CLAT PG Exam > CLAT PG Notes > Law of Contracts > Pledge and Hypothecation
Pledge and Hypothecation | Law of Contracts - CLAT PG PDF Download
Pledge and Hypothecation
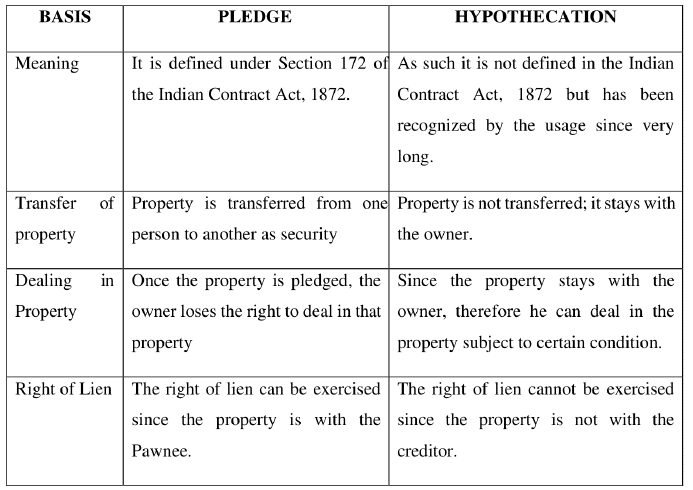
Pledge and hypothecation are both methods of securing a loan or the fulfillment of a promise using movable property as collateral. However, they differ in terms of possession and rights associated with the property.
Pledge
- In a pledge, the debtor (pawnor) transfers possession of the movable property to the creditor (pawnee) as security.
- The pawnor loses possession of the property and the right to deal with it.
- The pawnee has the right to sell the pledged property to recover the loan amount if the debtor defaults.
Hypothecation
- In hypothecation, the debtor retains possession of the movable property while using it as security for a loan.
- The debtor has the right to deal with the goods, but must adhere to the terms of the contract.
- Hypothecation involves the transfer of rights or interests, but not possession.
- The creditor has the right to inspect the goods and, if necessary, sell them to recover the loan amount.
Key Differences
- Pledge involves the transfer of possession, whereas hypothecation involves the transfer of rights or interests without possession.
- In pledge, the pledgee (creditor) takes possession of the goods, while in hypothecation, the hypothecator (debtor) retains possession.
- Both pledge and hypothecation give the creditor the right to sue and sell the goods to recover the loan amount.
In summary, pledge and hypothecation are legal agreements used to secure loans with movable property, differing primarily in the transfer of possession and rights associated with the collateral.
The Differences Pledge and Hypothecation
[Question: 1754499]
Pledge vs. Lien
- Pledge creates a special property interest in the item pledged, while a lien is simply a personal right that the party can exercise when payment is due.
- Rights : In a pledge, the pledgee has the right to retain, sue, and even sell the pledged property. In contrast, a lien only grants the right of retention.
- Possession vs. Rights : A lien can be seen as the opposite of hypothecation. While a lien involves the transfer of possession, hypothecation involves the transfer of rights without possession.
Pledge vs. Mortgage
- Pledge involves the transfer of possession of an item in exchange for a certain sum or as security for fulfilling an obligation. It grants the pledgee special rights, such as remedies in case of default.
- In a mortgage , along with these special rights, legal rights are also transferred. For example, the right of enjoyment is not transferred in a pledge, but it is in a mortgage.
The document Pledge and Hypothecation | Law of Contracts - CLAT PG is a part of the CLAT PG Course Law of Contracts.
All you need of CLAT PG at this link: CLAT PG
|
80 docs|19 tests
|
FAQs on Pledge and Hypothecation - Law of Contracts - CLAT PG
| 1. What is the difference between a pledge and a lien? |  |
Ans. A pledge is a form of security interest where the borrower hands over physical possession of an asset to the lender until the loan is repaid. In contrast, a lien is a legal right or interest that a lender has in the borrower's property, granted until the debt obligation is satisfied, but the borrower retains possession of the property.
| 2. How does hypothecation differ from pledge? |  |
Ans. Hypothecation is a process where a borrower pledges collateral to secure a loan while retaining possession of the collateral. In a pledge, the lender takes physical possession of the item. Thus, hypothecation allows the borrower to continue using the asset while providing security to the lender.
| 3. Can you provide examples of assets that can be pledged or hypothecated? |  |
Ans. Common examples of assets that can be pledged include stocks, bonds, and tangible goods like jewelry or vehicles. Hypothecation often involves assets like real estate or inventory, where the borrower maintains possession while using the item as collateral.
| 4. What happens if a borrower defaults on a pledge or hypothecation? |  |
Ans. If a borrower defaults on a pledge, the lender has the right to sell the pledged asset to recover the owed amount. In the case of hypothecation, the lender can take possession of the asset and sell it to satisfy the debt, though the borrower retains possession until default occurs.
| 5. Are there any legal formalities required for creating a pledge or hypothecation? |  |
Ans. Yes, both pledge and hypothecation require legal documentation to be enforceable. A pledge typically involves a written agreement that details the terms, while hypothecation may also require registration of the secured interest to establish the lender's rights against third parties.
Related Searches




















