Advance Payment of Tax | Crash Course for UGC NET Commerce PDF Download
Tax liabilities apply to anyone whose earnings exceed the exemption limits. Individuals must evaluate their income and determine their tax obligations. It's essential to both file and pay these taxes, as they are a crucial source of government revenue that supports infrastructure development. Being aware of how much you owe and following payment regulations can help prevent penalties or fines. Paying taxes in advance offers convenience and supports steady income flow. Understanding advance tax payments can also assist in filing returns accurately.
What is Advance Payment of Tax?

Meaning of Advance Payment of Tax
- Advance Payment of Tax Provisions: The provisions for advance tax necessitate taxpayers to settle tax liabilities in accordance with their income sources, such as salaries, business earnings, rents, and interests.
- Payment of Advance Tax Section: This section determines the overall tax liability for the fiscal year by assessing the taxpayer's income and corresponding tax obligations.
- Calculation of Advance Tax Payment: The calculation of advance tax payments is predicated on income evaluations, allowing for adjustments based on tax variations. Tax refunds or payments are facilitated to accommodate any changes.
- Advance Payment of Tax Nature: Advance tax payments are structured as periodic installments throughout the year, providing taxpayers with the flexibility to pay their taxes in installments rather than a lump sum.
- Provision of Advance Payment of Tax: Section 208 of the Income Tax Act outlines the guidelines regarding advance tax, specifying the due dates, amounts, and eligible entities for advance tax payments.
The concept of advance payment of tax is crucial for taxpayers as it streamlines the taxation process for both individuals and the government.
Payment of Advance Tax Rules
Taxpayers must adhere to precise guidelines regarding the timing and amounts for advance tax payments. Not complying with these advance tax regulations can result in penalties. Continue reading to learn about the various rules for advance tax.
- Advance Tax Due Date and Amount: The advance payment of tax involves specific dates and tax amounts. Taxpayers are required to pay a portion of their total tax liability by these specified dates.
Advance Payment for Business Owners and Self-employed
Business owners must adhere to these regulations regarding the due dates and amounts for advance tax payments.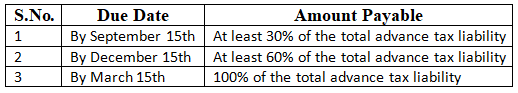
Advance Payment for Companies
Companies must adhere to these regulations regarding the due dates and amounts for advance tax payments.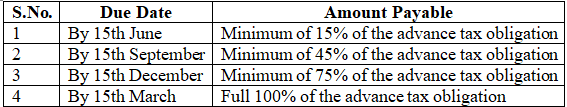
Who needs to pay Advance Tax?
Advance tax applies to anyone with an annual tax liability exceeding ₹10,000, after accounting for TDS adjustments. Below are the various categories of individuals required to make advance tax payments.
Salaried Professionals and Freelancers
- If their tax liability exceeds ₹10,000 after TDS adjustments, they must pay advance tax.
- Individuals above 60 years without business income are exempt from this requirement.
Presumptive Earnings (Business)
- Businesses opting for the presumptive tax regime under Section 44AD need to pay their full advance tax by March 15 in a single installment.
- The tax amount should be settled before March 31.
Presumptive Earnings (Professionals)
- Professionals such as doctors, consultants, architects, etc., covered by Section 44ADA must fulfill their advance tax obligations by March 15 in a single payment.
- The tax payment deadline is March 31.
Advance Tax Payment Calculation
Correctly calculating your advance tax is crucial to avoid interest charges for default in payment. Understanding how advance tax works ensures timely payments and prevents any penalties.
- Step 1: Estimate Your Annual Tax Obligations: Begin by estimating your yearly tax responsibilities based on your expected earnings from various sources such as business profits, interest income, rental income, and more.
- Step 2: Calculate Applicable Taxable Income: Determine your taxable income for the year, excluding salary income. Combine earnings from diverse sources to calculate your gross revenue.
- Step 3: Check Latest Tax Slabs: Refer to the current tax slabs to ascertain your tax liability based on your total income.
- Step 4: Deduct TDS Amount: Subtract the Tax Deducted at Source (TDS) from your various earnings. TDS is the tax amount already deducted at the source. Consider different tax slabs to determine your TDS liability accurately.
- Step 5: Determine Advance Tax Obligation: If your tax liability exceeds ₹10,000 after accounting for TDS, you are required to pay advance tax. Adhere to the specified due dates for advance tax payments to avoid penalties.
Incorrect estimations can result in improper advance tax payments. However, taxpayers who have overpaid can request a refund. Conversely, if the calculated tax liability exceeds what was paid, they will need to pay the additional amount.
Refunds and additional payments are processed during tax return submissions. Taxpayers also have the option to settle their tax obligations before reaching the full 100% liability.
Steps for Online Advance Payment of Tax

- Open the Income Tax Department online portal for tax payments.
- Find and select the relevant Challan number. (Challan 280 for individual taxpayers)
- Select (100) Advance Tax as the payment type.
- Fill in relevant details like address, payment mode, assessment year, etc.
- Click the "Proceed" button.
- Complete the payment on the redirected payment portal.
- Save the Challan for your payment, useful during return filing.
Exemptions of Advance Tax Payment
Advance tax payments have certain exemptions. Let's explore these exemptions in detail:
Advance Tax Payment Exemptions:
- People above 60 years of age are exempt from making advance tax payments.
- If the Tax Deducted at Source (TDS) amount deducted for an individual exceeds their actual tax liability, then advance tax is not applicable.
- Salaried professionals who have TDS deducted from their income are not required to make advance tax payments. However, income from non-salary sources is still subject to advance tax payments.
Benefits of Advance Tax
The advantages of making advance tax payments are numerous and beneficial. Let's delve into the merits of paying taxes ahead of time.
Benefits of Advance Tax Payment
- Taxpayers are relieved from the stress of last-minute tax payments, reducing potential troubles.
- The advanced tax system eases the burden of making payments.
- Smooth and swift tax collection processes lead to a consistent flow of revenue for the government.
- Businesses can better forecast their annual incomes and tax obligations, aiding in financial planning.
- Government gains access to advance tax amounts, enabling them to earn interest on these funds.
- Advance tax payments help in avoiding missing tax payment deadlines.
Advance Tax Late Payment and Interest
Advance tax, also referred to as "pay-as-you-earn" tax, is a method where individuals and businesses are mandated to pay their income tax obligations beforehand, usually in periodic installments over the fiscal year. This approach aids governments in collecting tax revenue promptly and prevents the buildup of tax debts.
If an individual or business misses the deadline for paying their advance tax, they might face fines and interest fees. The specific regulations and rates concerning late payment of advance tax can differ by location, but here are some key points to consider:
Advance Tax Payment Guidelines
- Due Dates for Advance Tax Payment: Tax authorities set specific dates for paying advance tax installments throughout the fiscal year. Missing these deadlines can lead to penalties and interest charges.
- Late Payment Penalty: Failure to pay an installment on time may result in a penalty, usually a percentage of the unpaid tax amount, varying by jurisdiction.
- Interest on Late Payment: Besides penalties, interest accrues on the unpaid tax from the due date until payment, with rates set by tax authorities or based on market rates.
- Calculating Interest: The method to calculate interest on late payments can vary; some regions use simple interest while others employ more complex formulas.
Self-Assessment and Corrections
- Self-Assessment: Taxpayers estimate their tax liabilities and make advance payments based on these calculations. Underestimations may lead to interest charges on the shortfall.
- Correction of Underpayment: Taxpayers rectify underpayments by settling the remaining amount in the next installment or before the fiscal year-end to minimize interest charges.
Tax Filing Procedures
- Tax Filing and Adjustments: At the fiscal year-end, taxpayers file annual tax returns, calculating the actual liability considering advance tax payments. Shortfalls may require payment of the remaining balance plus any additional interest or penalties.
It's crucial for individuals and businesses to understand their jurisdiction's advance tax payment rules and deadlines. Timely payments help avoid unnecessary penalties and assure compliance. Seeking advice from tax professionals or tax authorities can provide specific details on late payment penalties and interest rates.
Conclusion
The concept of advance payment of taxes is crucial for both the government and taxpayers, streamlining the system and offering benefits to both parties. It enables the government to collect revenue while allowing taxpayers to defer actual payment. This practice also empowers businesses and professionals to forecast their incomes, understand their tax responsibilities, and manage their finances more effectively.
|
237 videos|236 docs|166 tests
|
FAQs on Advance Payment of Tax - Crash Course for UGC NET Commerce
| 1. What is Advance Payment of Tax and why is it necessary? |  |
| 2. Who is required to pay Advance Tax? |  |
| 3. How is the Advance Tax Payment calculated? |  |
| 4. What are the steps for making an online Advance Tax Payment? |  |
| 5. What are the penalties for late payment of Advance Tax? |  |





















