Sources of Finance | Crash Course for UGC NET Commerce PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
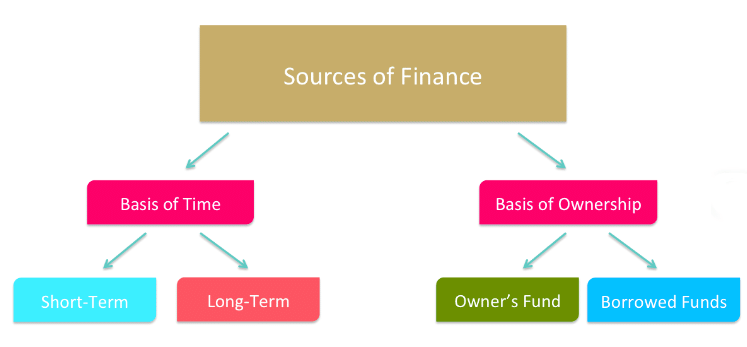
| Sources of Finance |

|
| Sources of Business Finance |

|
| Short-Term Sources of Finance |

|
| Long-Term Sources of Finance |

|
Sources of Finance
- Owner's Equity: Represents the initial capital injected by owners along with profits reinvested in the business. This is a primary source of internal funding for companies.
- Bank Loans: Companies opt for bank loans to support day-to-day operations, expansions, or asset acquisitions. Banks typically demand collateral and charge interest on the loan.
- Trade Credit: Suppliers extend short-term credit to firms, allowing them to pay invoices within a stipulated period, usually 30-60 days. This assists in managing cash flow fluctuations.
- Venture Capital: Investors inject capital into promising startups in exchange for a share in ownership. This avenue is suitable for ventures with high-risk, high-reward potential.
- Equity Finance: Firms issue new shares to investors in return for capital infusion. This process increases the company's share capital while diluting existing ownership.
- Mergers and Acquisitions: Companies can obtain funding through mergers or acquisitions with larger corporations, leveraging their resources and capital.
- Grants and Subsidies: Government funds are made available to firms for specific projects aligned with public objectives, which do not require repayment.
- Lease Financing: Businesses can acquire assets through leasing arrangements, making monthly payments for items like property, vehicles, or equipment.
- Mezzanine Financing: This blend of debt and equity grants lenders the option to convert the loan into ownership if repayment terms are not met.
- Revenue: Regular cash inflows from sales of goods and services provide consistent funding to cover operational costs and propel business growth.
Sources of Business Finance
Internal SourcesInternal sources refer to funds generated within the organization.
Owner's Equity:
Owner's equity comprises the initial investment by business owners and profits reinvested into the business. It serves as a primary internal funding source for companies.
- Initial Investment: This denotes the cash and assets injected by owners at the inception of the business, establishing their ownership stake in the company.
- Retained Earnings: After meeting expenses, a portion of profits is reinvested back into the business rather than distributed among owners. This reinvested sum, known as retained earnings, augments owner's equity. It allows the business to self-finance its growth without external funding.
- Retained earnings cumulatively represent the profits earned by the business since its inception. Over time, they often become the most substantial component of owner's equity for growing companies, facilitating self-funding for asset acquisition and expansion.
Collectively, the initial investment and retained earnings signify owners' ownership stake in the business, reflecting their equity or ownership interest. Owner's equity mirrors the business's net value attributable to its owners. It stands as a crucial internal financing source for companies, granting owners full discretion over reinvesting profits for growth. However, excessive retention of profits may impact owners' returns, necessitating a balance based on business growth requirements.
Revenue
- Revenue Importance: The sales of products and services generate cash inflows, crucial for covering operational costs and funding business expansion. A boost in revenue enhances internal fund generation.
- Revenue Source: Revenue signifies the cash inflows derived from selling goods and services to customers. It sustains daily operations and facilitates growth strategies.
External Sources
Debt Financing:
Bank Loans: Companies obtain funds from banks to cover both short- and long-term financial needs. Banks typically charge interest and may require collateral, such as assets, to secure the loan.
Trade Credit: Suppliers offer short-term credit to businesses, allowing them to delay payments for a period (usually 30-60 days). This helps businesses manage temporary cash flow issues.
Equity Financing:
Venture Capital: Investors provide funding to high-growth potential businesses in exchange for equity or a share of ownership. This is ideal for innovative and high-risk ventures.
Issuing New Shares: Companies raise capital by selling new shares to investors. However, this results in a dilution of existing shareholders' ownership.
Other Financing Options:
Lease Financing: Instead of purchasing assets, companies lease property, vehicles, and equipment. Leasing provides access to assets without large upfront costs.
Government Grants and Subsidies: Governments offer financial support that does not need to be repaid, aimed at projects aligning with broader policy objectives.
Asset Sales: Companies can generate funds by selling assets that are not being fully utilized.
Invoice Factoring: Businesses sell their outstanding invoices at a discount to a third party for immediate cash, which helps in managing working capital.
Short-Term Sources of Finance
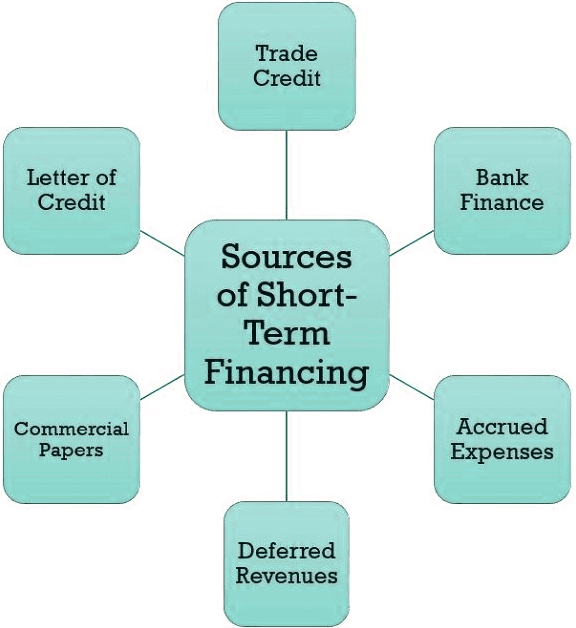
Trade Credit:
- Businesses frequently purchase goods and services on credit from suppliers, allowing them to acquire goods with an agreement to pay at a later date.
Bank Overdrafts:
- A bank overdraft offers a short-term borrowing option where a company can withdraw more than the available account balance, serving as a flexible and convenient source of short-term finance.
Short-Term Loans:
- Businesses may opt for short-term loans to address temporary fund shortages, typically repaying these loans within a year.
Commercial Paper:
- Large, creditworthy corporations can issue commercial paper, a short-term debt instrument. Investors purchase commercial paper at a discount and receive the full face value upon maturity.
Factoring:
- Companies can sell their accounts receivable at a discount to a third party (factor) to obtain immediate cash, enhancing cash flow by converting receivables into cash.
Accruals:
- Accruals involve recognizing and accounting for expenses or revenues before the actual cash transaction takes place, aiding businesses in managing short-term financial needs.
Crowdfunding:
- Crowdfunding platforms enable businesses to raise small amounts of capital from numerous individuals, often utilized for specific projects or product launches.
Supplier Credit:
- Negotiating extended payment terms with suppliers offers a form of short-term financing, allowing a company to defer cash outflows.
Long-Term Sources of Finance
Long-term sources of finance refer to funding options that are typically obtained for a period exceeding one year to support business operations and expansion. These sources are crucial for sustaining long-term growth and stability. Let's explore the various sources in detail:
Equity Capital:
- Common Stock: Companies can raise funds by issuing common stock, providing ownership shares to investors. Shareholders receive dividends and have voting rights in company decisions.
- Preferred Stock: Similar to common stock, preferred stock provides preference in dividend payments. Preferred stockholders typically receive fixed dividends before common stockholders.
Debt Capital:
- Bonds: Companies issue bonds to raise long-term capital. Investors purchase bonds, representing a debt obligation. Companies pay periodic interest and return the principal at maturity.
- Long-Term Loans: Companies secure long-term financing by obtaining loans from financial institutions or other lenders. These loans may have fixed or variable interest rates.
Retained Earnings:
- Companies utilize retained earnings, which are profits not distributed as dividends, as a source of internal long-term finance. This represents accumulated funds over the years.
Venture Capital and Private Equity:
- Startups and growing companies attract investments from venture capitalists or private equity firms. In return, investors receive ownership stakes and often play an active role in the company's operations.
Government Grants and Subsidies:
- Certain industries or projects qualify for government grants or subsidies. These funds are provided by the government to support specific activities such as research and development or renewable energy projects.
Leasing and Hire Purchase:
- Companies use leasing or hire purchase agreements to acquire assets over an extended period. While not a direct capital infusion, these arrangements enable businesses to use assets without an immediate need for full payment.
Conclusion
Businesses need funding for their daily activities, growth, and expansion. They can access internal and external sources of finance to cater to their requirements. Internal sources like owners' equity and revenue are usually the most cost-effective option, while external financing supports rapid growth. A well-balanced mix of funding sources enables businesses to achieve their financial goals efficiently. Depending on their capital needs, growth strategies, risk tolerance, and funding requirements, businesses can select from various long-term financing options. By combining debt and equity financing judiciously, businesses can optimize their cost of capital while fulfilling their liquidity needs.
|
157 videos|236 docs|166 tests
|
FAQs on Sources of Finance - Crash Course for UGC NET Commerce
| 1. What are some common methods of short-term financing for firms? |  |
| 2. What are some sources of long-term financing that firms can utilize? |  |
| 3. What are some government funding options available for businesses seeking financing? |  |
| 4. What are the sources of finance that UGC NET candidates should be familiar with for the exam? |  |
| 5. What are some frequently asked questions related to financing options for firms that candidates may come across in the UGC NET exam? |  |















