Government Intervention in International Trade | UGC NET Commerce Preparation Course PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Government Interventions in International Trade |

|
| Methods of Government Intervention |

|
| Reasons for Government Interventions |

|
| Examples of Government Intervention |

|
Government Interventions in International Trade
Governments often intervene in international trade for political and economic reasons, though free trade generally leads to greater overall benefits. Policymakers face the challenge of balancing domestic pressures with the need for more open and efficient trade systems.
Methods of Government Intervention
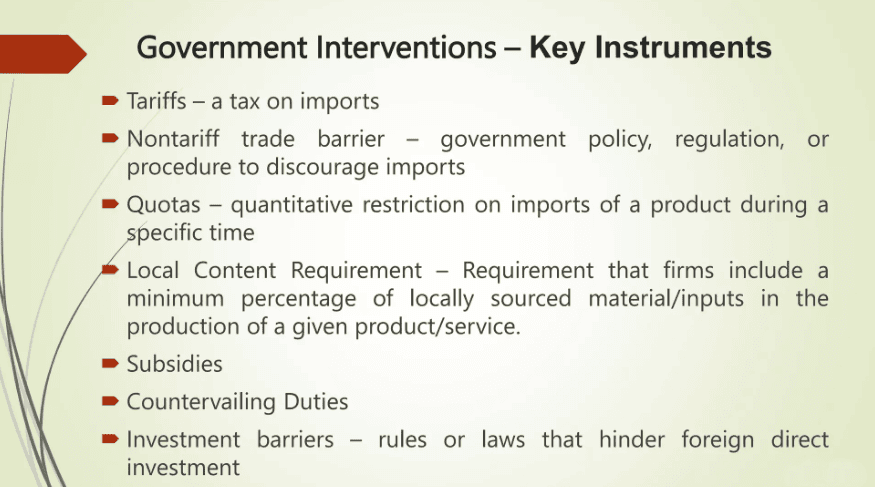
Tariffs Tariffs are taxes imposed on imported goods, increasing their price by a percentage of the value. This makes imports more expensive and decreases their consumption. While tariffs generate government revenue and protect domestic industries from foreign competition, they also raise consumer prices.
Quotas Quotas limit the quantity or total value of certain imports. Once the quota is reached, no additional goods can enter the country. Although quotas protect domestic producers from foreign competition, they reduce consumer choice and can lead to shortages.
Subsidies Subsidies involve financial aid given to domestic producers to help them compete with cheaper imports. While subsidies lower the cost of locally made goods, they can distort market conditions and result in overproduction.
Regulations Governments set standards, certification requirements, and rules that foreign goods must meet to be sold domestically. These regulations often aim to address safety and quality concerns but can increase costs for importers and limit product choices.
Currency Intervention Central banks may buy or sell their currency to influence its value relative to other currencies. This intervention affects export and import costs but can distort the allocation of resources within the economy.
Trade Agreements Trade agreements between governments establish rules and conditions for trade, such as reducing tariffs and setting standards for goods.
Non-Tariff Barriers (NTBs) NTBs include restrictions that are not physical limits or taxes, such as product standards, licensing requirements, and bureaucratic procedures.
Reasons for Government Interventions

- Protecting Domestic Industries: Tariffs and quotas shield emerging industries and sectors from foreign competition, helping to preserve jobs.
- Promoting National Security: Restrictions on imports of strategic materials and technology ensure the security of critical industries and military needs.
- Boosting the Economy: Import controls can improve a country's trade balance and short-term GDP growth by reducing imports and "saving" jobs.
- Environmental and Safety Concerns: Import standards ensure that foreign goods comply with domestic safety and environmental regulations.
Costs of Government Intervention
- Reduced Competition: Tariffs can decrease the incentive for local firms to innovate, harming productivity.
- Higher Prices: Consumers face higher prices and fewer choices due to tariffs.
- Retaliation: Foreign nations may impose retaliatory tariffs, which can negatively impact domestic exporters and jobs.
- Misallocation of Resources: Subsidies and tariffs can distort the economy by shifting resources to less productive sectors.
- Slowed Growth: Protectionist measures can hinder long-term economic growth by preventing the economy from fully benefiting from comparative advantage.
Examples of Government Intervention
- Tariffs: In 2018, the U.S. imposed tariffs of up to 25% on steel and 10% on aluminum imports to protect domestic producers, increasing costs for U.S. companies using these materials.
- Quotas: China sets quotas on agricultural imports like wheat and rice to protect its domestic farmers, limiting supply and choices for consumers.
- Subsidies: The EU provides substantial subsidies to agriculture and other sectors, leading to overproduction in some industries.
- Regulations: India mandates that 30% of components in electronics be sourced locally, benefiting domestic suppliers but raising costs for global companies.
- Currency Intervention: China has historically kept the yuan's value low through central bank actions, making Chinese exports cheaper and imports into China more expensive.
Conclusion
Understanding government intervention in international trade provides insight into the global economy's dynamics. It clarifies how nations interact economically and how different industries are impacted by international competition and policies. While interventions can protect domestic industries, maintain national security, and address other concerns, they can also lead to market distortions and inefficiencies. Balancing these factors is crucial for effective trade policy.
|
235 docs|166 tests
|
FAQs on Government Intervention in International Trade - UGC NET Commerce Preparation Course
Ans. Some common methods of government intervention in international trade include tariffs, quotas, subsidies, and export incentives.
2. Why do governments intervene in international trade?$#
Ans. Governments intervene in international trade to protect domestic industries, promote economic growth, ensure national security, and address trade imbalances.
3. Can you provide an example of government intervention in international trade?$#
Ans. One example of government intervention in international trade is the United States imposing tariffs on imported steel to protect its domestic steel industry.
4. How do tariffs affect international trade?$#
Ans. Tariffs increase the cost of imported goods, making them less competitive in the domestic market and potentially leading to a decrease in imports and an increase in domestic production.
5. What is the purpose of export incentives in international trade?$#
Ans. Export incentives are designed to promote exports by providing benefits such as tax breaks, subsidies, or grants to companies that export goods and services.

|
Explore Courses for UGC NET exam
|

|
















