Internet and it's Services | Computer Awareness and Proficiency - SSC CGL PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| History of the Internet |

|
| Internet Connections |

|
| Interconnecting Protocols |

|
| Terms Related to the Internet |

|
| Internet Services |

|
| Common Social Networking Sites |

|
| Video-Conferencing Apps |

|
The Internet is a global network of interconnected computers that can exchange information. The term "Internet" stands for International Network, and its origins trace back to the 1950s with Vint Cerf, often referred to as the Father of the Internet. It is a "network of networks" comprising millions of private and public networks ranging from local to global. Essentially, a network is a group of two or more computer systems linked together.
History of the Internet

- In 1969, the University of California at Los Angeles and the University of Utah were connected, marking the beginning of ARPANET (Advanced Research Projects Agency Network) using 50 kbps circuits.
- This was the world's first operational packet-switching network, aiming to connect computers at different universities and U.S. defense facilities.
- In the mid-1980s, the National Science Foundation created NSFnet, a high-capacity network that surpassed ARPANET.
- However, NSFnet restricted its use to academic research, excluding private business activities.
- Consequently, private organizations and individuals developed their own networks, which were later interconnected with ARPANET and NSFnet to form the Internet.
Advantages of the Internet
- Facilitates easy communication with others.
- Has a global reach, enabling connections with anyone online.
- Saves paper by allowing document publication online.
- Provides a valuable resource for companies to advertise and conduct business.
- Grants greater access to information, thereby reducing research time.
Disadvantages of the Internet
- A major source of computer viruses.
- Messages sent over the Internet can be intercepted and misused.
- Much of the information available may be unchecked, incorrect, or irrelevant.
- Contains unsuitable and undesirable material, sometimes used by malicious individuals like terrorists.
- Cyber frauds involving credit/debit card details can occur.
Internet Connections
 Bandwidth and cost are key factors in choosing an Internet connection, as speed depends on bandwidth. Various types of Internet connections include:
Bandwidth and cost are key factors in choosing an Internet connection, as speed depends on bandwidth. Various types of Internet connections include:
Dial-Up Connection
- This method uses an existing telephone line to connect to the Internet.
- The modem dials an ISP's phone number to establish a connection, typically taking about ten seconds and producing several beeping and buzzing sounds.
- Its transfer speed is 56 kbps.
Broadband Connection
Broadband refers to high-speed Internet access that is always on and faster than traditional dial-up. It uses telephone lines and includes several technologies:
- Digital Subscriber Line (DSL): Provides Internet access by transmitting digital data over local telephone network wires with a transfer speed of 256 kbps.
- Cable Modem: Uses the same coaxial cables as TV services, offering transmission speeds of 1.5 Mbps or more.
- Broadband over Power Line (BPL): Delivers broadband via existing electric power distribution networks with speeds up to 3 Mbps, suitable for rural areas with power infrastructure but no other broadband options.
Wireless Connection
Wireless broadband uses a radio link between the customer and the service provider. It does not require modems or cables, making it feasible in areas where DSL or cable deployment is challenging. Methods of wireless connection include:
- Wireless Fidelity (Wi-Fi): A universal wireless networking technology using radio frequencies to transfer data. It allows high-speed Internet connections in public places like restaurants, coffee shops, hotels, airports, convention centers, and parks.
- Worldwide Interoperability for Microwave Access (WiMAX): Delivers broadband access to residential and enterprise customers, even in areas difficult for wired infrastructure to reach.
- Mobile Wireless Broadband Services: Offered by mobile phone service providers, these services require a special PC card with a built-in antenna and provide lower speeds of several hundred kbps.
Intranet, Extranet and Podcast
- Intranet: A private network using Internet tools but available only within an organization, facilitating easy access to corporate information for employees.
- Extranet: A private network using Internet protocols and public telecommunication systems to securely share part of a business's information.
- Podcast: A podcast is a form of audio broadcasting on the web, which can be listened to on the go, while commuting, or even while working.
Interconnecting Protocols
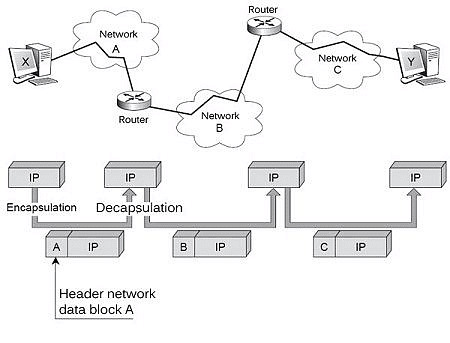
A protocol is a set of rules governing data communications, defining what, how, and when information is communicated. Some commonly used Internet protocols include:
Transmission Control Protocol/Internet Protocol (TCP/IP):
- Transmission Control Protocol (TCP): Ensures reliable transport service by properly routing messages from sender to receiver. TCP converts messages into packets at the source and reassembles them at the destination.
- Internet Protocol (IP): Enables different computers to communicate by creating a network of networks, handling the dispatch of packets, and maintaining their addresses. Each IP packet contains source and destination addresses.
Note: An IP address is a 32-bit number.
File Transfer Protocol (FTP): Transfers files between any computers with an Internet connection, even those with different operating systems. Examples of FTP software include FileZilla, Kasablanca, gFTP, and Konqueror.
HyperText Transfer Protocol (HTTP): Defines how messages are formatted and transmitted, and what actions Web servers and browsers should take in response to various commands.
- HyperText Markup Language (HTML): Used to design Web pages with markup tags that instruct the Web browser on how to display text and images. Each markup code is called an element or tag.
Telnet Protocol: A program that connects a PC to a server on the network, starting a session by entering a valid username and password.
Usenet Protocol: Allows a group of Internet users to exchange views, ideas, and information on common topics through newsgroups. Usenet has no central server or administration.
Point-to-Point Protocol (PPP): A dial-up connection that puts a computer directly on the Internet, requiring a modem that transmits data at 9600 bits per second.
Simple Mail Transfer Protocol (SMTP): The standard protocol for email services on a TCP/IP network, enabling the sending and receiving of email messages.
Wireless Application Protocol (WAP): A Web browser commonly used for small mobile devices like cell phones.
Voice over Internet Protocol (VoIP): Delivers voice communication over IP networks, such as IP calls.
Post Office Protocol version 3 (POP3): An Internet standard protocol used by local email clients to retrieve emails from a remote mail server over a TCP/IP connection.
Terms Related to the Internet
World Wide Web (WWW): A system of Internet servers that supports hypertext and multimedia to access various Internet protocols on a single interface. Introduced on March 13, 1989, the Web facilitates information exchange between computers on the Internet.
Web Page:
- The backbone of the WWW, containing information and links to text and multimedia resources throughout the Internet. Created using HTML, web pages can be static or dynamic.
- The main page of a website is known as the home page.
- Note: Bookmarks are links to web pages for easy access. A hyperlink is a piece of text connecting different documents on a web page.
Website: A collection of web pages following the same theme and connected with hyperlinks, existing under the same domain.
Web Browser: A software application used to locate, retrieve, and display content on the WWW. Web browsers can navigate files, folders, and websites, with the ability to install multiple browsers on a single computer.
Note: The F11 key on a Windows keyboard sets the browser to full-screen mode.
Types of Web browsers:
- Text Web Browser: Displays only text-based information (e.g., Lynx).
- Graphical Web Browser: Supports both text and graphic information (e.g., Internet Explorer, Firefox, Netscape, Safari, Google Chrome, Opera).
Note: The first graphical web browser was NCSA Mosaic.
Web Server: A
- A computer that runs websites, delivering web pages to requesting computers.
- Each web server connected to the Internet has a unique IP address.
- Examples include Apache HTTP Server, Internet Information Services (IIS), and Lighttpd.
- Note: A cookie is a small message given to a web browser by a web server, storing information about the user’s web activity.
Web Address and URL: A web address identifies the location of a specific web page on the Internet, also known as a URL (Uniform Resource Locator). Tim Berners-Lee created the first URL in 1991. For example,
http:// — Protocol identifier
www — World Wide Web
google.com — Domain name
/services/ — Directory
index.htm — Web page
Domain Name: Identifies and locates computers on the Internet, consisting of two or more parts separated by periods (e.g., google.com, yahoo.com).
- Domain Abbreviation: Indicates the type of organization and the country.
- Common abbreviations: .info (Informational), .com (Commercial), .gov (Government), .edu (Educational), .mil (Military), .net (Network resources), .org (Non-profit organization).
- Country abbreviations: .in (India), .au (Australia), .fr (France), .nz (New Zealand), .uk (United Kingdom).
Domain Name System (DNS): Translates domain names to IP addresses and lists mail exchange servers for each domain. DNS is essential for contemporary Internet use.
Blog: A website or web page where individuals regularly record opinions and link to other sites. Blogs often combine text, images, and links related to their topics, with entries known as posts.
Newsgroup: An online discussion forum accessible through Usenet, devoted to specific topics. Allows interaction via bulletin boards and chat sessions.
Search Engine: A website that provides data on specific topics, turning the web into a powerful tool for finding information. Popular search engines include Google, AltaVista, Yahoo, Hotbot, Lycos, Excite, and WebCrawler.
- Note: Project Loon is a Google initiative providing internet access to rural and remote areas using high-altitude helium-filled balloons.
Internet Services
 Internet users have access to a wide variety of services, including email, file transfer, interest group membership, multimedia displays, real-time broadcasting, and shopping. Some of the important services provided by the Internet are:
Internet users have access to a wide variety of services, including email, file transfer, interest group membership, multimedia displays, real-time broadcasting, and shopping. Some of the important services provided by the Internet are:
Chatting
Chatting is the online exchange of text or multimedia messages, enabling interactive communication over the Internet. Users can send and receive messages, and share audio and video with others worldwide. Examples include Skype, Yahoo Messenger, etc.
E-Mail (Electronic Mail)
- Email is an electronic method for sending and receiving messages.
- An email address consists of two parts separated by the "@" symbol: the username and the host name (domain name).
- Email messages are exchanged between computer systems following specific Internet protocols.
- Emoticons or smileys are used to express emotions, and the storage area for email messages is called a mailbox.
Video-Conferencing

- Video-conferencing integrates video and audio to connect users as if they were in the same room, often involving three or more users in different locations.
- Participants typically need a computer, camera, microphone, video screen, and sound system.
E-Learning
E-learning (Electronic Learning) refers to delivering educational programs electronically, allowing users to acquire knowledge through the Internet and computer-based training programs.
E-Banking
- E-Banking (Electronic Banking) or Internet Banking enables users with a personal computer and a browser to access their bank’s website and perform various banking functions online.
- All permitted services are displayed in a menu.
E-Shopping
- Objective: E-Shopping (Electronic Shopping) or online shopping involves buying goods and services from Internet merchants.
- Products available online include: books, clothing, household appliances, toys, hardware, software, and health insurance.
- Examples of e-shopping sites: Naaptol, Flipkart, Yebhi, and Homeshop 18
E-Reservation
E-Reservation (Electronic Reservation) allows users to make reservations for services such as railways, airways tickets, hotel rooms, and tourist packages online, eliminating the need to visit an office or counter.
Social Networking
Social networking involves using Internet-based social media to connect with friends, family, classmates, customers, and clients for social or business purposes. Popular social networking sites include Facebook, MySpace, and Orkut.
Common Social Networking Sites

- LinkedIn: Founded by Reid Hoffman in 2002, LinkedIn provides business and employment-oriented services, connecting professionals worldwide.
- Facebook: Founded by Mark Zuckerberg in 2004, Facebook helps users connect with family and friends, share photos, and maintain photo albums.
- Twitter: Founded by Jack Dorsey, Noah Glass, Biz Stone, and Evan Williams in 2006, Twitter allows users to send and read short messages called tweets.
- Instagram: Acquired by Facebook in 2012, Instagram is a free online photo-sharing application and social network platform.
E-Commerce
E-Commerce (Electronic Commerce) involves sharing business information, maintaining business relationships, and conducting transactions via telecommunication networks. It includes the electronic transfer of business transactions (EDI).
M-Commerce
M-Commerce (Mobile Commerce) involves buying and selling goods or services through wireless Internet-enabled handheld devices, introduced by Kevin Duffey in 1997.
Video-Conferencing Apps
- Zoom: Developed by Zoom Video Communications in September 2012, Zoom is compatible with Windows, macOS, iOS, Android, Chrome OS, and Linux. It supports up to 100 participants for free meetings with a 40-minute time limit. Paid plans offer more features, supporting up to 1000 participants for meetings lasting up to 30 hours.
- Google Meet: Launched by Google in 2017, it supports up to 100 free participants for 60 minutes. Paid versions range from $6 to $12 per month.
- Microsoft Teams: Introduced by Microsoft in 2017, it offers unlimited meetings for up to 24 hours. It is compatible with Windows, macOS, iOS, and Android, requiring a monthly subscription.
- Skype: Developed by Skype Technologies (Microsoft) in August 2003, Skype supports up to 50 free participants, with paid subscriptions for larger meetings up to 250 participants.
Tit-Bits
- A cluster comprises multiple servers working together and potentially providing backup if one fails.
- Through the Webmail Interface, emails become accessible globally.
- Rich Text Formatting allows email senders to style their messages with font changes, sizes, bold, italics, and more.
|
48 videos|44 docs|33 tests
|
FAQs on Internet and it's Services - Computer Awareness and Proficiency - SSC CGL
| 1. What are some common social networking sites mentioned in the article? |  |
| 2. What are some popular video-conferencing apps mentioned in the article? |  |
| 3. What are some interconnecting protocols discussed in the article? |  |
| 4. What are some internet services mentioned in the article? |  |
| 5. How does the history of the internet relate to SSC CGL exam preparation? |  |




















