Class 6 Exam > Class 6 Notes > Chapter Notes For Class 6 > Chapter Notes: India's Cultural Roots
India's Cultural Roots Chapter Notes | Chapter Notes For Class 6 PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| The Richness of Indian Culture |

|
| The Vedas and Vedic Culture |

|
| Folk and Tribal Roots |

|
| Conclusion |

|
The Richness of Indian Culture
Indian culture is very old and has a rich history, like a vast tree with deep roots and strong branches. The roots represent shared traditions, while the branches include art, literature, science, medicine, religion, governance, and martial arts. These diverse aspects stem from a common foundation.Indian culture also includes many "schools of thought," groups that share similar views on life. Experts believe it began with the Indus Valley civilization, and over time, various ideas developed, making India's heritage, or Bharat, even more unique.
The Vedas and Vedic Culture
The Vedas are very old and important books from India, full of hymns, prayers, and teachings. They are some of the oldest books in the world and show us what life was like in ancient India. The Vedas were passed down orally for many years before being written down. They include not only religious rituals but also ideas about life, society, and the universe. The culture that developed from these teachings, called Vedic culture, has influenced many beliefs and traditions in India even today.

A. What are the Vedas?
- The Vedas are ancient texts from India, considered the oldest in the country and among the oldest in the world.
- There are four Vedas : Rig Veda, Yajur Veda, Sāma Veda, and Atharva Veda.
- The word "Veda" comes from the Sanskrit word "vid," meaning "knowledge."
- The Vedas contain thousands of hymns, which are prayers written in the form of poems and songs.

- These hymns were not written down but were recited orally, passed down through generations.
- The hymns were composed in the Sapta Sindhava region, an area in ancient India.
- The Rig Veda, the oldest of the four Vedas, was composed a long time ago, but experts disagree on the exact date.
- Some experts think it was written between the 5th and 2nd millennium BCE, which is a very long time ago.
- The Vedas were passed down orally for many generations, between 100 and 200, with very few changes.
Who wrote the Vedic hymns?
- The hymns were composed by rishis (male sages) and rishikas (female sages) in an early form of Sanskrit, an ancient Indian language.
- These sages addressed various deities (gods and goddesses) in their poems, such as Indra, Agni, Varuna, Mitra, Sarasvati, and Ushas.
- The rishis and rishikas saw these deities as different names for the same supreme reality. As one famous hymn puts it.

What was important in the Vedic worldview?
- In the Vedic worldview, "Truth" was very important and was often considered another name for God.
- The Rig Veda also emphasizes the importance of unity among people, encouraging them to come together, speak together, and share a common purpose.
- For example, one verse from the Rig Veda says,

UNESCO Recognition of Vedic Chanting (2008)
- Vedic chanting was acknowledged by UNESCO in 2008 as a significant part of humanity's oral and intangible heritage.
- This recognition was due to the careful transmission of Vedic chanting over thousands of years.
Let's Revise: Who composed the Vedic hymns, and what themes did they explore?
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: The hymns were composed by male and female sages known as rishis and rishikas. They addressed deities like Indra, Agni, and Sarasvati, and reflected themes of devotion, truth, and unity.
B. Vedic society
- The early Vedic society was made up of different janas or clans, which were large groups of people. The Rig Veda mentions over 30 such clans, including the Bharatas, Purus, Kurus, Yadus, and Turvaéhas. Each clan was linked to a specific area in the northwestern part of the Indian subcontinent.
- There is limited information about how these clans were governed. The Vedas offer some insights with terms like rājā (meaning king or ruler), sabhā, and samiti, which refer to gatherings or assemblies of people.
- The Vedic texts also mention various jobs, including agriculturist (farmer), weaver, potter, builder, carpenter, healer, dancer, barber, and priest.
Core Values
- In this worldview, certain values were particularly significant, starting with 'Truth', which was often regarded as another name for God.
- The final verses of the Rig Veda also urge unity among people:
Come together, speak together; common be your mind, may your thoughts agree... United be your purpose, united your heart... may your thoughts be united, so all may agree!
Let's Revise: What were janas in early Vedic society, and can you name some of them?
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: Janas were large clans or groups of people in early Vedic society. Some of the clans mentioned in the Rig Veda include the Bharatas, Purus, Kurus, Yadus, and Turvaśas.
C. Vedic schools of thought

- Vedic culture developed various rituals called yajna, often pronounced as 'yagya,' aimed at different deities for personal or community benefits.
- Daily rituals typically included prayers and offerings to Agni, the fire deity, but they became increasingly intricate over time.
- A collection of texts known as the Upanishads expanded on Vedic ideas, introducing concepts like rebirth (the cycle of being born again) and karma (the principle of cause and effect in actions).
- From a philosophical viewpoint called Vedanta, everything—human life, nature, and the universe—is viewed as one divine essence called brahman (not to be confused with the god Brahma) or simply tat ('that').
- Two well-known mantras express this idea:

Let's Revise: What are yajnas, and what role did they play in Vedic culture?
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: Yajnas, or rituals, were offerings made to various deities in Vedic culture for personal or community benefit. They often involved fire sacrifices and prayers to gods like Agni.
Concept of Atman
- The Upanishads introduced the idea of atman or Self, which is the divine essence within every being, ultimately one with brahman.
- This concept suggests that all things in the world are interconnected and dependent on one another.
- A common prayer reflecting this idea begins with sarve bhavantu sukhinah, meaning "May all creatures be happy."
- It continues with wishes for freedom from disease and sorrow.
Birth of New Philosophical Schools
- In the early 1st millennium BCE, various philosophical schools arose from the Vedas, including Yoga.
- Yoga developed practices aimed at realising brahman in one's consciousness.
- These diverse schools of thought collectively formed the foundation of what we now call Hinduism.
- For instance, the 'Chārvāka' school (also known as ‘Lokāyata’) claimed that the material world is the only reality, denying life after death.
- While the Vedic, Buddhist, and Jain schools had significant differences, they also shared essential concepts like dharma, karma, rebirth, and the quest to end suffering and ignorance, along with many important values.
Many archaeologists and scholars suggest that some aspects of India's cultural roots trace back to the Indus or Harappan or Sindhu-Sarasvatī civilisation.
Let's Revise: What was the main belief of the Chārvāka or Lokāyata school?
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: The Chārvāka school believed that only the material world is real and denied life after death, focusing purely on physical existence.
Buddhism
Can we be certain about the exact year of Siddhārtha Gautama's birth?
We don’t know the exact year Siddhārtha Gautama was born. In Chapter 4, we chose 560 BCE as an approximate year.

The Life of Siddhartha Gautama: From Prince to the Buddha
- About 2,500 years ago, a young prince named Siddhārtha Gautama was born in Lumbini, now in Nepal. Lumbini is a UNESCO World Heritage site, showing its importance.
- He grew up in a very sheltered environment in the palace. At 29 years old, he ventured into the city for the first time. During this trip, he encountered an old man, a sick man, and a dead body. He also met an ascetic who seemed happy and peaceful.
- These experiences led Siddhārtha to leave his royal life and family. He wandered as an ascetic, meeting others and seeking the root cause of human suffering.
- After meditating for many days under a pipal tree in Bodh Gaya (now in Bihar), known as the "Bodhi Tree," he achieved enlightenment; he realized that avidyā (ignorance) and attachment are the sources of suffering and developed a way to overcome these issues.
- He became known as the 'Buddha', meaning the 'enlightened' or 'awakened' one.
- The Buddha began teaching his insights, including the principle of ahimsa, which is often translated as 'non-violence', but originally means 'non-hurting' or 'non-injuring'.
- He founded the Sangha, a community of bhikṣus (monks) and later bhikṣunīs (nuns) dedicated to practicing and spreading his teachings, highlighting the significance of this community in preserving and sharing the Buddha's insights.
- His teachings have significantly influenced the spiritual landscape of Asia.
The following saying of the Buddha expresses the importance of inner discipline:
“Not by water is one made pure, though many people may bathe here [in sacred rivers]. But one is pure in whom truth and dharma reside. Conquering oneself is greater than conquering a thousand men on the battlefield a thousand times.”
Let's Revise: What is the Sangha, and why is it important?
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: The Sangha is the community of monks (bhikṣus) and nuns (bhikṣunīs) established by the Buddha. It plays a vital role in preserving and spreading his teachings.
Stories from the Upanishads about Asking Questions
The Upanishads are ancient Indian texts that teach us important lessons about life and knowledge. One of the key lessons is that asking questions is essential to learning and understanding the truth, no matter who you are. Here are three stories from the Upanishads that show the importance of asking questions:
Shvetaketu and the Seed of Reality (Chhāndogya Upanishad)
The Upanishads, ancient Indian texts, highlight the significance of asking questions, no matter who is asking—men, women, or children.
- Rishi Uddālaka Āruṇi sent his son, Shvetaketu, to a gurukula to study the Vedas. Upon returning after 12 years, Uddālaka noticed Shvetaketu had become quite proud of his knowledge. To test him, Uddālaka asked questions about the nature of brahman, which Shvetaketu could not answer.
- Uddālaka explained that brahman, although unseen, is present everywhere. He provided examples:
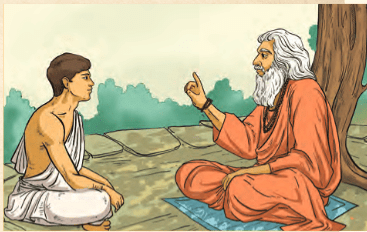 Banyan Seed: Just like a seemingly empty banyan seed holds the future banyan tree, brahman is the essence behind all things.
Banyan Seed: Just like a seemingly empty banyan seed holds the future banyan tree, brahman is the essence behind all things.
Clay Pots: Different pots made from the same clay illustrate that everything around us arises from this same essence—brahman. - Uddālaka concluded by stating, "You are That, Shvetaketu," stressing the link between Shvetaketu and Brahman.
Nachiketa and His Quest (Katha Upanishad)
- Once, a man was giving away all his possessions in a ritual. As his son Nachiketa repeatedly asked which god he would be offered to, the father became angry and replied, "I give you to Yama"—the god of death.
- Nachiketa then made his way to Yama's realm and, after a long wait, met the powerful god. His main question was about what occurs after the body dies.
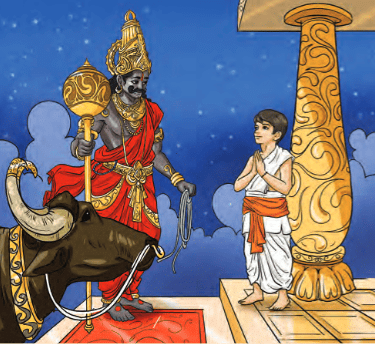
- Yama initially tried to dodge Nachiketa's question, but he persisted. Pleased with his resolve, Yama revealed that the ātman, or self, is hidden within all living beings. It is neither born nor dies; it is immortal.
- With this profound knowledge, Nachiketa returned to his father, who welcomed him with joy.
The Debate of Gārgi and Yājñavalkya (Brihadāraṇyaka Upanishad)
- Once, wise king Janaka announced a prize for the winner of a philosophical debate. Yājñavalkya, a well-known rishi, came to the king's court and defeated many scholars.
- When Gārgi, a rishika, asked him a series of questions about the world and finally about brahman, Yājñavalkya asked her to cease her inquiries.
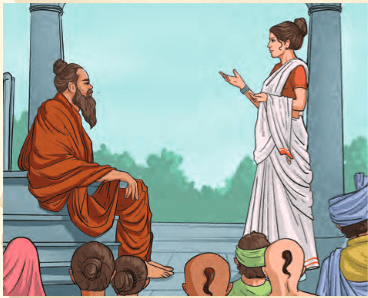
- Later, Gārgi continued her questioning, and Yājñavalkya explained that brahman is the force behind the world, seasons, rivers, and everything else.
Question for Chapter Notes: India's Cultural RootsTry yourself:What is the concept highlighted in the stories from the Upanishads?
View Solution
Jainism
Can we say that Jainism is believed to have much older origins than Buddhism?
Yes, Jainism is thought to have roots that go back further than Buddhism, even though both religions became well-known around the same period.

The Origin
- Jainism is a very old religion. It became popular at the same time as Buddhism but is believed to be even older.
- A prince named Vardhamana, just like Buddha, was born in a royal family in the 6th century BCE.
He was born near Vaishali (in Bihar, India). - When he turned 30 years old, he left his home to find true knowledge.
He lived a very simple and strict life. After 12 years, he gained infinite knowledge (very deep understanding).
People started calling him Mahavira, which means "great hero." He then began teaching others.
Main Teachings of Jainism:
Ahimsa (Non-violence):
We should never hurt any living being, not even small insects.
Mahavira said that all living creatures must be treated kindly.Anekantavada (Many-sided truth):
There are many sides to truth. No one can know everything with just one view.Aparigraha (Non-possessiveness):
We should not collect too many things. Just keep what we need in life.
Spreading the Teachings:
- Like Buddhist monks and nuns, Jain monks and nuns also traveled to teach people.
- Some lived in caves and slept on stone beds.
- Archaeologists found old caves with names of monks carved in them.
Other Beliefs at That Time:
- There were also other groups, like the Charvaka or Lokayata school, who believed in only the things we can see and feel.
- They thought there was no life after death.
- However, this belief did not become popular and slowly faded away.
Similar Ideas in Vedic, Buddhist, and Jain Beliefs:
Even though they were different, these three had some common thoughts:
Dharma: Doing what is right.
Karma: Our actions have results.
Rebirth: We are born again after death.
Ending suffering: All aimed to stop pain and ignorance.
These shared ideas are like the main trunk of a tree, with each religion growing like different branches.
Meaning of 'Jain' or 'Jaina'
- The term 'Jain' or 'jaina' comes from 'jina', which means 'conqueror.'
- However, this conquest does not refer to taking over land or defeating enemies. Instead, it means overcoming ignorance and attachments to reach enlightenment.

Buddhist and Jain Stories with Important Lessons
Buddhist and Jain stories teach us important lessons about how to live a good life. These stories show the value of kindness, doing the right thing, and changing for the better. The Buddha and Mahavira, the founders of Buddhism and Jainism, shared these lessons through simple stories. Here are two stories that teach us about helping others and making good choices in life.
The Jataka Tale of the Monkey King
- The Jataka tales have entertained both children and adults in India for ages, telling stories of the Buddha's previous lives and teaching Buddhist values in an easy way.
- In a well-known tale, the Buddha was the leader of a large group of monkeys.
- These monkeys lived near a magnificent tree that produced delicious and fragrant fruit.
- One day, despite the monkey-king's orders to protect all the fruit, a ripe fruit fell into the stream below.
- The current carried the fruit away, where it got caught in a net and was taken to the palace.
- The king tasted the fruit and was so impressed by its flavour that he sent his soldiers to find the tree it came from.
- After searching for a long time, the soldiers discovered the tree and saw the monkeys enjoying the fruit.
- The soldiers attacked the monkeys.
- The monkey-king realised that the only way to save his troop was to help them cross the stream, but they couldn't do it alone.
- Being much bigger, the monkey-king held onto a tree on the opposite bank, allowing his body to be used as a bridge, even though he was badly hurt and eventually died.
- The king, observing from afar, was deeply touched by the monkey-king's selfless sacrifice and reflected on a king's duty to his subjects.

A Jain Story of Transformation
- Rohineya was an exceptionally skilled thief who managed to avoid capture. While on his way to a city, he accidentally overheard part of a sermon by Mahavira about attaining freedom from a life of ignorance.
- When he reached the city, Rohineya was recognised and arrested. He pretended to be a simple farmer.
- A minister came up with a clever plan to make Rohineya reveal his true identity. However, Rohineya, recalling Mahavira's teachings, was able to see through the minister's trick and evade it.
- Feeling guilty, Rohineya approached Mahavira, admitted his wrongdoings, returned the stolen items, and sought forgiveness. He then became a monk, recognised the illusion he had been living in, and focused on gaining deeper understanding.
- This tale highlights the significance of right actions and thoughts, and it underscores that everyone deserves a second chance.

Question for Chapter Notes: India's Cultural RootsTry yourself:Which concept is common to both Buddhism and Jainism?
View Solution
Folk and Tribal Roots
Can India's cultural roots be traced through oral traditions and texts like the Vedas?Yes, India's cultural roots are well-documented in texts like the Vedas and have a rich history of oral traditions passed down through everyday practices.

The Interaction Between Tribal, Folk, and Hindu Traditions in India's Cultural Evolution:
- India's cultural roots are well-documented in texts and have a rich history of oral traditions, where teachings and practices were shared through everyday life without written texts, as seen in the case of the Vedas.
- Among these traditions are folk traditions, passed on by common people, and tribal traditions, shared by tribes.
- There has been a constant interaction between folk and tribal traditions, and the leading schools of thought mentioned in this chapter. Deities, concepts, legends, and rituals have been exchanged in both directions.
- For example, Jagannath, worshipped in Puri (Odisha), was originally a tribal deity; this also applies to various forms of the mother goddess worshipped across India. Some tribes have long adopted Hindu deities and possess their versions of the Mahabharata and Ramayana, as noted from India's north-eastern states to Tamil Nadu.
- This long interaction has resulted in mutual enrichment. Folk and tribal beliefs and practices also contribute to India's cultural roots.
What is a tribe?
- Definition: A tribe is considered a group of families or clans with a shared tradition of common descent, culture, and language. They live closely under a chief and do not own private property.
- Historical Context: Interestingly, ancient India did not have a specific word for 'tribe.' Tribes were seen as different janas (social groups) adapted to specific environments like forests or mountains.
- Modern Usage: The Indian Constitution uses the terms 'tribes' and 'tribal communities' in English, and janjati in Hindi.
- Population: According to the 2011 census, India had 705 tribes with a population of about 104 million people, which is greater than the combined populations of Australia and the United Kingdom.
- Anthropological Views: In the 19th century, tribes were often viewed as 'primitive' or 'inferior' by anthropologists. However, with more research into the rich and complex cultures of tribal communities, these biased views have largely been discarded.
Conclusion
- The Vedas are the oldest texts in India, comprising four main texts: the Rig Veda, the Yajur Veda, the Sāma Veda, and the Atharva Veda.
- They are among the most ancient texts worldwide and have inspired various philosophical schools, including Vedanta and Yoga.
- While Buddhism and Jainism moved away from Vedic authority, they focused on specific values and practices.
- Despite differing principles and methods, these schools shared common ideas, such as exploring the reasons for suffering and how to eliminate ignorance.
Question for Chapter Notes: India's Cultural RootsTry yourself:What is the meaning of the term 'Jain' or 'Jaina'?
View Solution
Key Words
- Spiritual: Related to the spirit or soul (ātman in Sanskrit and many Indian languages). Spirituality involves seeking a deeper meaning beyond our everyday selves.
- Seeker: A person who looks for the truths of life, such as a sage, saint, yogi, or philosopher.
- UNESCO: This stands for 'United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization', which encourages dialogue between people and nations through education, science, and culture.
- Cosmos: Refers to the universe as a well-organised and harmonious system.
- Worldview: A specific understanding or perspective on the world, including its origins and functions.
- Healer: Someone who uses traditional methods to help cure or relieve illnesses.
- Consciousness: The state of being aware, especially of one's own thoughts and feelings.
- Ascetic: A person who practices strict self-discipline to reach a higher state of awareness.
- Attachment: The emotional bond one has with someone or something, often due to feelings or habits.
- Monk: A man who leaves regular life to focus on religious or spiritual goals, usually following strict rules.
- Nun: The female counterpart of a monk.
- Interdependence: The idea that everything is connected and relies on each other, a key concept in Upanishadic teachings.
- Common Prayer: A well-known prayer that starts with "sarve bhavantu sukhinah", wishing happiness and freedom from suffering for all beings.
- Foundations of Hinduism: The philosophical schools that emerged from the Vedas, forming the basis of what we now call 'Hinduism'.
- Buddhism and the Buddha's Teachings: Siddhartha became the 'Buddha' and shared important ideas like ahimsa (non-violence) and self-discipline.
The document India's Cultural Roots Chapter Notes | Chapter Notes For Class 6 is a part of the Class 6 Course Chapter Notes For Class 6.
All you need of Class 6 at this link: Class 6
FAQs on India's Cultural Roots Chapter Notes - Chapter Notes For Class 6
| 1. What are the main components of Vedic culture? |  |
Ans.Vedic culture primarily comprises the texts of the Vedas, which are ancient scriptures that include hymns, rituals, and philosophical discussions. It also encompasses the practices, beliefs, and social structures that evolved in ancient India, such as the caste system, rituals, and the importance of dharma (duty).
| 2. How do folk and tribal roots contribute to India's cultural diversity? |  |
Ans.Folk and tribal roots play a significant role in India's cultural diversity by preserving unique traditions, languages, and art forms. These communities often have their own customs, music, and dance, which enrich the broader tapestry of Indian culture and showcase the country’s regional variations.
| 3. What is the significance of the Vedas in understanding Indian history? |  |
Ans.The Vedas are crucial for understanding Indian history as they provide insights into the early societal norms, religious practices, and philosophical thought of ancient India. They reflect the socio-political dynamics of the time and serve as primary sources for historians studying the evolution of Indian civilization.
| 4. How did Vedic culture influence later Indian religions? |  |
Ans.Vedic culture laid the foundation for many later Indian religions, particularly Hinduism. Key concepts such as karma, samsara (cycle of rebirth), and moksha (liberation) have their roots in Vedic texts. Additionally, the rituals and practices from the Vedic period were adapted and evolved in various religious traditions that followed.
| 5. What are some examples of folk traditions that are influenced by Vedic culture? |  |
Ans.Examples of folk traditions influenced by Vedic culture include various regional dance forms, music, and festivals that incorporate Vedic themes and deities. For instance, the celebration of Diwali in many parts of India has its roots in Vedic rituals, and folk songs often reference Vedic mythology and teachings.
Related Searches






















