Computer Security | Computer Awareness and Proficiency - SSC CGL PDF Download
Computer Security: An Overview
Computer security, also known as cybersecurity or IT security, is a branch of information technology focused on protecting computers and information from unauthorized access, damage, or theft.
Sources of Cyber Attacks
 One of the most significant threats to computer users is virus attacks. A computer virus is a small software program that spreads from one computer to another and disrupts normal operations. The common sources of cyber attacks include:
One of the most significant threats to computer users is virus attacks. A computer virus is a small software program that spreads from one computer to another and disrupts normal operations. The common sources of cyber attacks include:
- Downloadable Programs: Executable files such as games and screensavers are major sources of viruses. It's crucial to scan any program before downloading it from the Internet.
- Cracked Software: Illegal software versions often contain viruses and bugs that are hard to detect and remove. Always download software from legitimate sources.
- Email Attachments: These are common virus carriers. Be cautious with email attachments, especially from unknown senders.
- Booting from Unknown CDs: If a computer boots from an unknown CD, it can introduce viruses. Remove CDs when not in use to avoid this risk.
Methods to Provide Protection
There are four primary methods to protect computer systems:
- System Access Control: Ensures that unauthorized users cannot access the system by encouraging security awareness among authorized users.
- Data Access Control: Monitors who can access data and for what purpose, based on security levels.
- System and Security Administration: Implements offline procedures to maintain or break system security.
- System Design: Utilizes basic hardware and software security features to protect the system.
Components of Computer Security
Computer security involves several core components:
- Confidentiality: Ensures that data is accessed only by authorized persons.
- Integrity: Ensures that information is not altered by unauthorized persons in a detectable manner.
- Authentication: Verifies users' identities through login names and passwords.
- Access Control: Restricts users to resources they are allowed to access.
- Non-Repudiation: Prevents senders from denying that they sent a message.
- Availability: Ensures that systems function correctly and service is available to authorized users.
- Privacy: Protects individuals' rights to use information and permits others to use it under controlled conditions.
- Steganography: Hides the existence of messages to aid confidentiality and integrity.
- Cryptography: Protects data during transmission and storage through encryption.
Cryptography Terms
- Plain Text: The original message.
- Cipher: Transforms plain text bit-by-bit without regard to meaning.
- Cipher Text: The encrypted message.
- Encryption: Converts plain text to cipher text.
- Decryption: Converts cipher text back to plain text.
Malware

Malware is a broad term for malicious software designed to damage systems, gather information, or gain unauthorized access. Types of malware include:
Viruses: Programs that can negatively affect computers by performing destructive actions, replicating, and spreading.
- Example: The first computer virus was "Creeper" in 1971, and the first boot sector PC virus was "Brain" in 1986.
- Effects: Viruses can monitor activities, slow performance, destroy data, affect networks, and display error messages, among other issues.
Worms: Standalone programs that replicate and spread via networks.
- Example: Bagle, I Love You, Morris, Nimda.
- Payload: Designed to spread on a larger scale than worms.
Trojans: Malicious programs that appear beneficial but facilitate unauthorized access.
- Example: Beast, Sub7, Zeus, ZeroAccess Rootkit.
Spyware: Programs that spy on user activity and collect information, which can be misused.
- Example: CoolWeb Search, FinFisher, Zango, Zlob Trojan, Keyloggers.
Symptoms of Malware Attack
Indications of a malware attack include:
- Odd messages on the screen.
- Missing files.
- Slow system performance.
- Frequent crashes and restarts.
- Inaccessible drives.
- Non-functional antivirus software.
- Unexpected sounds or music.
- Changes in mouse pointer graphics.
- Strange emails with odd attachments.
- Unusual system behavior like opening/closing windows or running programs automatically.
Some Other Threats to Computer Security
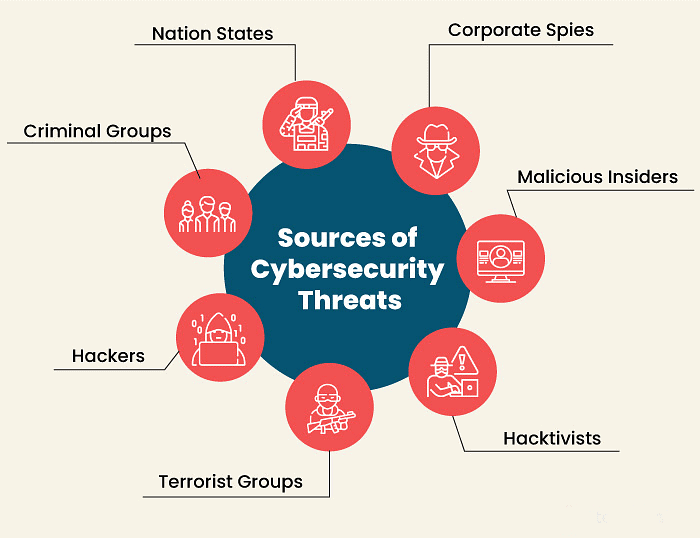
There are several other significant threats to computer security:
- Spoofing: This technique involves unauthorized access to data by disguising oneself as an authorized user, often over a network. IP spoofing is a method used to gain access to a computer by using a false IP address.
- Salami Technique: This method involves diverting small amounts of money from numerous accounts.
- Hacking: Unauthorized intrusion into someone else's computer or network, potentially causing a Denial of Service (DoS) attack, which prevents legitimate users from accessing resources. A hacker is the individual performing the hacking.
- Cracking: Breaking into computers, often using tools like password crackers, trojans, viruses, and war-dialers. Cyber crackers use computers to harm people or destroy critical systems.
- Phishing: Fraudulently attempting to acquire sensitive information like passwords and credit card details by pretending to be a trustworthy entity.
- Spam: The abuse of messaging systems to send unsolicited bulk messages, typically through email.
- Adware: Software that automatically displays advertisements to generate revenue, sometimes displaying unwanted ads.
- Rootkit: Malware designed to gain administrative-level control over a computer system without detection.
Solutions to Computer Security Threats
There are several safeguards to protect a computer system from unauthorized access:
- Anti-virus Software: Designed to prevent, detect, and remove viruses and other malicious software like worms, trojans, and adware. Popular antivirus programs include Avast, AVG, K7, Kaspersky, Trend Micro, Quick Heal, Symantec, Norton, and McAfee.
- Digital Certificate: An attachment to an electronic message used to verify the sender's identity and enable the receiver to encode a reply.
- Digital Signature: An electronic form of a signature that authenticates the sender's identity and ensures the integrity of the message or document.
- Firewall: Software or hardware-based systems that control incoming and outgoing network traffic based on predetermined security rules, often working with a proxy server.
- Password: A secret word or string of characters used for user authentication. Passwords can be weak (easily remembered) or strong (difficult to break, combining alphabets and symbols).
- File Access Permission: Assigning permissions or access rights to specific users or groups, controlling their ability to view, modify, or execute files. Permissions include read, write, and execute.
Terms Related to Security
- Eavesdropping: Unauthorized real-time interception of private communications, such as phone calls or instant messages.
- Masquerading: An attacker impersonates an authorized user to gain unauthorized privileges.
- Patches: Software designed to fix issues, including security vulnerabilities and bugs, improving usability and performance. Vendor-created program modifications are also called patches.
- Logic Bomb: Malicious code inserted into a computer's memory, triggered by specific conditions. Also known as slag code, it does not replicate itself.
- Application Gateway: Security mechanisms applied to specific applications like File Transfer Protocol (FTP) and Telnet services.
- Proxy Server: Acts as a firewall by responding to input packets like an application while blocking others, hiding true network addresses, and intercepting messages entering and leaving the network.
Tit-Bits
Key Pointers:
- The right to use software under specific rules is granted through a Software License.
- Software Piracy involves copying data or software without the owner's permission.
|
48 videos|43 docs|33 tests
|
FAQs on Computer Security - Computer Awareness and Proficiency - SSC CGL
| 1. What are some common sources of cyber attacks that individuals and organizations need to be aware of in terms of computer security? |  |
| 2. How can individuals and organizations protect their computer systems from cyber attacks according to the article? |  |
| 3. What is malware and how does it pose a threat to computer security? |  |
| 4. What are some other threats to computer security that individuals and organizations should be aware of? |  |
| 5. What are some solutions that can help mitigate computer security threats according to the article? |  |
















