Year 6 Exam > Year 6 Notes > Year 6 Computing > How is all our digital data stored?
How is all our digital data stored? | Year 6 Computing PDF Download
How do computers store information?
- A lot of information is stored on our computers, and without it, they wouldn't function.
- Types of information stored include:
- Software applications: the programs we use
- Drivers: the instructions that enable communication between different parts of the computer system
- Files: the content we create when using the computer
- Regardless of the type of information, it is all stored in the same way.
- Information is converted into the numbers 1 and 0, known as binary.
- Once converted to binary, information can be stored on our computers.
- Binary is a base two system because it uses only two digits.

How are numbers represented in binary?
- In the world of computing, numbers are represented using the binary system, which consists of only two digits: 0 and 1. To comprehend how individual numbers are encoded in binary, we rely on a binary place value chart that helps us determine the binary code for a given number.
- The binary system operates on a base-2 numbering system, where each column in the place value chart represents a value that is a power of 2.
- Example: Let's take the number 11, which in binary is represented as 1011.
- Starting from the right, we have:
- 1 lot of 1
- 1 lot of 2
- 0 lots of 4
- 1 lot of 8
- Adding these values together (8 + 0 + 2 + 1), we get the decimal value 11.
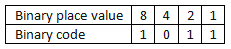
Question for How is all our digital data stored?Try yourself: In the binary system, what does the digit 1 represent?View Solution
Understanding Binary Data Storage
- Computers store information in their memory, which is made up of special switches.
- To store information, computers turn these switches on or off.
- When a switch is on, it represents the binary value of 1, and when it is off, it represents the binary value of 0.
- The data stored in one switch is called a bit.
- Information on digital devices is usually grouped into sets of eight bits, known as a byte.
- A byte can store a single number, letter, or character.
- By combining bytes, words can be stored in the computer's memory.
- For example, the eight switches representing the binary code 01101101 save the letter M.

Storing larger amounts of information
- Similar to measurements in math and science, computer memory size uses linked units.
- As memory size increases, we move to the next unit of measurement to avoid writing longer numbers.
Memory Storage Requirements and Evolution
- The space required to store a three-minute song amounts to:
- 3 megabytes
- 3,072 kilobytes
- 3,145,728 bytes
- 25,165,824 bits
- This indicates that storing a single song on a digital device utilizes over 25 million switches!
- For storing software applications, digital images, and music, computers necessitate memory capacities in gigabytes. This implies the presence of billions of switches within a computer's memory.
In contemporary times, computer switches responsible for storing information are minuscule, permitting even pocket-sized digital devices to accommodate vast amounts of data. - In the past, computers utilized significantly larger switches to store data, contributing to the substantial physical space computers occupied.
Different types of computer memory
Computers, laptops, and some tablets consist of two main types of memory:
- Volatile Memory:
- Volatile memory retains data and information only when the device is powered and operational. This means that the data stored in volatile memory is lost when the device is switched off or loses power.
- Example: Random Access Memory (RAM) in a computer is a type of volatile memory where data is temporarily stored while the system is running.
- Non-Volatile Memory:
- Non-volatile memory, on the other hand, does not require power to maintain stored data and information. It retains data even when the device is powered off.
- Example: Hard disk drives (HDDs) and solid-state drives (SSDs) in computers are non-volatile memory types where data remains intact even when the device is turned off.

Other places where information is stored
- Some people choose to store information in the cloud, which is actually stored on servers in large data centers.
- When information is stored in the cloud, it can be accessed from anywhere in the world with an internet connection.
- Information in the cloud needs password protection to ensure that only the owner can control who sees and uses it.
The document How is all our digital data stored? | Year 6 Computing is a part of the Year 6 Course Year 6 Computing.
All you need of Year 6 at this link: Year 6
|
19 videos|26 docs|3 tests
|
FAQs on How is all our digital data stored? - Year 6 Computing
| 1. How is digital data stored? |  |
Ans. Digital data is stored using various storage devices such as hard drives, solid-state drives, and cloud storage services. Data is saved in binary code (1s and 0s) on these storage devices.
| 2. What is cloud computing? |  |
Ans. Cloud computing is a technology that allows users to access and store data and applications over the internet instead of on a physical hard drive or local storage device.
| 3. What are the benefits of cloud computing for storing data? |  |
Ans. Some benefits of cloud computing for storing data include scalability, cost-effectiveness, accessibility from anywhere with an internet connection, automatic backups, and enhanced security measures.
| 4. How secure is cloud storage for storing sensitive data? |  |
Ans. Cloud storage providers implement various security measures such as encryption, authentication, and regular security audits to ensure the safety of sensitive data stored on their servers.
| 5. How can schools benefit from utilizing cloud computing for data storage? |  |
Ans. Schools can benefit from cloud computing for data storage by having centralized access to educational resources, enabling collaboration among students and teachers, reducing IT infrastructure costs, and ensuring data backup and disaster recovery.
Related Searches















