Mindful Eating: A Path to a Healthy Body Chapter Notes | Science Class 6 PDF Download
Introduction
Healthy Eating is essential for maintaining good health and overall well-being. A healthy diet includes a variety of foods that provide essential nutrients in the right quantities. This includes carbohydrates, proteins, fats, vitamins, and minerals. Eating wholesome food in moderate quantities and considering factors like season, time, and place is crucial for a healthy lifestyle.
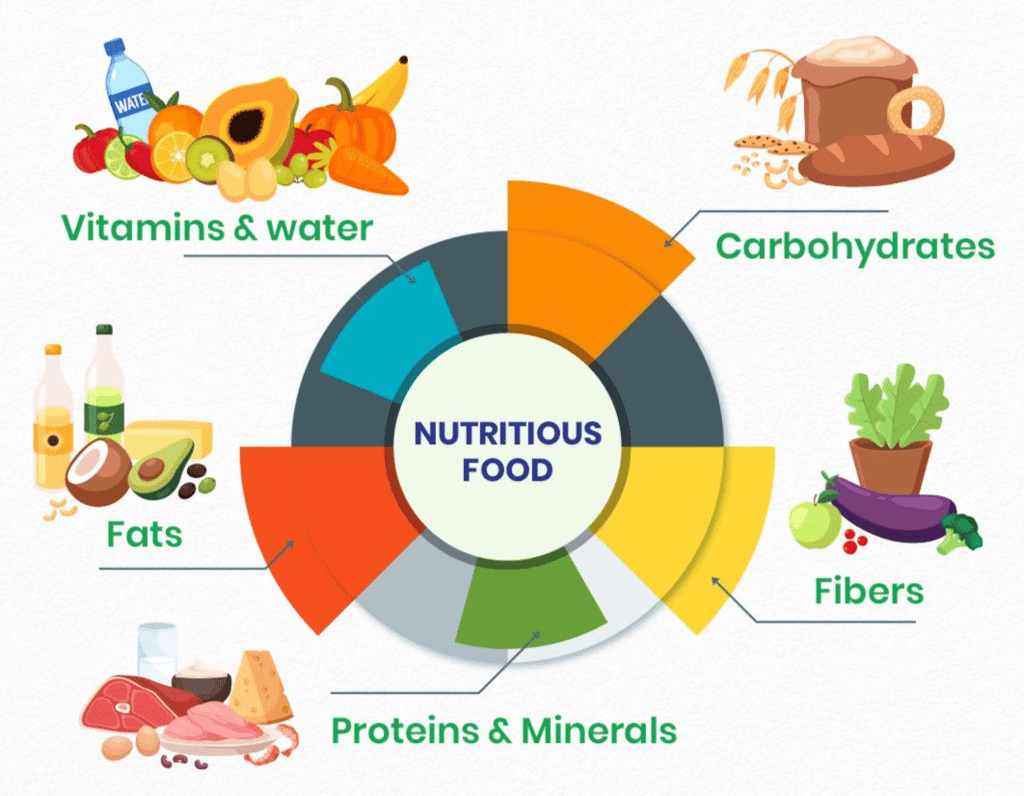 Nutritious Food
Nutritious Food
What Do We Eat?
People's food preferences are influenced by local availability, cultural traditions, and personal tastes. For example, rice is a staple in Asia, while bread is common in Europe.
Food in Different Regions
Different regions grow various crops based on the types of soil and climate.
- Knowing about these local specialities helps us appreciate India's rich cultural and agricultural diversity.
- The food choices in each area vary according to the crops grown, local tastes, cultural influences, and traditions.
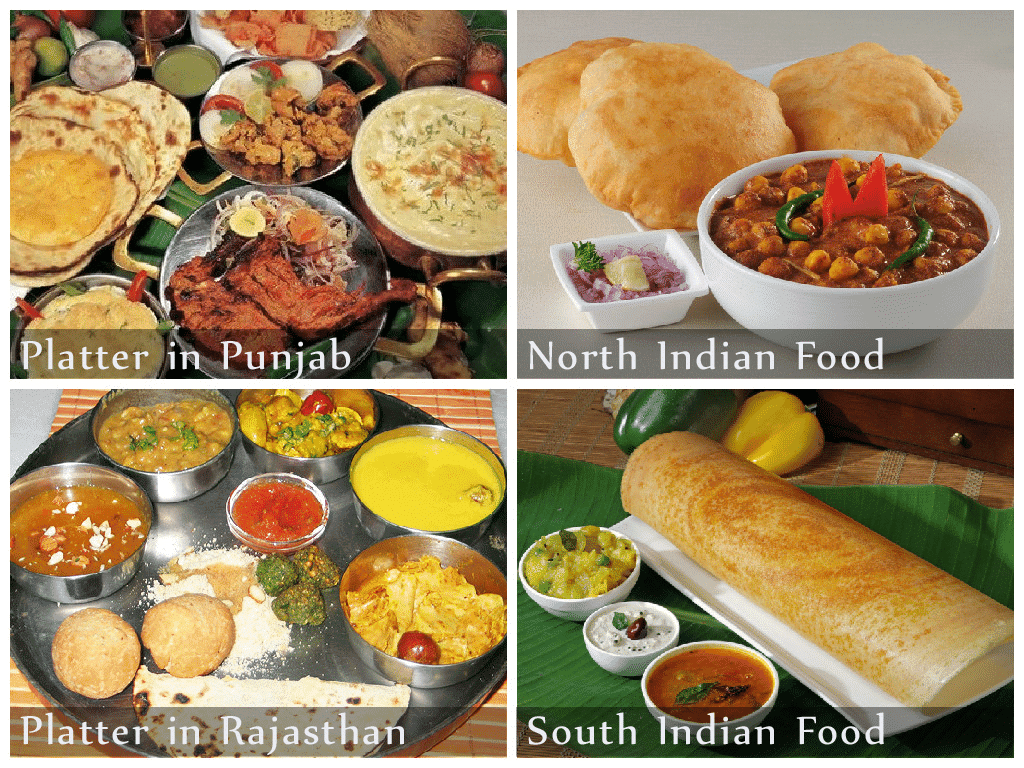 Food in different regions
Food in different regions
Traditional Food and Beverages in Different States of India:
Punjab
 Traditional Food of Punjab
Traditional Food of Punjab
- Locally Grown Crops: In Punjab, they grow crops like maize, wheat, chickpea, and pulses.
- Traditional Food Items: Some popular traditional foods in Punjab are Makki di roti (a type of bread made from maize), Sarson da saag (a curry made from mustard leaves), Chhole bhature (a spicy chickpea dish with fried bread), Parantha (stuffed flatbread), Halwa (a sweet dish), and Kheer (a sweet rice pudding).
- Beverages: Common drinks in Punjab include Lassi (a yogurt-based drink), Chhach (buttermilk), milk, and tea.
Karnataka
 Traditional food of Karnataka
Traditional food of Karnataka
- Locally Grown Crops: In Karnataka, they grow crops like rice, ragi (finger millet), urad (black gram), and coconut.
- Traditional Food Items: Traditional foods in Karnataka include Idli (steamed rice cakes), Dosa (crispy pancakes), Sambhar (a spicy lentil soup), Coconut chutney, Ragi mudde (ragi balls), Palya (vegetable stir-fry), Rasam (a tangy soup), and rice.
- Beverages: Popular drinks in Karnataka include buttermilk, coffee, and tea.
Manipur
 Food served in Manipur
Food served in Manipur
- Locally Grown Crops: In Manipur, they grow crops like rice, bamboo, and soybean.
- Traditional Food Items: Some traditional foods in Manipur are Eromba (a spicy chutney), Utti (a curry made with yellow peas and green onion), Singju (a salad), and Kangsoi (a vegetable stew).
- Beverages: A common drink in Manipur is black tea.
These examples show how different states in India have their own unique foods and drinks, which are made using the crops grown locally in their regions.
Relationship Between Traditional Food and Locally Grown Crops
- The traditional food of any state is usually made from the crops that are grown in that region.
- In India, different areas grow different crops based on their soil and climate. Because of this, the food people eat in each region is often based on what crops are available.
- This also reflects the taste preferences, culture, and traditions of the people living in that area.
How Have Cooking Practices Changed Over Time
Cooking methods have evolved significantly from traditional to modern times.
- Traditional cooking methods often involved using chulhas (clay stoves) and firewood or cow dung cakes. Grinding spices and grains was done using sil-battas (stone grinders).
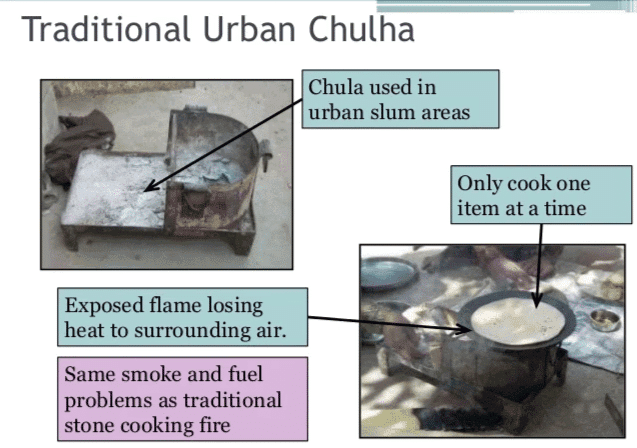 Traditional Chulha
Traditional Chulha
- Modern cooking methods have introduced gas stoves, electric grinders, microwave ovens, and induction cooktops. These advancements have made cooking more efficient and convenient.
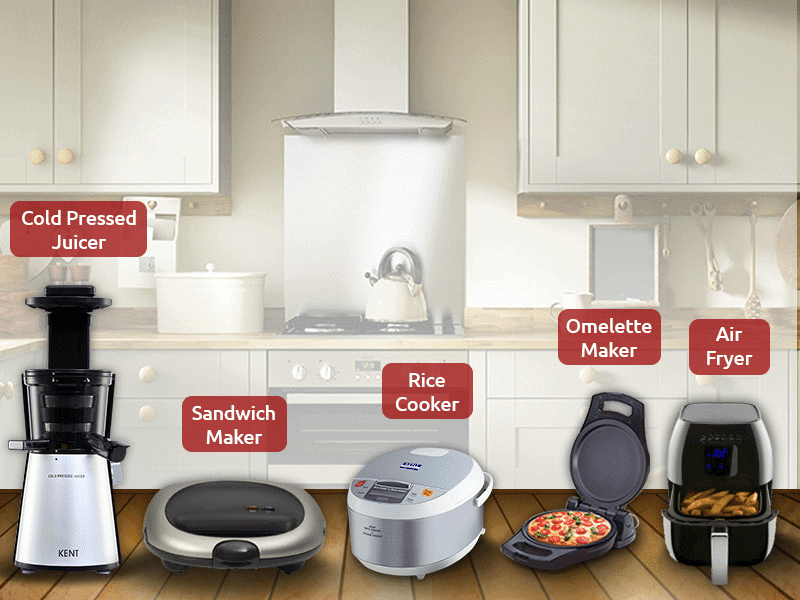 Modern cooking equipments
Modern cooking equipments
The factors driving these changes include:
- Technological Development: Innovations in kitchen appliances and cooking technology.
- Improved Transportation: Easier access to a variety of ingredients and cooking tools.
- Better Communication: Better communication allows people to easily share and learn new recipes and cooking tips from around the world.
What are the Components of Food?
The components of food are the essential nutrients that our bodies need to function properly. These include:
 Components of food
Components of food
1. Carbohydrates
Carbohydrates are the primary source of energy for our body. They are essential for performing daily activities and bodily functions.
Carbohydrates can be found in:
 Sources of carbohydrates
Sources of carbohydrates
- Cereals: Wheat, rice, maize
- Vegetables: Potato, sweet potato
- Fruits: Banana, pineapple, mango
These foods provide the necessary fuel for our muscles and brain to function efficiently.
2. Fats
Fats provide stored energy and are crucial for the absorption of vitamins. They also help in maintaining healthy skin and hair.
Sources of fats include:

- Nuts and Seeds: Almonds, sunflower seeds
- Dairy Products: Ghee, butter, curd, milk
- Oils: Olive oil, sunflower oil
While fats are essential, consuming them in moderation is important to avoid health issues like obesity and heart disease.
Why We Eat Laddoos in Winter?
 Laddoos
Laddoos
In winter, our body needs extra energy to stay warm. Laddoos are a traditional food that helps us do just that. They are made from ingredients like besan (chickpea flour) or wheat flour (aata), ghee, goond (edible gum), nuts, and seeds. These ingredients are rich in fats, which provide stored energy that keeps us warm during the cold weather.
Examples of Fats in Laddoos:
- Ghee: A type of clarified butter that is high in fat and helps keep our body warm.
- Nuts: Such as groundnuts (peanuts), walnuts, coconuts, and almonds, which are rich in healthy fats.
- Seeds: Like pumpkin seeds and sunflower seeds, which also provide fats.
These fats not only give us energy but also help our body stay warm, which is why laddoos are popular in winter.
3. Proteins
Proteins are vital for growth, repair, and maintenance of body tissues. They are the building blocks of muscles, skin, and bones.
Proteins can be obtained from:
- Plant Sources: Pulses, beans, peas, nuts
- Animal Sources: Milk, paneer, eggs, fish, meat
 Sources of Proteins
Sources of Proteins
Proteins also play a key role in producing enzymes and hormones that regulate various body functions.
Some More Information
- Polar bears: Polar bears build up a significant amount of fat beneath their skin, which acts as an energy reserve. This fat helps sustain them through their long winter sleep (hibernation), allowing them to survive without food.
- Mushrooms: They typically grow in dark and moist environments. Edible mushrooms are rich in protein.
- Scurvy: Scurvy is a disease that causes symptoms like bleeding and swollen gums. In the past, sailors on long trips often got scurvy. In 1746, Dr. James Lind found that sailors who ate lemons and oranges, which are rich in vitamin C, got better and their symptoms improved.
- Goitre: Goitre is a disease that causes swelling at the front of the neck. In the 1960s, Indian scientists noticed this problem in people from the Himalayan region and Northern plains. It was found that the soil in these areas had little iodine, which led to a lack of iodine in their food and water. To solve this, iodised salt was introduced. Eating iodised salt helped reduce the swelling and symptoms of goitre.
4. Vitamins and Minerals
Vitamins and minerals are essential nutrients that support various bodily functions. They are required in small amounts but are crucial for maintaining health.
 Vitamins and Minerals
Vitamins and Minerals
Vitamins and Minerals: Functions, Sources, Deficiency Diseases, and Symptoms
Vitamin A
- Functions: Keeps eyes and skin healthy.
- Sources: Found in foods like papaya, carrots, mangoes, and milk.
- Deficiency Disease: Loss of vision (night blindness).
- Symptoms: Poor vision, especially in the dark, and sometimes complete loss of vision.
 Night Blindness and Normal Vision
Night Blindness and Normal Vision
Vitamin B1 (Thiamine)
- Functions: Keeps the heart healthy and helps the body perform various functions.
- Sources: Found in legumes, nuts, whole grains, seeds, and milk products.
- Deficiency Disease: Beriberi.
- Symptoms: Swelling, tingling, or burning sensation in feet and hands, trouble breathing.
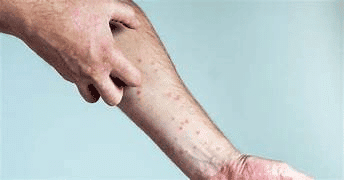 Beri Beri Symptoms
Beri Beri Symptoms
Vitamin C
- Functions: Helps the body fight diseases.
- Sources: Found in amla, guava, green chilies, oranges, and lemons.
- Deficiency Disease: Scurvy.
- Symptoms: Bleeding gums, slow healing of wounds.
 Scurvy Disease Symptoms
Scurvy Disease Symptoms
Vitamin D
- Functions: Helps the body absorb calcium for bone and teeth health.
- Sources: Found in sunlight, milk, butter, fish, and eggs.
- Deficiency Disease: Rickets.
- Symptoms: Soft and bent bones.
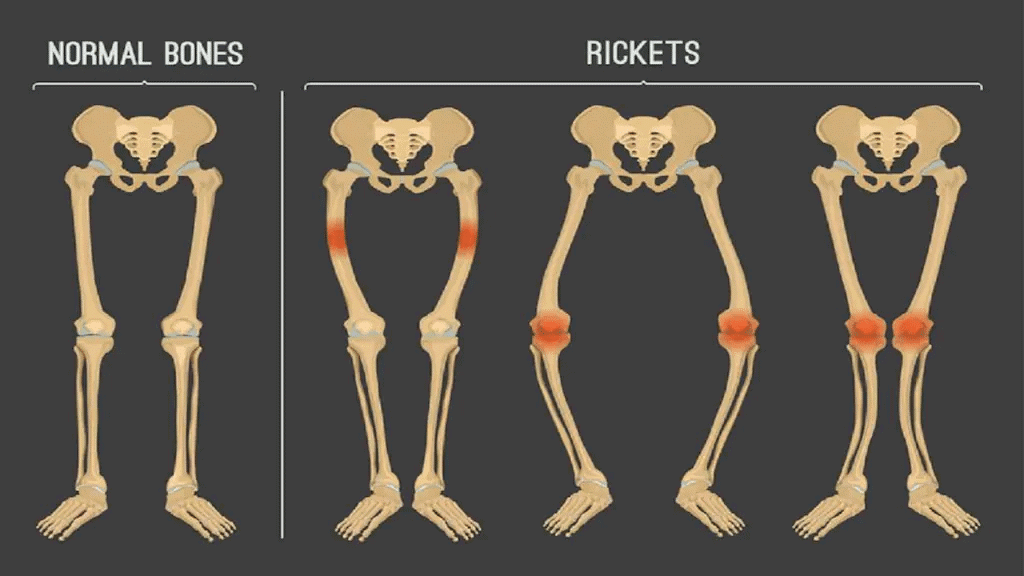 Normal Bones & Rickets
Normal Bones & Rickets
Calcium
- Functions: Keeps bones and teeth healthy.
- Sources: Found in milk, curd, cheese, and paneer.
- Deficiency Disease: Bone and tooth decay.
- Symptoms: Weak bones, tooth decay.
Iodine
- Functions: Helps the body perform physical and mental activities.
- Sources: Found in seaweed, water chestnut (singhada), and iodised salt.
- Deficiency Disease: Goitre.
- Symptoms: Swelling at the front of the neck.
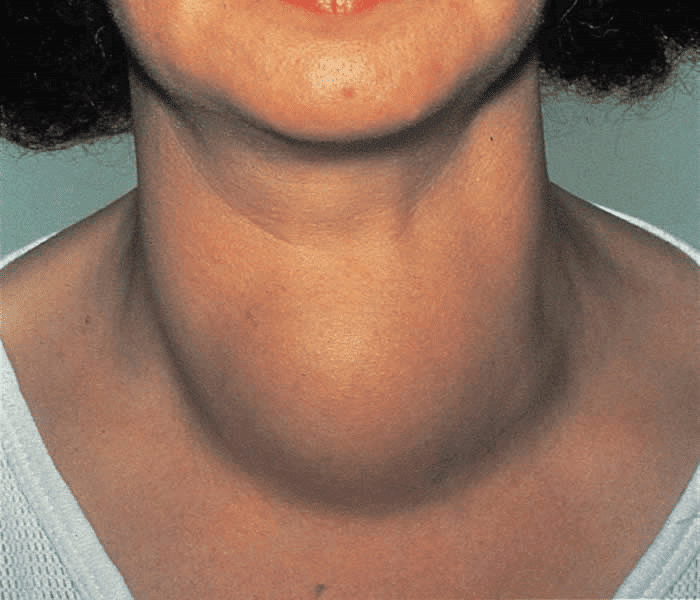 Goitre Disease Symptoms
Goitre Disease Symptoms
Iron
- Functions: Important for making blood in the body.
- Sources: Found in green leafy vegetables, beetroot, and pomegranate.
- Deficiency Disease: Anaemia.
- Symptoms: Weakness, shortness of breath.
Importance of Nutrients in Our Diet
- Nutrients are the substances in food that give us energy, help us grow, repair our body, and keep us healthy. The main nutrients we need include carbohydrates, proteins, fats, vitamins, and minerals.
- Vitamins and minerals are special nutrients known as protective nutrients because they protect our body from diseases and keep us healthy. Foods like milk, green vegetables, fruits, and whole grains are good sources of these important nutrients. Even though we only need small amounts of vitamins and minerals, they are essential for our health.
- When we cook vegetables, you might notice that they sometimes lose their bright color or become softer. This happens because some nutrients, like vitamin C, can be lost when exposed to high heat. That's why it’s a good idea to also eat fruits and raw vegetables as part of our diet. However, it's important to wash all fruits and vegetables thoroughly before eating them to ensure they are clean and safe.
5. Dietary Fibres
Dietary fibres are essential for digestion and excretion. They help in maintaining a healthy digestive system by promoting regular bowel movements.
Sources of dietary fibres include:
- Green Leafy Vegetables: Spinach, kale
- Fresh Fruits: Apples, oranges, berries
- Whole Grains: Brown rice, oats
- Pulses and Nuts: Lentils, almonds
6. Water
Water is vital for all bodily functions. It helps absorb nutrients and remove waste from the body. Drinking adequate water daily is essential to stay hydrated and maintain bodily functions.
How to Test Different Components of Food?
1. Test for Starch

- To test for starch in food, an iodine solution can be used.
- When iodine is added to a food sample, a blue-black colour indicates the presence of starch.
- This is a simple way to identify foods that are rich in carbohydrates.
2. Test for Fats

- To test for fats, place a food sample on a piece of paper and press it.
- If an oily patch appears, it indicates the presence of fats.
- This test helps in identifying foods that contain significant amounts of fat.
3. Test for Proteins

- To test for proteins, a mixture of copper sulphate and caustic soda solutions is used.
- A violet colour in the mixture indicates the presence of proteins.
- This test is useful for identifying foods that are rich in protein.
Balanced Diet
A balanced diet is a way of eating that gives your body all the nutrients it needs to work properly. This means eating a variety of foods in the right amounts.
Importance of a Balanced Diet
A balanced diet includes all essential nutrients in the right proportions. It ensures proper growth, development, and maintenance of the body.
A balanced diet should include:
- Carbohydrates: For energy
- Proteins: For growth and repair
- Fats: For energy and vitamin absorption
- Vitamins and Minerals: For overall health
- Dietary Fibres: For digestion
- Water: For hydration
It is important to adjust your diet to make sure all these nutrients are included.
Millets: Nutrition-rich Cereals
Millets are highly nutritious and easy to cultivate. They are rich in vitamins, minerals, and dietary fibres, making them an important part of a healthy diet.
 MilletsExamples of millets include:
MilletsExamples of millets include:
- Jowar (Sorghum)
- Bajra (Pearl Millet)
- Ragi (Finger Millet)
- Sanwa (Barnyard Millet)
Millets are beneficial for health as they help in managing diabetes, improving digestion, and reducing the risk of heart diseases.
Food Miles: From Farm to Our Plate
Food Miles: This term refers to the distance food travels from its source to the consumer. For instance, locally grown apples have fewer food miles than imported ones.
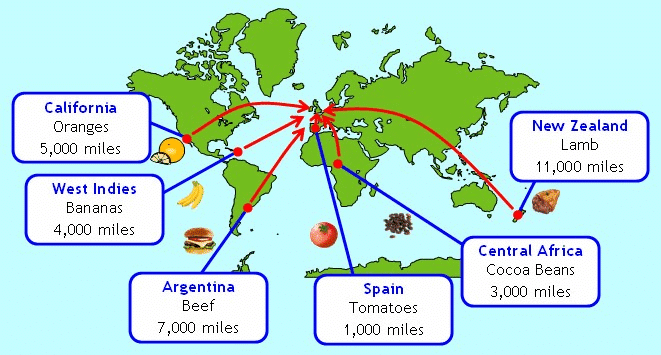 Food Miles
Food Miles
- Reducing Food Miles: We can reduce food miles by choosing locally grown produce and prevent food waste by taking only what we can eat. By reducing food miles, we can support local agriculture, reduce carbon footprint, ensure fresher and more nutritious food.
- Diet Variety: The variety in diets highlights the unique foods consumed in different regions, such as bananas in tropical areas and potatoes in colder climates.
Keywords
- Carbohydrate: Primary source of energy.
- Culinary practices: Methods of cooking and preparing food.
- Deficiency diseases: Health problems caused by a lack of essential nutrients.
- Fats: Provide stored energy and aid in vitamin absorption.
- Food components: Essential nutrients in food.
- Food miles: Distance food travels from farm to consumer.
- Minerals: Essential nutrients for various bodily functions.
- Nutrients: Substances that provide nourishment.
- Millets: Nutritious cereals like jowar, bajra, ragi.
- Proteins: Essential for growth and repair.
- Roughage: Dietary fibres that aid digestion.
- Vitamins: Essential nutrients for various bodily functions.
- Iodized salt: Salt fortified with iodine to prevent deficiency diseases.
|
100 videos|261 docs|49 tests
|
FAQs on Mindful Eating: A Path to a Healthy Body Chapter Notes - Science Class 6
| 1. What is a balanced diet and why is it important? |  |
| 2. How have cooking practices evolved over time? |  |
| 3. What are millets and why are they considered nutrition-rich? |  |
| 4. What are food miles and why do they matter? |  |
| 5. How can we test different components of food? |  |

|
Explore Courses for Class 6 exam
|

|

















