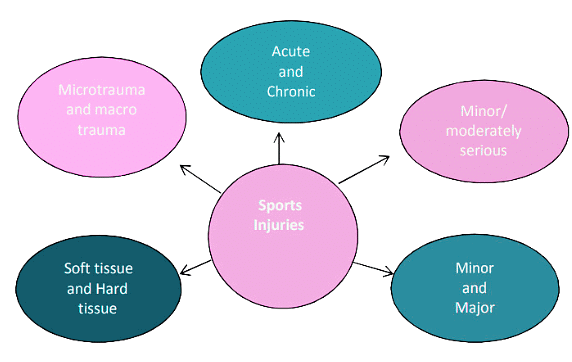
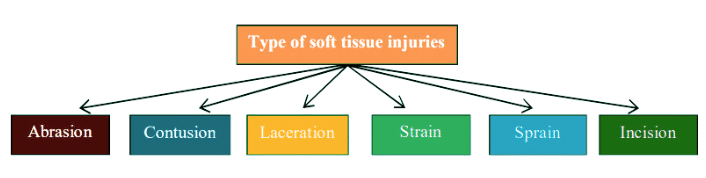
Soft Tissue Injuries
Abrasion:
- Definition: Damage to the upper layers of the skin due to rubbing against a rough surface.
- Cause: Contact between exposed skin and rough surfaces.
- Prevention: Use protective gear.
- Treatment: Clean the affected area, apply compression bandages, and administer an anti-tetanus injection if needed.
Contusion:
- Definition: Collection of blood outside a vessel, often resulting from a blunt force.
- Cause: Blows or falls impacting muscles and connective tissues.
- Prevention: Use safety gear.
- Treatment: Pain relief medication as prescribed by a doctor.
Laceration:
- Definition: Tear-like wounds caused by blunt trauma.
- Cause: Skin hitting an object or vice versa with force.
- Prevention: Use personal protective equipment.
- Treatment: Clean the wound and stop bleeding with compression bandages.
Strain:
- Definition: Injury to muscles or tendons due to overuse, force, or stretching.
- Cause: Overexertion during activities like lifting heavy objects, running, etc.
- Prevention: Regular stretching and strengthening exercises.
- Treatment: Apply ice packs, rest, and use compression and elevation (RICE method).
Sprain:
- Definition: Stretching or tearing of ligaments due to joint overextension.
- Cause: Overextending or tearing a ligament while stressing a joint.
- Prevention: Regular exercises for flexibility and strength.
- Treatment: RICE method.
Incision:
- Definition: Cut into tissues to expose underlying structures.
- Cause: Sharp object injuries.
- Prevention: Ensure safety and avoid sharp edges.
- Treatment: Clean the wound and apply dressing.
Hard Tissue Injuries
Dislocation:
- Definition: Abnormal separation of bones in a joint.
- Cause: Trauma, falls, or weak muscles and tendons.
- Symptoms: Pain, swelling, bruising, instability, loss of joint movement.
- Treatment: Rest, ice, elevation, medication, manipulation, physical therapy, and surgery if necessary.
Fractures:
- Types:
- Stress fracture: Due to overuse.
- Greenstick: Young, soft bone fracture.
- Comminuted: Bone breaks into pieces.
- Transverse: Straight break across a bone.
- Oblique: Diagonal break.
- Impacted: Bones jammed together.
- Causes: Direct impact or overuse.
- Prevention: Exercise, safety equipment, and a calcium-rich diet.
- Treatment: Rest, ice, elevation, medication, splints, reduction, and surgery if needed.
Understanding these types of injuries and their treatments is crucial for athletes' safety and proper management of injuries during sports and exercise activities.
First Aid
First aid refers to the immediate and temporary care provided to a person suffering from an illness, injury, or accident. It aims to preserve life, prevent worsening conditions, and promote recovery. First aid can be administered by individuals with basic medical training.
Objectives of First Aid:
- Provide immediate care.
- Protect the casualty from further harm.
- Relieve pain.
- Promote recovery.
Aims and Objectives:
- Prepare properly for emergencies.
- Assess and care for life-threatening conditions first.
- Minimize further injury, infection, and complications.
- Ensure the victim's comfort.
- Transport the victim to a medical facility as needed.
Key Guiding Objectives of First Aid:
- Promote recovery.
- Preserve life.
- Prevent further injury.
P.R.I.C.E. Protocol
P.R.I.C.E. is a modified protocol for dealing with sports injuries, adding "Protection" to Rest, Ice, Compression, and Elevation.
- Protection:
- Limit or avoid weight-bearing on the injured area.
- Use crutches, splints, or braces for partial immobilization.
- Rest:
- Stop using the injured part or discontinue activity to prevent further damage and promote healing.
- Use crutches or splints as needed.
- Ice:
- Apply ice to the injured area to reduce swelling and hasten healing.
- Use a cloth between the skin and ice pack.
- Apply ice for 10 to 20 minutes every hour.
- Compression:
- Use elastic bandages or compression sleeves to reduce swelling and fluid seeping into the injured area.
- Wrap firmly but not too tight to avoid impairing blood supply.
- Wrap over ice and loosen if necessary.
- Elevation:
- Elevate the injured part above the heart level to reduce swelling and pain.
- Use objects or pillows for elevation.
Following the P.R.I.C.E. protocol promptly after a sports injury can significantly aid in the healing process and minimize complications.
|
12 videos|72 docs|31 tests
|
FAQs on Sport Injuries - Physical Education Class 12(XII) - Notes & Model Test Papers - Humanities/Arts
| 1. What are the common causes of sports injuries? |  |
| 2. How are sports injuries classified? |  |
| 3. What are the different types of sports injuries? |  |
| 4. What are soft tissue injuries in sports? |  |
| 5. What is the P.R.I.C.E. protocol for treating sports injuries? |  |















