Mastering Development in Python: Assignment 5 | Python- Mastering Development in Python - Software Development PDF Download
Q1: Given a 0-indexed integer array nums, return true if it can be made strictly increasing after removing exactly one element, or false otherwise. If the array is already strictly increasing, return true.
The array nums is strictly increasing if nums[i - 1] < nums[i] for each index (1 <= i < nums.length).
Example 1:
Input: nums = [1,2,10,5,7]
Output: true
Explanation: By removing 10 at index 2 from nums, it becomes [1,2,5,7].
[1,2,5,7] is strictly increasing, so return true.
Example 2:
Input: nums = [2,3,1,2]
Output: false
Explanation:
[3,1,2] is the result of removing the element at index 0.
[2,1,2] is the result of removing the element at index 1.
[2,3,2] is the result of removing the element at index 2.
[2,3,1] is the result of removing the element at index 3.
No resulting array is strictly increasing, so return false.
Example 3:
Input: nums = [1,1,1]
Output: false
Explanation: The result of removing any element is [1,1].
[1,1] is not strictly increasing, so return false.
Constraints:
2 <= nums.length <= 1000
1 <= nums[i] <= 1000
Ans:
Approach
- Starting from the second element of the array we check if it is less or equal to the previous one. In this case the array is not strictly increasing and we need to fix it and we have two way to do this:
- - if nums[i-2] < nums[i] < nums[i-1] ( e.g 2, 10, 5 (i), 6 ) remove i-1 (10) fix the situation.
- - If nums[i] < nums[i-1] and nums[i] <= nums[i-2] (e.g 2, 3, 2(i), 4(j), 5 ) we need to remove i to fix the situation.
- Since we compare always the i value with i-1 value the first case does not alter the algorithm. This is not true for the second case, because at the next iteration we should compare the position j=i+1 with the position i-1 (because we have removed the i position). To avoid this issue we are going to copy the i-1 element in i position.
- In each case we keep track of the removal using a variable removed_once. If we found another element that is not strictly increasing we return False.
Complexity
Time complexity: O(n)
Space complexity: O(1)
Code: 
Q2: You have a long flowerbed in which some of the plots are planted, and some are not. However, flowers cannot be planted in adjacent plots.
Given an integer array flowerbed containing 0's and 1's, where 0 means empty and 1 means not empty, and an integer n, return true if n new flowers can be planted in the flowerbed without violating the no-adjacent-flowers rule and false otherwise.
Example 1:
Input: flowerbed = [1,0,0,0,1], n = 1
Output: true
Example 2:
Input: flowerbed = [1,0,0,0,1], n = 2
Output: false
Constraints:
1 <= flowerbed.length <= 2 * 104
flowerbed[i] is 0 or 1.
There are no two adjacent flowers in flowerbed.
0 <= n <= flowerbed.length
Ans: Here's how the method works:
- If n is equal to 0, meaning there are no flowers to plant, it returns True immediately.
- It then iterates over the flowerbed list using a for loop, examining each plot one by one.
- Inside the loop, it checks if the current plot (flowerbed[i]) is empty (i.e., equal to 0) and if both adjacent plots are also empty (i.e., flowerbed[i-1] and flowerbed[i+1] are equal to 0). This condition ensures that the current plot can have a flower planted on it.
- If the condition is met, it plants a flower (flowerbed[i] = 1), decrements n by 1 to indicate that one flower has been planted, and checks if n has become 0. If n becomes 0, it means all flowers have been planted, so it returns True.
- If the loop completes without planting all flowers (n is still not 0), it returns False, indicating that it's not possible to plant all the flowers in the given flowerbed.
- This algorithm basically tries to plant as many flowers as possible in the given flowerbed while ensuring that each flower is planted in a valid location. If it manages to plant all the required flowers, it returns True; otherwise, it returns False.

Q3: You are given a 0-indexed integer array nums and an integer threshold.
Find the length of the longest subarray of nums starting at index l and ending at index r (0 <= l <= r < nums.length) that satisfies the following conditions:
nums[l] % 2 == 0
For all indices i in the range [l, r - 1], nums[i] % 2 != nums[i + 1] % 2
For all indices i in the range [l, r], nums[i] <= threshold
Return an integer denoting the length of the longest such subarray.
Note: A subarray is a contiguous non-empty sequence of elements within an array.
Example 1:
Input: nums = [3,2,5,4], threshold = 5
Output: 3
Explanation: In this example, we can select the subarray that starts at l = 1 and ends at r = 3 => [2,5,4]. This subarray satisfies the conditions.
Hence, the answer is the length of the subarray, 3. We can show that 3 is the maximum possible achievable length.
Example 2:
Input: nums = [1,2], threshold = 2
Output: 1
Explanation: In this example, we can select the subarray that starts at l = 1 and ends at r = 1 => [2].
It satisfies all the conditions and we can show that 1 is the maximum possible achievable length.
Example 3:
Input: nums = [2,3,4,5], threshold = 4
Output: 3
Explanation: In this example, we can select the subarray that starts at l = 0 and ends at r = 2 => [2,3,4].
It satisfies all the conditions.
Hence, the answer is the length of the subarray, 3. We can show that 3 is the maximum possible achievable length.
Constraints:
1 <= nums.length <= 100
1 <= nums[i] <= 100
1 <= threshold <= 100
Ans:
Intuition
Here we have a list of nums and threshold. You should find the longest alternating subarray according to the problem.
Approach
Simply use Two Pointers to define such an array.
Complexity
Time complexity: O(N)
Space complexity: O(1)
Code
class Solution:
def longestAlternatingSubarray(self, nums: list[int], threshold: int) -> int:
left = 0
ans = int(nums[0] % 2 == 0 and nums[0] <= threshold)
n = len(nums)
for right in range(n):
if nums[left] % 2 != 0 or nums[left] > threshold \
or nums[right] > threshold \
or (right and nums[right] % 2 == nums[right - 1] % 2):
left = right
if nums[left] % 2 == 0 and nums[left] <= threshold:
ans = max(ans, right - left + 1)
return ans
Q4:
You are given an integer array deck where deck[i] represents the number written on the ith card.
Partition the cards into one or more groups such that:
Each group has exactly x cards where x > 1, and
All the cards in one group have the same integer written on them.
Return true if such partition is possible, or false otherwise.
Example 1:
Input: deck = [1,2,3,4,4,3,2,1]
Output: true
Explanation: Possible partition [1,1],[2,2],[3,3],[4,4].
Example 2:
Input: deck = [1,1,1,2,2,2,3,3]
Output: false
Explanation: No possible partition.
Constraints:
1 <= deck.length <= 104
0 <= deck[i] < 104
Ans: 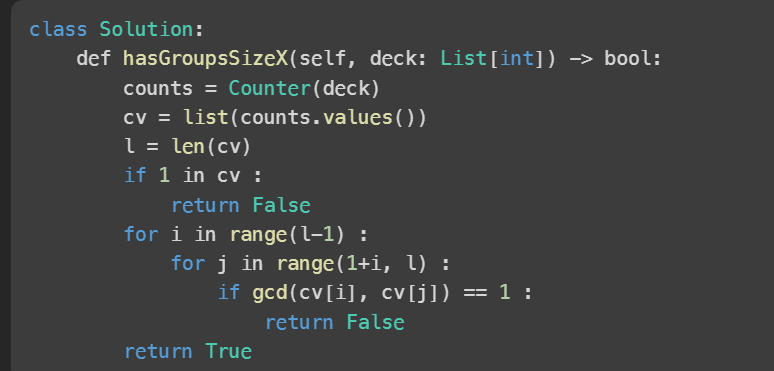
Q5: You are given a 0-indexed array of integers nums.
A prefix nums[0..i] is sequential if, for all 1 <= j <= i, nums[j] = nums[j - 1] + 1. In particular, the prefix consisting only of nums[0] is sequential.
Return the smallest integer x missing from nums such that x is greater than or equal to the sum of the longest sequential prefix.
Example 1:
Input: nums = [1,2,3,2,5]
Output: 6
Explanation: The longest sequential prefix of nums is [1,2,3] with a sum of 6. 6 is not in the array, therefore 6 is the smallest missing integer greater than or equal to the sum of the longest sequential prefix.
Example 2:
Input: nums = [3,4,5,1,12,14,13]
Output: 15
Explanation: The longest sequential prefix of nums is [3,4,5] with a sum of 12. 12, 13, and 14 belong to the array while 15 does not. Therefore 15 is the smallest missing integer greater than or equal to the sum of the longest sequential prefix.
Constraints:
1 <= nums.length <= 50
1 <= nums[i] <= 50
Ans: 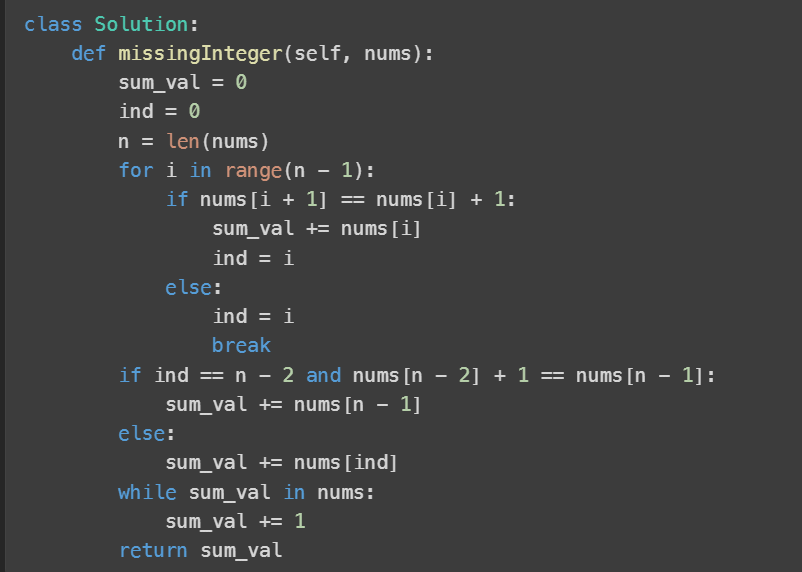
|
8 videos|5 docs
|



















