Grassroots Democracy — Part 1: Governance NCERT Solutions | Social Studies (SST) Class 6 PDF Download
Questions, Activities and Projects
Q1: Test yourself— What is the meaning of democracy? What is the difference between direct democracy and representative democracy?
Ans: Democracy is a form of government where the power to make decisions lies with the people. In a democracy, citizens have the right to participate in decision-making processes, either directly or through elected representatives.
- Direct Democracy: In a direct democracy, all citizens have the opportunity to participate directly in decision-making. This means that every citizen can vote on laws and policies. Examples include ancient Athens and modern-day referendums where citizens vote on specific issues.
- Representative Democracy: In a representative democracy, citizens elect representatives who make decisions on their behalf. These representatives are accountable to the people and are expected to act in their best interests. Examples include most modern democracies like India, the United States, and the United Kingdom, where elected officials such as Members of Parliament (MPs) or Members of Legislative Assembly (MLAs) represent the citizens.
Q2: Recall the three organs of government. What are their different roles?
Ans: The three organs of government are:
- Legislature:
- The legislature is responsible for making laws. This process involves debating and passing legislation that governs the country.
- It also has the power to amend or repeal existing laws.
- The legislature represents the will of the people and holds the executive accountable.
- Executive:
- The executive is responsible for implementing and enforcing laws. This includes the head of state (such as the President or Prime Minister), ministers, and various government agencies.
- It administers public policy and oversees the functioning of the government.
- The executive also manages public services and ensures law and order.
- Judiciary:
- The judiciary interprets laws and ensures they are applied fairly. This includes courts and judges who resolve disputes and determine the legality of actions.
- It protects the rights of citizens and ensures justice.
- The judiciary can review the constitutionality of laws and executive actions.
Q3: Why do we need three tiers of government?
Ans: The three tiers of government—local, state, and national—allow for effective administration and governance by addressing issues at different levels. This structure helps in better resource management, localized decision-making, and efficient implementation of policies.
Local Government:
- Local governments handle issues and services that are specific to towns, cities, and villages. These include sanitation, local roads, and community services.
- They are closer to the people and can address local needs and problems more effectively.
State Government:
- State governments manage matters that are beyond the scope of local governments but are still specific to a particular region or state. These include education, health, and infrastructure development.
- They have the authority to make decisions that reflect the needs and priorities of their state’s population.
National Government:
- The national government handles issues that affect the entire country. These include defense, foreign policy, and national economic policies.
- It ensures unity and coordination among the states and represents the country at the international level.
Having three tiers of government allows for a more balanced distribution of power and responsibilities. It ensures that decisions are made at the appropriate level, taking into account local, regional, and national considerations. This structure promotes efficiency, accountability, and responsiveness to the diverse needs of the population.
Q4: Project: Many of you will remember the lockdown that took place during the COVID-19 pandemic. Make a list of all the actions that were taken at that time? Which tiers of government were involved in managing the situation? What was the role of each of the organs of government?
Ans: Actions Taken:
- Nationwide lockdown was imposed.
- Implementation of social distancing and mask mandates.
- Establishment Of quarantine centres and hospitals.
- Distribution of food and essentials to vulnerable populations.
- Financial relief packages for affected industries and individuals.
- Online education systems were set up.
Tiers of Government Involved
- Central Government: Imposed the nationwide lockdown, provided financial relief, and coordinated international efforts for medical supplies.
- State Governments: Managed the health response within states, enforced lockdown measures, and provided state-specific relief efforts.
- Local Governments: Handled the distribution of essentials, maintained law and order at the local level, and set up quarantine centres.
Roles of the Three Organs
- Legislature: Passed laws and regulations to manage the pandemic response, including financial relief and healthcare measures.
- Executive: Implemented the lockdown, managed public health responses, and coordinated resources across states.
- Judiciary: Ensured that the actions taken during the lockdown were within legal boundaries and addressed any legal disputes arising from the lockdown measures.
The Big Questions
Q1: What is the meaning of ‘governance’?
Ans: Governance is the process of taking decisions, organizing the society’s life with different sets of rules, and ensuring that they are followed.
Q2: Why do we need a government?
Ans: We need a government to create and enforce rules that maintain order and harmony in society, provide public services, protect rights, and ensure justice and equality.
Q3: What is the meaning of ‘democracy’? Why is it important?
Ans: Democracy is a system of government where the people rule, either directly or through elected representatives. It is important because it ensures the participation of citizens in decision-making, protects individual freedoms, and promotes equality and justice.
Let's Explore
Page 150
Q1: Describe the two pictures given in Fig. 10.1 on page 151 — what differences do you see between them? Ans: The two pictures in Fig 10.1 on page 151 describes the Traffic scene on a busy road in urban place (City). However both the pictures are contrasting in nature in which Picture 1 depicts smooth flow of vehicles and 2 reflects complete breakdown, chaos, with no rules and regulations.
Ans: The two pictures in Fig 10.1 on page 151 describes the Traffic scene on a busy road in urban place (City). However both the pictures are contrasting in nature in which Picture 1 depicts smooth flow of vehicles and 2 reflects complete breakdown, chaos, with no rules and regulations.
Let us see the differences in Picture 1 and Picture 2:
Q2: How do you connect this with our discussion on rules?
Ans: Rules are essential for social order and better life. Rules made once can be changed. In school and home we also have rules.
Q3: What are some of the rules in your school? Who made them?
Ans: Some common school rules might include:
- Attendance: Students must attend school regularly and be on time.
- Dress Code: Students must wear the school uniform.
- Behaviour: Students must respect teachers and peers and avoid any disruptive behaviour.
- Homework: Students must complete and submit their homework on time.
- Examinations: Students must follow the guidelines during exams to prevent cheating.
These rules are usually made by the school administration, which may include the principal, vice-principal, and school board. They may also be influenced by the input of teachers, parents, and sometimes even students through student councils or representatives.
Page 153
Q1: Can you identify the categories of public service or other activities that are represented in the ten pictures in Fig. 10.2 on page 152? Ans:
Ans:
- Picture 1: Public development and infrastructure services.
- Picture 2: Transport service.
- Picture 3: Security and safety services.
- Picture 4: Healthcare services
- Picture 5: Disaster management and relief services.
- Picture 6: Road traffic safety (Traffic – Police)
- Picture 7: Judicial services.
- Picture 8: Educational services.
- Picture 9: Postal services.
- Picture 10: Banking services.
Q2: What role do you think the government plays in each of these activities?
Ans: Government is directly involved in providing all kind of public service. It ensures that these services are provided to all people with minimum hindrance and on time. It creates adequate infrastructure, employs trained manpower and ensures free flow of service. All levels of government from union to state and local authorities are involved in providing these services.
Q3: Can you think of other aspects of your daily life where the government plays an important role?
Ans: There are others areas of our daily life where the government plays an important role, for example:
- Checking and ensuring quality and prices of food articles, milk etc.
- Helping to preserve forest cover, environment and reduction of pollution.
- Ensuring regular supply of water and electricity.
- Maintenance of parks, cleaning of roads, providing, streets lamps etc.
- Providing health and education services.
Page 154
Q: Explain how the three government organs are at work in the case of the cyber criminals described above. How do they intervene?
Ans: Digital technologies have eased the life of people and at the same time created a new class of criminals who, finds digital ways of stealing people’s money.
To prevent cybercrime government (legislative) has pass new laws in order to fight such criminal activities. Many criminals, who have been involved in robbing innocent people of their hard-earned money, have been arrested (executive) and convicted in court (judiciary). They are usually fined as well as jailed for some years.
Page 155
Q: As a class activity, can you imagine the sort of disorder we might witness if all three organs were under the control of the same group of people? Can you describe any such real-life situation you may have heard of?
Ans: If all three government organs—legislature, executive, and judiciary—were controlled by the same group, it would lead to unchecked power, resulting in corruption, oppression, and erosion of democratic values. There would be no independent body to challenge unjust laws, leading to widespread abuse and suppression of dissent. A real- life example is North Korea, where the ruling regime controls all branches, leading to severe human rights violations and lack of freedom, Similarly, in Nazi Germany, the concentration of power in Hitler's hands led to widespread persecution and the collapse of democratic governance, demonstrating the dangers of such a system.
Page 156
Q1: Observe the table (Fig. 10.5). Highlight the functions and responsibilities that affect your life the most.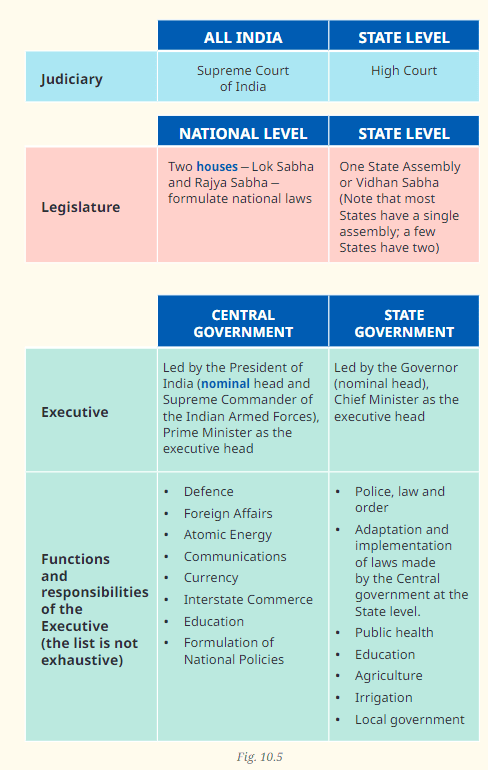 Ans: The functions and responsibilities from the table that most likely affect your life the most:
Ans: The functions and responsibilities from the table that most likely affect your life the most:
- Police, Law, and Order (State Government): Ensures personal safety and security in your daily life, and maintains peace and order in society.
- Public Health (State Government): Influences the availability of healthcare services, vaccination programs, and the overall quality Of health services you can access.
- Education (Central and State Governments): Affects the quality of education you receive, the curriculum, and the functioning Of educational institutions.
- Local Government (State Government): Directly impacts your daily living through services like sanitation, water supply, road maintenance, and local infrastructure.
These functions play a crucial role in ensuring a safe, healthy, and well-governed environment for your everyday life.
Q2: Ask two or three adults about their connection or interaction with the government—at what levels does it take place and for what purpose?
Ans: Interactions with the Government (Based on Adult Responses):
- Interaction at the State Level: One adult mentioned dealing with the State Government to obtain a driving license, which involved interacting with the regional transport office (RTO) for the necessary paperwork and driving tests.
- Interaction at the Local Level: Another adult described engaging with the Local Government for property tax payments and seeking approval for home renovation, which required interaction with the local municipal corporation.
These interactions highlight how different levels of government are involved in various aspects of daily life, from legal documentation to infrastructure development.
|
67 videos|386 docs|80 tests
|
FAQs on Grassroots Democracy — Part 1: Governance NCERT Solutions - Social Studies (SST) Class 6
| 1. What is grassroots democracy? |  |
| 2. How does grassroots democracy promote transparency and accountability? |  |
| 3. What are some examples of grassroots democracy initiatives in India? |  |
| 4. How can individuals participate in grassroots democracy? |  |
| 5. What are the benefits of grassroots democracy for a society? |  |

|
Explore Courses for Class 6 exam
|

|

















