Structure of GST | Goods and Services Tax (GST) - B Com PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| What is the structure of GST in India? |

|
| Importance of Understanding GST Structure |

|
| Structure of GST |

|
| Introduction to Zero Rate in GST |

|
What is the structure of GST in India?
The Goods and Services Tax (GST) structure in India is determined by the GST Council and consists of a four-tier system. This framework is designed to categorize essential goods and some edibles into the lower tax brackets, while placing high-value goods and services in the higher tax brackets. The four GST tax rates are 0%, 5%, 12%, 18%, and 28%.
Importance of Understanding GST Structure
Understanding the GST structure in India is crucial for compliance, reducing tax liabilities, and conducting business ethically and responsibly. This knowledge helps you make informed decisions, avoid potential penalties, and protect your financial well-being.
Structure of GST
There are different taxes levied under the structure of GST in India. To help you understand what these mean, we will explain each one of them here: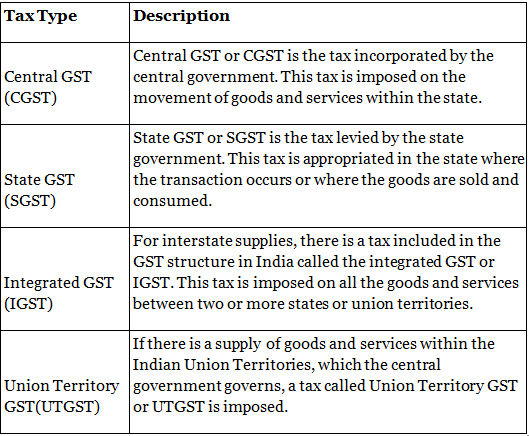
Introduction to Zero Rate in GST
A zero rate in GST means that no tax is levied on certain goods and services, effectively granting them a tax exemption. The government determines which goods and services qualify for this zero-tax rate. Examples include fresh fruits, bread, milk, and curd. Additionally, supplies made to Special Economic Zone (SEZ) developers or for overseas export are also subject to a zero-rate tax.
Lower Rate (5%)
The lower rate of GST, set at 5%, applies to certain commodities and services. Examples include footwear priced under Rs. 500, clothing under Rs. 1000, packaged food items, branded paneer, cream, and skimmed milk powder.
Standard Rate (12-18%)
The standard GST rate ranges from 12% to 18%. A 12% GST applies to items such as butter, cheese, frozen meat products, ghee, animal fat, sausages, packaged dry fruits, snacks, fruit juices, ketchup, and sauces. An 18% GST rate is imposed on items such as pastries, pasta, cakes, hairdryers, panels, vacuum cleaners, wires, telecom services, and IT services.
Higher Rate (28%)
The highest GST rate of 28% is reserved for luxury items. This rate applies to goods such as paint, washing machines, cement, automobiles, shampoo, aerated water, sunscreen, and motorcycles. Additionally, some items in the 28% bracket may also incur an extra cess as determined by the government.
|
130 videos|45 docs|14 tests
|
FAQs on Structure of GST - Goods and Services Tax (GST) - B Com
| 1. What is the overall structure of GST in India? |  |
| 2. What are the different components of GST in India? |  |
| 3. How does the input tax credit system work under the GST structure in India? |  |
| 4. Can you explain the concept of Zero Rate in GST? |  |
| 5. How does understanding the structure of GST in India benefit businesses and consumers? |  |

|
Explore Courses for B Com exam
|

|

















