Indian Accounting Standards and IFRS | Crash Course for UGC NET Commerce PDF Download
What is Indian Accounting Standards (IND AS)?

Indian Accounting Standards (Ind AS) are a set of accounting guidelines issued by the Central Government of India. They are developed under the oversight of the Accounting Standards Board (ASB) of the Institute of Chartered Accountants of India (ICAI) and in consultation with the National Financial Reporting Authority (NFRA).
These standards are designed to align closely with International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS) and are applicable to Indian companies. The ASB, which was established in 1977, is responsible for formulating these standards.
Accounting Standards Overview
- Accounting standards are principles, guidelines, and procedures that form the basis for financial accounting policies and practices.
History of Indian Accounting Standards (Ind AS)
- Prior to the adoption of Ind AS, Indian companies followed Indian Generally Accepted Accounting Principles (IGAAP). Indian GAAP included 18 accounting standards established by the ICAI and regulated under the Companies Act, 1956.
Issuers of Accounting Standards in India
- The ICAI is responsible for preparing accounting standards in India, under the administrative control of the Ministry of Corporate Affairs, Government of India. Currently, the ICAI has published 41 accounting standards.
Objectives of Accounting Standards (IND AS)
The objectives of Indian Accounting Standards (Ind AS) include:
Accurate Accounting: To ensure that large-scale activities are accurately recorded through continuous disclosure, proper treatment, and periodic reformation.
Standardization: To standardize accounting policies and principles across the country, fostering consistency in financial reporting.
Unified Framework: To provide a unified framework for preparing financial statements, thereby enhancing financial transparency.
Global Acceptance: To ensure that institutions and governmental bodies adhere to standards that are recognized and accepted globally.
List of Indian Accounting Standards (IND AS)
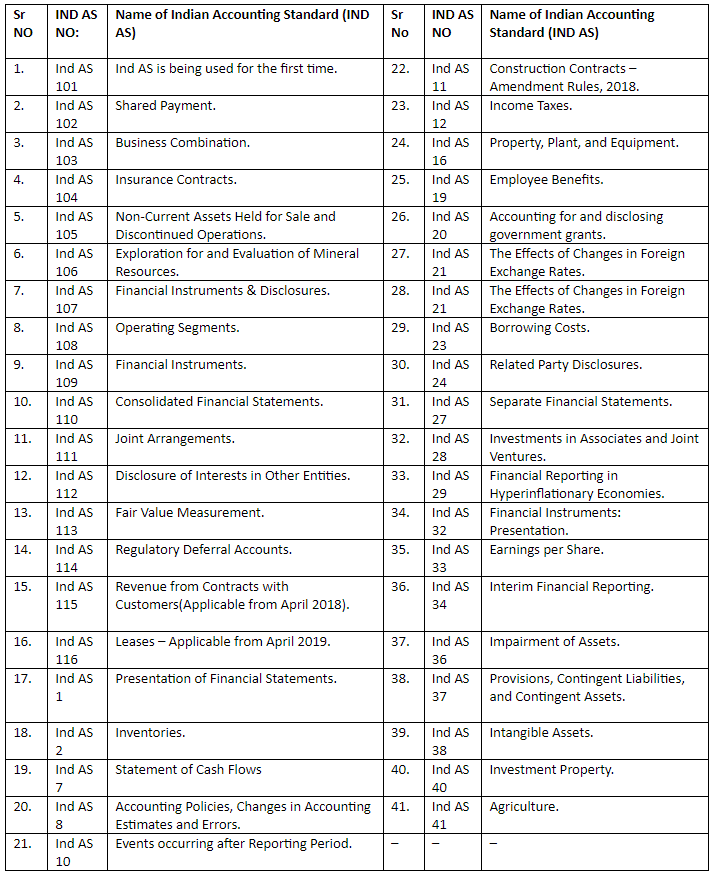
Applicability of Ind AS
Indian Accounting Standards (Ind AS) were implemented gradually rather than all at once:
- 2015: Ind AS was initially mandatory for large and listed companies, with voluntary adoption for others.
- 2016-17: All companies with a net worth above ₹500 crores, including both listed and unlisted firms, were required to adopt Ind AS.
- 2017-18: Companies with a net worth between ₹250-500 crores were also required to implement Ind AS.
- Up to ₹250 crores: Small companies with a net worth up to ₹250 crores could continue using Indian GAAP but had the option to voluntarily adopt Ind AS.
For listed companies:
- Net worth above ₹1,000 crores: Mandatory implementation of Ind AS started from 2016-17.
- Net worth between ₹500-1,000 crores: These companies had until 2018-19 to comply with Ind AS.
The phased approach allows companies time to transition smoothly and considers factors such as company size, resources, and implementation capabilities.
Concept of Indian Accounting Standards (Ind AS)
Ind AS was developed to align accounting practices with global reporting standards. Its objectives include:
- Harmonizing accounting standards for consistency in global reporting.
- Standardizing accounting procedures across the Indian economy.
- Ensuring uniform transaction recording by all businesses.
- Making the accounting system more comprehensible for the business sector.
Indian Accounting Standards and Its Adoption
Ind AS was adopted by Indian companies in 4 phases, which are mentioned below.
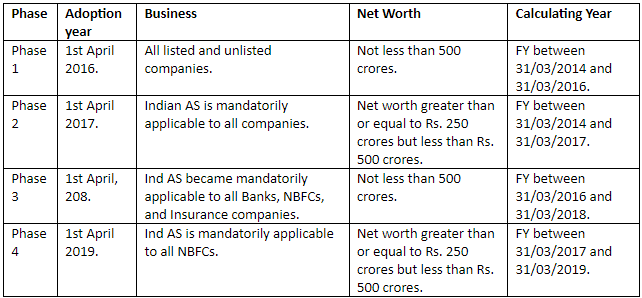
Note: Once a company has adopted Indian Accounting Standards (Ind AS), whether mandatorily or voluntarily, it cannot revert to the previous accounting method.
Advantages of Accounting Standards
Accounting Standards offer several benefits:
- Simplify and clarify accounting information.
- Ensure uniformity in accounting systems.
- Facilitate global acceptance.
- Enable easier comparison of financial statements.
- Assist in auditing processes.
- Enhance the credibility of financial statements.
- Aid in evaluating management performance.
- Help prevent fraud and manipulation.
Need for Ind AS Adoption
The adoption of Ind AS addresses several needs:
- Facilitates cross-border financial transactions.
- Supports global listing of companies.
- Ensures comparability of financial statements on a global scale.
- Enhances investors' ability to compare global investments.
- Simplifies global investment processes and benefits capital market stakeholders.
Accounting Standards Board of India (ASB)
Established in 1977 by the Council of the Institute of Chartered Accountants of India (ICAI), the ASB was created to address the need for accounting standards in India. It:
- Recommends Accounting Standards (Ind AS and AS) for notification under relevant statutes, including the Companies Act 2013 and the Limited Liability Partnership Act, 2008.
- Issues accounting standards for non-corporate entities in India.
Accounting Standards Committee:
The International Accounting Standards Committee (IASC) was an independent private-sector organization aimed at establishing uniform accounting principles for global financial reporting. On April 1, 2001, the IASC was succeeded by the International Accounting Standards Board (IASB).
International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS) and Its Convergence with Ind AS
Globalization has integrated economies worldwide, creating a need for a unified global accounting language to enhance business reporting and ensure consistency in accounting policies. Adopting a single set of accounting standards would improve the comparability of financial statements across different entities.
To address this need, more than 120 countries have adopted International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS). IFRS aims to provide a consistent accounting framework globally.
Components of IFRS:
- 13 IFRS standards
- 28 International Accounting Standards (IAS) issued before the introduction of IFRS
- 15 IFRIC interpretations issued by the International Financial Reporting Interpretations Committee
- 9 SIC interpretations issued by the Standard Interpretation Committee
This convergence with IFRS helps streamline accounting practices and enhances the comparability of financial statements internationally.
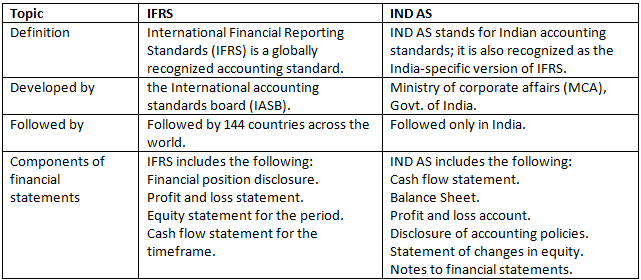
Difference between IFRS and IND AS
The following are the major differences between IFRS and Indian Accounting Standards (IND AS):
|
237 videos|236 docs|166 tests
|
FAQs on Indian Accounting Standards and IFRS - Crash Course for UGC NET Commerce
| 1. What are Indian Accounting Standards (IND AS)? |  |
| 2. What are the objectives of Accounting Standards (IND AS)? |  |
| 3. When are the Indian Accounting Standards (IND AS) applicable? |  |
| 4. What is the relationship between International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS) and Indian Accounting Standards (IND AS)? |  |
| 5. What is the significance of the convergence of Indian Accounting Standards (IND AS) with International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS)? |  |
















