Year 11 Exam > Year 11 Notes > History for GCSE/IGCSE > Consequences of the Failures of the League of Nations in the 1930s
Consequences of the Failures of the League of Nations in the 1930s | History for GCSE/IGCSE - Year 11 PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| The Impact of Manchuria and Abyssinia |

|
| Germany Leaves the League |

|
| The Saar, 1935 |

|
| Remilitarisation of the Rhineland, 1936 |

|
| The Spanish Civil War |

|
The Impact of Manchuria and Abyssinia
- The League of Nations faced significant challenges in the 1930s due to its failures in handling crises like the Manchurian and Abyssinian conflicts.
- These failures weakened the League's credibility and exposed its inability to maintain peace and security globally.
- The Manchurian Crisis (1931) highlighted Japan's aggression and expansionist policies, leading to the League's ineffective response.
- Similarly, the Abyssinian Crisis (1935) demonstrated the League's failure to prevent Italy's invasion of Abyssinia and enforce collective security.
- These events showcased the limitations of the League of Nations in preventing aggressor nations from disrupting international stability.
- The League's inability to address these crises effectively paved the way for further aggression and ultimately contributed to the outbreak of World War II.
- In conclusion, the failures of the League of Nations in the 1930s significantly undermined its authority and set the stage for greater conflicts in the future.
Germany Leaves the League
- Germany withdrew from the League of Nations in November 1933. This decision allowed Hitler to aggressively pursue his foreign policy objectives.
- Hitler initiated a rearmament program during this period, which provided him with the necessary military strength to launch invasions into neighboring countries.
- Several reasons led many in Britain to support Germany's decision to rearm:
- The Treaty of Versailles was viewed as excessively harsh towards Germany.
- Other countries were also engaging in military build-up, creating a sense of insecurity.
- Hitler could openly showcase Germany's military might and challenge the restrictions imposed by the Treaty of Versailles through elaborate rallies.
- Nazi Germany utilized large-scale rallies as a propaganda tool to:
- Demonstrate the strength of the German armed forces.
- Showcase Germany's defiance of the military limitations outlined in the Treaty of Versailles.
- The 1935 'Rally of Freedom' in Nuremberg marked the reintroduction of compulsory military service and was captured in the propaganda film "Day of Freedom: Our Armed Forces" by renowned filmmaker Leni Riefenstahl.
- Despite early military posturing, Hitler's attempts at militaristic expansion faced initial setbacks. For instance, in 1934, his endeavor to annex Austria was thwarted by Mussolini's deployment of troops along the Austrian border.
- By 1939, the German armed forces boasted a strength of approximately 1.4 million men, reflecting a substantial increase from earlier years.
- Significant escalations in armament spending were observed, rising from 3.5 billion marks in 1933 to a staggering 26 billion marks by 1939.
- The employment landscape also witnessed a notable transformation, with the number of individuals engaged in aircraft construction soaring from 4,000 in 1933 to 72,000 by 1935.
Question for Consequences of the Failures of the League of Nations in the 1930sTry yourself: What was one of the main reasons for Germany's withdrawal from the League of Nations in 1933?View Solution
The Saar, 1935

What were the Impacts of the Saar Plebiscite?
- The plebiscite served as a significant propaganda victory for Hitler, showcasing widespread support for his policies, even within a region where Nazi opposition existed.
- The League of Nations effectively resolved the dispute through legal means, adhering to the 15-year time limit stipulated in the Treaty of Versailles. This diplomatic resolution prevented a potential conflict between France and Germany, ultimately allowing the people of the Saar region to achieve their goal of reunification with Germany.
- Hitler aimed to leverage his popularity to realize his vision of a Greater Germany, necessitating the acquisition of territories lost under previous treaties.
- The League's primary objective was to avert the outbreak of war at all costs, while Hitler capitalized on the plebiscite to bolster his rearmament efforts.
- The Saar region, rich in key natural resources, provided vital materials for Hitler's expanding rearmament industries, further strengthening his military capabilities.
- Additionally, the League of Nations sought to promote disarmament as a means to foster peace and stability on a global scale.


Remilitarisation of the Rhineland, 1936


How was the Remilitarisation of the Rhineland a Failure for the League of Nations?
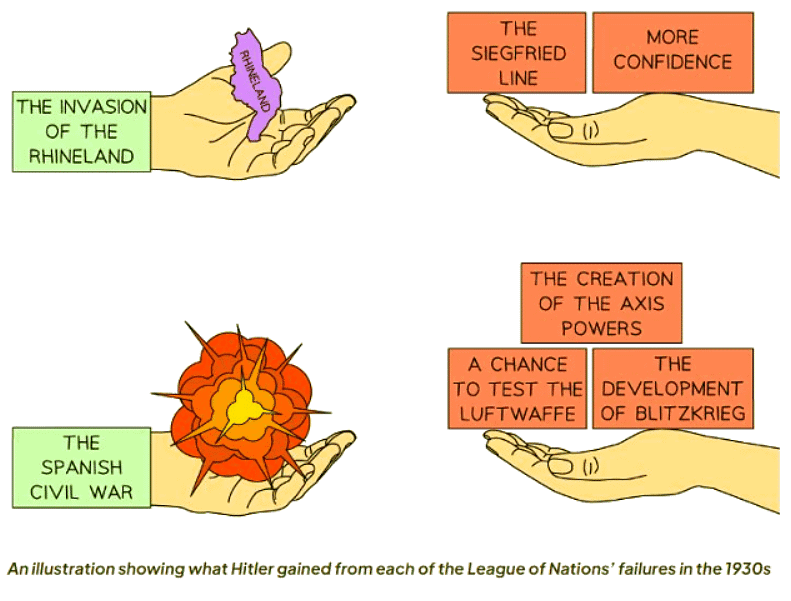
- After the 1936 invasion, Hitler fortified his defenses along the French border. Germany constructed the Siegfried Line, which was a complex system of fortifications. The League of Nations failed to effectively respond to Hitler's breach of the Treaty of Versailles.
- Hitler's actions following the invasion illustrated his growing confidence and the League's inability to enforce consequences for his actions. This emboldened Hitler to further expand Germany without fear of repercussions.
- Historians view this event as a missed opportunity for the League to curb Hitler's aggression without resorting to a full-scale world war. Hitler skillfully manipulated the League's response to his advantage.
- Post-invasion, Hitler even went as far as signing a 25-year non-aggression pact with France and Britain. However, it became evident that Hitler had no intention of honoring this agreement, using it to portray Germany as less hostile than it truly was.
 A map showing how far Hitler had extended Germany’s territory by 1936
A map showing how far Hitler had extended Germany’s territory by 1936
The Spanish Civil War
The conflict erupted in Spain in July 1936 involving:
- The leftist Spanish government
- Right-wing nationalist rebels commanded by General Franco
European Reactions to the Spanish Civil War

How was the Spanish Civil War a Failure for the League of Nations?
- The Spanish Civil War Overview:
- The Spanish Civil War resulted in the death of approximately 750,000 individuals, a stark violation of the League of Nations' objective to prevent the use of warfare.
- Victory of General Franco and Rise of Fascism:
- In 1939, General Franco emerged victorious, marking a triumph of fascism over democracy.
- The alliance between Hitler and Mussolini solidified with the signing of the Rome-Berlin Axis in 1937, showcasing a tightening bond between the two dictators.
- German Military Advancements and Tactics:
- Germany made significant strides in military tactics, with Hitler pioneering the concept of blitzkrieg, characterized by swift and overwhelming attacks.
- The Luftwaffe, Germany's air force, developed innovative bombing techniques, exemplified by the devastating bombing of Guernica in April 1937.
- The ruthless aerial assault on Guernica by German and Italian bombers, resulting in widespread destruction and loss of civilian lives, sent shockwaves across the globe.
- Global Responses and Anticipation of War:
- The brutal tactics employed in the conflict prompted heightened rearmament efforts in Britain and France as world leaders and populations recoiled in horror.
- The looming specter of war led to widespread apprehension among civilians, many of whom fervently sought to avert the catastrophic consequences of another conflict.
The League's Actions Leading to Hitler's Success
- The League's actions in the 1930s inadvertently contributed to Hitler's success and provided him with opportunities.

The document Consequences of the Failures of the League of Nations in the 1930s | History for GCSE/IGCSE - Year 11 is a part of the Year 11 Course History for GCSE/IGCSE.
All you need of Year 11 at this link: Year 11
|
81 videos|86 docs|18 tests
|
FAQs on Consequences of the Failures of the League of Nations in the 1930s - History for GCSE/IGCSE - Year 11
| 1. How did the Manchuria and Abyssinia crises impact the League of Nations in the 1930s? |  |
Ans. The Manchuria and Abyssinia crises highlighted the League of Nations' inability to prevent aggressive actions by powerful nations, undermining its authority and effectiveness.
| 2. Why did Germany leave the League of Nations in the 1930s? |  |
Ans. Germany left the League of Nations in the 1930s as a result of discontent with the Treaty of Versailles and a desire to pursue its own aggressive foreign policy objectives without international interference.
| 3. What was the significance of the remilitarisation of the Rhineland in 1936? |  |
Ans. The remilitarisation of the Rhineland by Germany in 1936 violated the Treaty of Versailles and further weakened the League of Nations' ability to maintain peace and stability in Europe.
| 4. How did the Spanish Civil War impact the failures of the League of Nations in the 1930s? |  |
Ans. The Spanish Civil War exposed the League of Nations' inability to effectively intervene in conflicts and uphold its principles of collective security, further eroding its credibility and influence on the world stage.
| 5. What were the consequences of the League of Nations' failures in the 1930s? |  |
Ans. The League of Nations' failures in the 1930s ultimately led to the outbreak of World War II, as aggressive actions by countries such as Germany went unchecked, highlighting the organization's inability to maintain peace and prevent conflict.

|
Explore Courses for Year 11 exam
|

|
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.
Related Searches
















