NCERT Solution: Trial Balance and Rectification of Errors | Accountancy Class 11 - Commerce PDF Download
Short Question Answers
Q1: State the meaning of a trial balance?
Ans: A trial balance is a bookkeeping spreadsheet which carries the balances of all ledgers arranged into debit and credit account column totals that are equal on both sides. The trial balance is generally prepared once a year, usually at the end of the fiscal period. The key goal of preparing a trial balance is to make sure that the entries in an organization's bookkeeping process are monetarily correct. According to William Pickles, "the statement is prepared using ledger balances, at the end of the fiscal year to determine whether the debit total agrees with the credit total is known as trial balance.”
Q2: Give two examples of errors of principle?
Ans: The two following examples of errors of principle are as follows:
- Incorrect casting: The total of the purchase book has been increased by Rs. 7000. As soon as the total is posted on the purchase account's debit column, it will exceed the debit side by a small amount of Rs. 7000, and the trial balance will not agree.
- Incorrect posting of amount: ABC was charged Rs. 900 for goods. It should have been correctly entered in the book, but the amount was misappropriated as Rs. 90 instead of Rs. 900 while posting to ABC's credit column. As a result, the trial balance will not agree.
Q3: Give two examples of errors of commission?
Ans: The following are two examples of errors of commission:
- Incorrect amount posted: Mohit purchased goods for Rs. 9000. However, if the amount posted to Mohit's credit in the purchase book is Rs. 900 instead of Rs. 9000, the trial balance will be different.
- Posting on the wrong side: Ram has sold me goods for Rs. 5000. Instead of posting it to the credit side of Ram's account, the entry was recorded on the debit side, causing the trial balance to increase the credit by Rs. 5000.
Q4: What are the methods of preparing trial balance?
Ans: The following methods are used to prepare trial balance:
- Balance Method: The balance method enters only the amounts that show balances in the trial balance, along with the amount of balances. The amount displaying the debit balance is written on the trial balance's debit side, and the amount displaying the credit balance is recorded on the trial balance's credit side.
- Total amount Method: In this method, the sum total of the debit and credit sides of each account is individually written in the trial balance's debit and credit columns.
- Total and balance Method: In this method, the balance and total of both sides of the account are displayed in the same trial balance side by side.
Q5: What are the steps taken by an accountant to locate the errors in the trial balance?
Ans: An accountant will take the following steps to locate errors in the trial balance:
- To double-check the Dr. and Cr. Side additions.
- Examine the ledger to see if there is any account with a balance equal to the difference between the trial balance and the current balance.
- To double-check the initial balances.
- To reassess the ledger account balances.
- To double-check that the posting in the ledger account corresponds to the journal and other books of original entry.
- If the potential error cannot be found or located, the difference between the trial balances is transferred to a temporary account known as the suspense account.
Q6: What is a suspense account? Is it necessary that is suspense account will balance off after rectification of the errors detected by the accountant? If not, then what happens to the balance still remaining in suspense account?
Ans: The suspense account is the account that is created when there are errors in the trial balance and the balances on the debit and credit sides do not match. As a result, this account records the difference between both sides of the trial balance in order to record the difference under its heading. The discrepancy between the amounts in the debit and credit columns is caused by an error in the accounting process.
It is not required that a suspense account shall balance off after rectification of the errors found by an accountant. If the errors for which the suspense account is opened, once those errors get rectified then only the suspense account automatically gets closed. But if the errors are not rectified the balance will still remain in the suspense account.
Q7: What kinds of errors would cause difference in the trial balance. Also list examples that would not be revealed by a trial balance?
Ans: The types of errors that can impact in the difference in trial balance are given below:
i. Error of Omission
ii. Error of Commission
iii. Error of Principle
iv. Compensating Errors
Errors could occur in the following situations: -
i. When the subsidiary book displays either the undercast or overcast amount.
ii. When no posting has been made to one of the accounts involved in the transaction.
iii. When a post is made on the incorrect side of an account.
iv. When an incorrect amount is posted in any column.
Q8: State the limitations of trial balance?
Ans: The trial balance has the following limitations:
- It is not a conclusive proof of accuracy:The trial balance does not provide assurance of the correctness of the accounting process when the debit and credit sides may even match evenly.
- It does not reveal the error in the books of original entry: The trial balance cannot point out the error in any of the trial balance's specific accounts when it is simply indicated by the sides of the trial balance not being evenly matched with one another.
- It does not reveal any operational results:There may be cases where transactions were forgotten and not recorded at all. As a result, their impact on the debit and credit sides of the respective accounts was not recorded, causing the trial balance to match evenly. As a result, such operational errors cannot be recorded.
Long Question Answers
Q1: Describe the purpose for the preparation of trial balance.
Ans: The following is the goal of preparing the trial balance:
- It allows you to check the arithmetic accuracy of ledger accounts.
- It also aids in the detection of posting errors in necessary accounts.
- It also aids in summarizing the accounts.
- It aids in the completion of final accounts.
- Finally, it aids in determining the necessary adjustments to be made in the future.
Q2: Explain errors of principle and give two examples with measures to rectify them.
Ans: When an accounting error is made while recording a transaction, it violates the fundamental principles of accounting and is referred to as an error of principle. Here are two examples:
- Incorrect item posting:When an item is posted to the debit side of an account instead of the credit side, or vice versa. To correct this type of error, we must journalize the entry correctly, i.e. items on the debit side must be posted to the credit side of an account and vice versa.
- Incorrect posting of amount: Incorrect posting of an amount in an account must be corrected by posting the original amount in that account.
Q3: Explain the errors of commission and give two examples with measures to rectify them.
Ans: Errors of commission are mistakes that occur as a result of a bookkeeper's or clerk's negligence in recording a transaction with incorrect amounts, incorrect balancing, incorrect posting, and/or incorrect carrying forward of an account item. The examples below will aid in the process of understanding and correcting the errors listed below.
(i) Let's look at the first example. Mr. X's sales of Rs10,000 were recorded as 1,000 from the invoice. In this case, Mr. X's account was debited with Rs. 1,000 rather than Rs. 10,000, resulting in a commission error. To correct this commission error, it should be further debited with Rs.9000. This will be fixed by enacting the following legislation: (Rs. 10,000 in goods sold to Mr X was incorrectly recorded as Rs. 1,000, which has now been corrected).
(Rs. 10,000 in goods sold to Mr X was incorrectly recorded as Rs. 1,000, which has now been corrected).
(ii) The purchase book was overestimated by Rs. 10,000.
This mistake can be corrected in one of two ways:
(a) If an error is discovered prior to preparing the trial balance, Rs. 10,000 should be recorded on the debit side of the Purchases Account.
(b) If an error is discovered after preparing the Trial Balance, the following entry must be recorded.
Q4: What are the different types of errors that are usually committed in recording business transaction.
Ans: The following are the various types of errors that commonly occur when recording business transactions:
- Errors of Omission:Errors of omission are errors that occur when the person in charge of building and maintaining the accounts fails to record a specific transaction in the books of account.
- Errors of Commission: Errors of commission are defined as errors or mistakes that occur as a result of certain liable actions of the individual who is responsible for maintaining accounts. These errors occur due to a lack of expertise and accounting knowledge, as well as carelessness on the part of the accounting staff.
Q5: As an accountant of a company, you are disappointed to learn that the totals in your new trial balance are not equal. After going through a careful analysis, you have discovered only one error. Specifically, the balance of the Office Equipment account has a debit balance of Rs. 15,600 on the trial balance. However, you have figured out that a correctly recorded credit purchase of pendrive for Rs. 3,500 was posted from the journal to the ledger with a Rs. 3,500 debit to Office Equipment and another Rs. 3,500 debit to creditors accounts. Answer each of the following questions and present the amount of any misstatement :
(a) Is the balance of the office equipment account overstated, understated, or correctly stated in the trial balance?
(b) Is the balance of the creditors account overstated, understated, or correctly stated in the trial balance?
(c) Is the debit column total of the trial balance overstated, understated, or correctly stated?
(d) Is the credit column total of the trial balance overstated, understated, or correctly stated?
(e) If the debit column total of the trial balance is Rs. 2,40,000 before correcting the error, what is the total of credit column.
Ans:The purchase of pendrive is wrongly debited to the office equipment account.
(a) The balance of office equipment is overstated by Rs. 3500. This is so because the cost of the pendrive of Rs. 3500 was debited twice under two heads.
(b) Since, the cost of the pendrive of Rs. 3500 was debited twice under two heads; the balance of the creditor account is understated by Rs.7000.
(c) The total of the debit column is correctly stated.
(d) The total of the credit column is understated by Rs. 7000. The credit side needs to be balanced against the debit side.
(e) The total of credit column is Rs. 233000 (i.e. Rs. 240000-7000) because it has been wrongly understated by Rs. 7000.
Numerical Question Answers
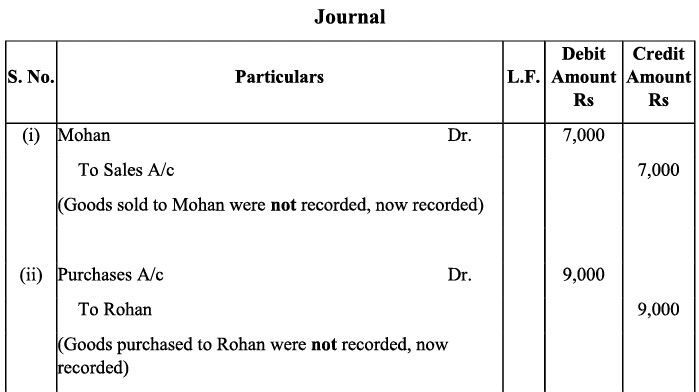
Q1: Rectify the following errors:
(i) Credit sales to Mohan Rs. 7,000 were not recorded.
(ii) Credit purchases from Rohan Rs. 9,000 were not recorded.
(iii) Goods returned to Rakesh Rs. 4,000 were not recorded.
(iv) Goods returned from Mahesh Rs. 1,000 were not recorded.
Ans:

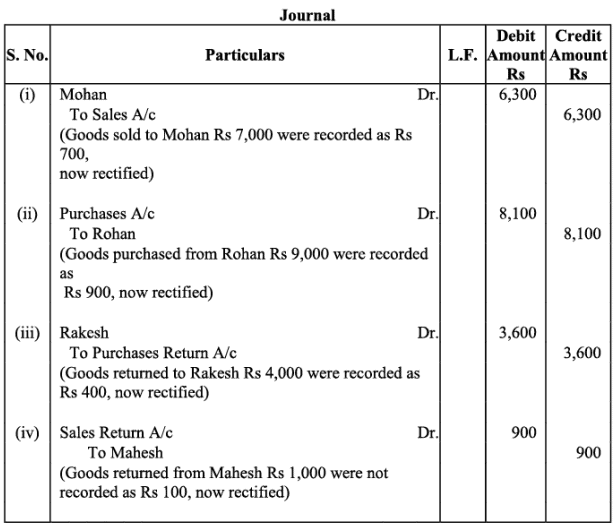
Q2: Rectify the following errors:
(i) Credit sales to Mohan Rs. 7,000 were recorded as Rs.700.
(ii) Credit purchases from Rohan Rs. 9,000 were recorded as Rs. 900.
(iii) Goods returned to Rakesh Rs. 4,000 were recorded as Rs. 400.
(iv) Goods returned from Mahesh Rs. 1,000 were recorded as Rs.100.
Ans:
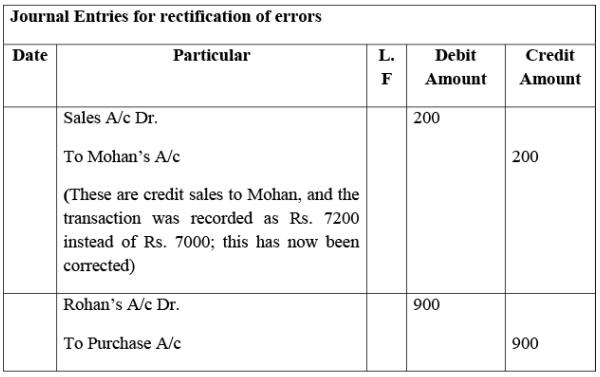
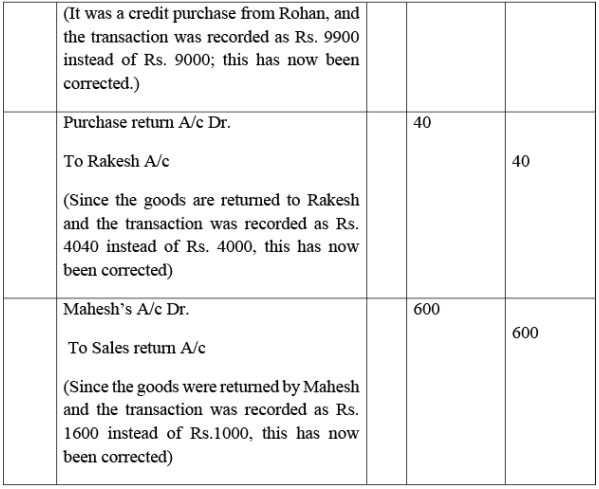
Q3: Rectify the following errors:
(i) Credit sales to Mohan Rs. 7,000 were recorded as Rs.7,200.
(ii) Credit purchases from Rohan Rs. 9,000 were recorded as Rs. 9,900.
(iii) Goods returned to Rakesh Rs. 4,000 were recorded as Rs. 4,040.
(iv) Goods returned from Mahesh Rs. 1,000 were recorded as Rs.1,600.
Ans:
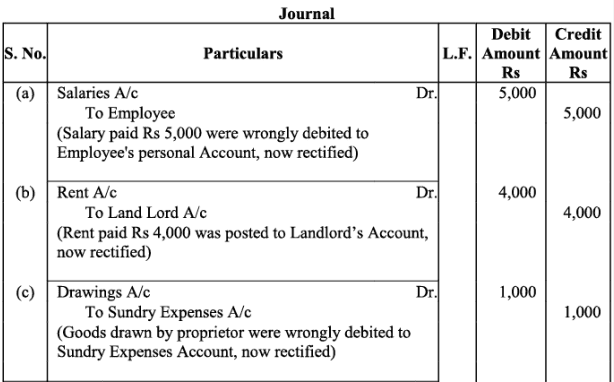
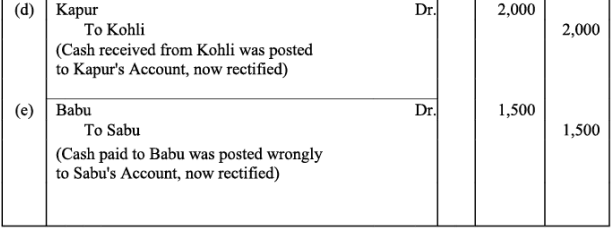
Q4:Rectify the following errors:
(a)Salary paid Rs. 5,000 was debited to employee’s personal account.
(b)Rent Paid Rs. 4,000 was posted to landlord’s personal account.
(c)Goods withdrawn by proprietor for personal use Rs. 1,000 were debited to sundry expenses account.
(d)Cash received from Kohli Rs. 2,000 was posted to Kapur’s account.
(e)Cash paid to Babu Rs. 1,500 was posted to Sabu’s account.
Ans:
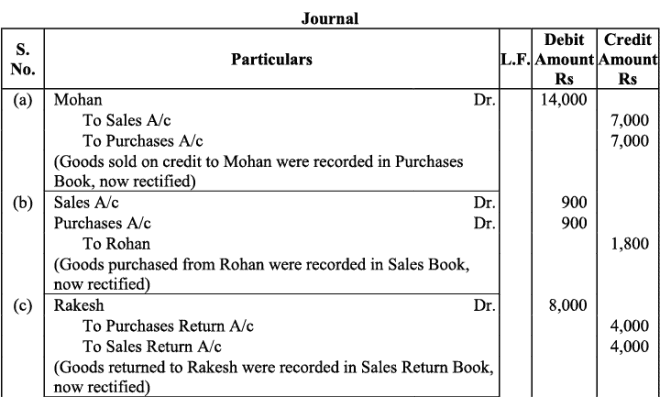
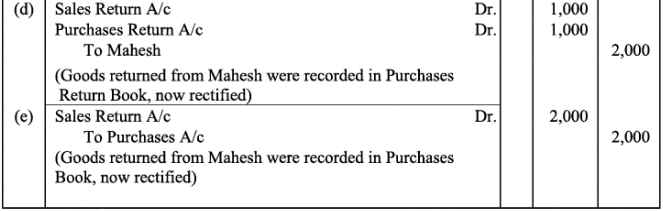
Q5:Rectify the following errors:
(a)Credit Sales to Mohan Rs. 7,000 were recorded in purchases book.
(b)Credit Purchases from Rohan Rs. 9,00 were recorded in sales book.
(c)Goods returned to Rakesh Rs. 4,000 were recorded in the sales return book.
(d)Goods returned from Mahesh Rs. 1,000 were recorded in purchases return book.
(e)Goods returned from Nahesh Rs. 2,000 were recorded in purchases book.
Ans:
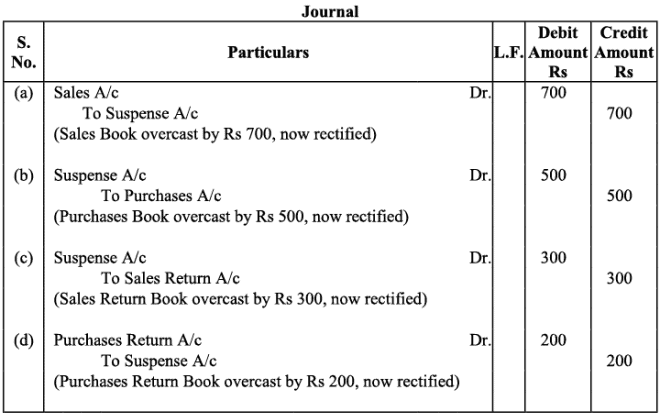
Q6:Rectify the following errors:
(a)Sales book overcast by Rs. 700.
(b)Purchases book overcast by Rs. 500.
(c)Sales return book overcast by Rs. 300.
(d)Purchase return book overcast by Rs. 200.
Ans:
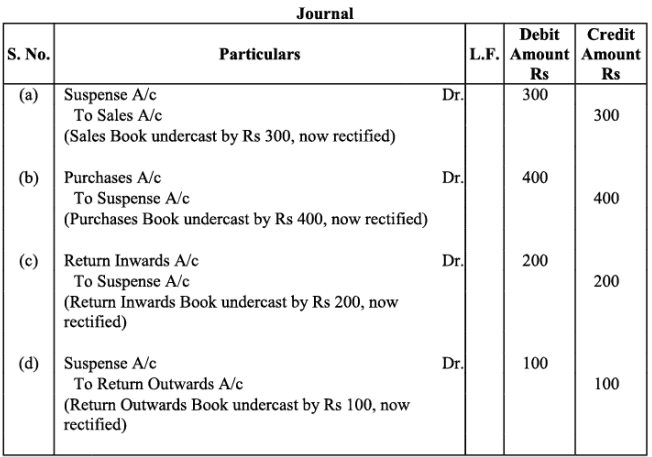
Q7:Rectify the following errors:
(a)Sales book undercast by Rs.300.
(b)Purchases book undercast by Rs.400.
(c)Return Inwards book undercast by Rs.200.
(d)Return outwards book undercast by Rs. 100.
Ans:
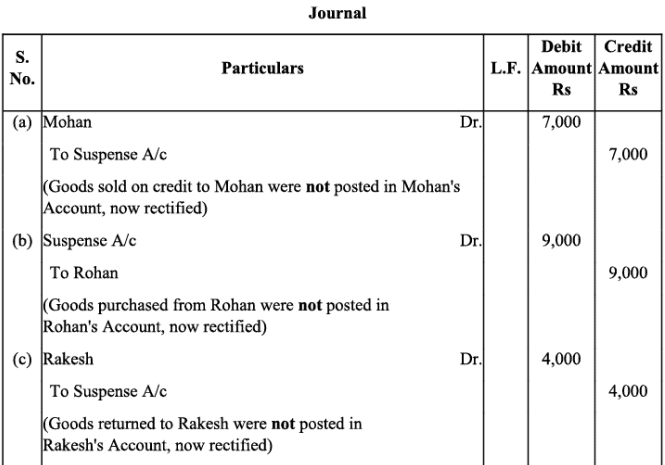
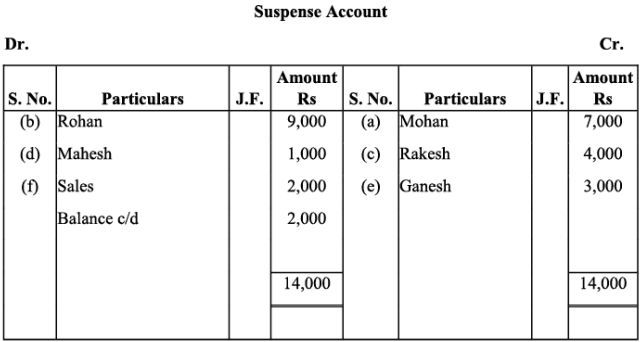
Q8: Rectify the following errors and ascertain the amount of difference in trial balance by preparing suspense account:
(a) Credit sales to Mohan Rs. 7,000 were not posted.
(b) Credit purchases from Rohan Rs. 9,000 were not posted.
(c) Goods returned to Rakesh Rs. 4,000 were not posted.
(d) Goods returned from Mahesh Rs. 1,000 were not posted.
(e) Cash paid to Ganesh Rs. 3,000 was not posted.
(f) Cash sales Rs. 2,000 were not posted.
Ans:


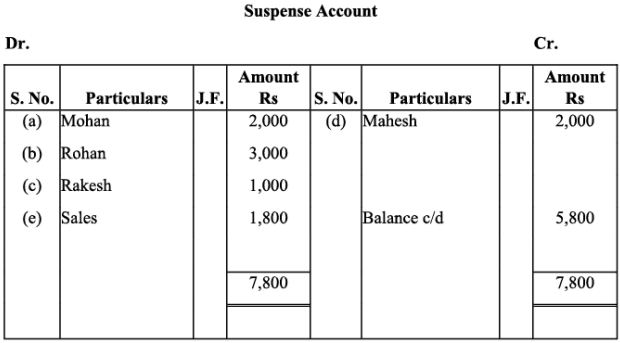
Q9: Rectify the following errors and ascertain the amount of difference in trial balance by preparing suspense account:
(a) Credit sales to Mohan Rs. 7,000 were posted as Rs. 9,000.
(b) Credit purchases from Rohan Rs. 9,000 were posted as Rs. 6,000.
(c) Goods returned to Rakesh Rs. 4,000 were posted as Rs. 5,000.
(d) Goods returned from Mahesh Rs. 1,000 were posted as Rs. 3,000.
(e) Cash sales Rs. 2,000 were posted as Rs. 200.
Ans:
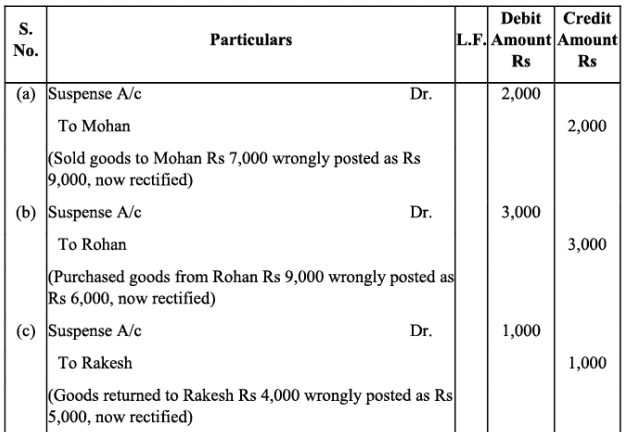

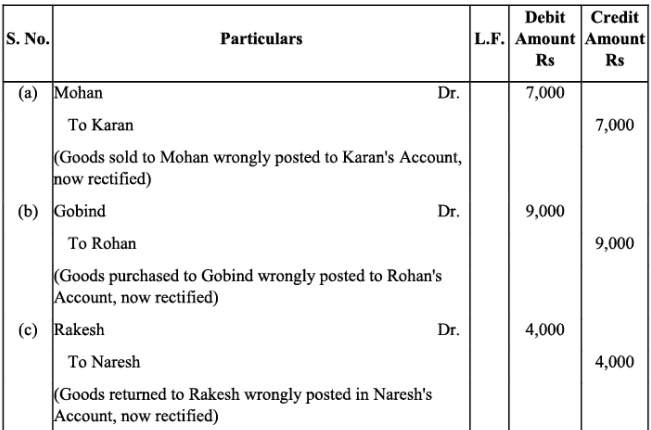
Q10: Rectify the following errors:
(a) Credit sales to Mohan Rs. 7,000 were posted to Karan.
(b) Credit purchases from Rohan Rs. 9,000 were posted to Gobind.
(c) Goods returned to Rakesh Rs. 4,000 were posted to Naresh.
(d) Goods returned from Mahesh Rs. 1,000 were posted to Manish.
(e) Cash sales Rs. 2,000 were posted to commission account.
Ans:

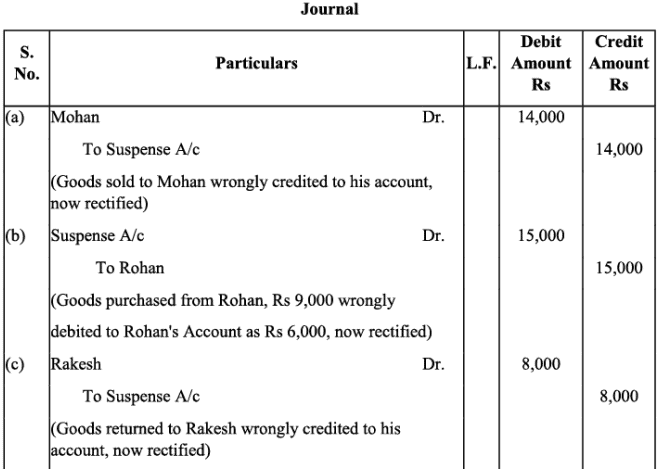
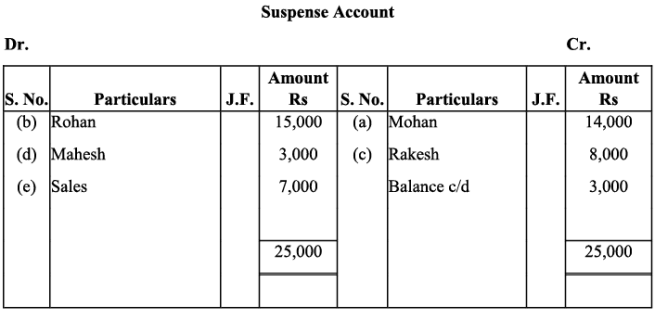
Q11: Rectify the following errors assuming that a suspense account was opened. Ascertain the difference in trial balance:
(a) Credit sales to Mohan Rs. 7,000 were posted to the credit of his account.
(b) Credit purchases from Rohan Rs. 9,000 were posted to the debit of his account as Rs. 6,000.
(c) Goods returned to Rakesh Rs. 4,000 were posted to the credit of his account.
(d) Goods returned from Mahesh Rs. 1,000 were posted to the debit of his account as Rs. 2,000.
(e) Cash sales Rs. 2,000 were posted to the debit of sales account as Rs. 5,000.
Ans:

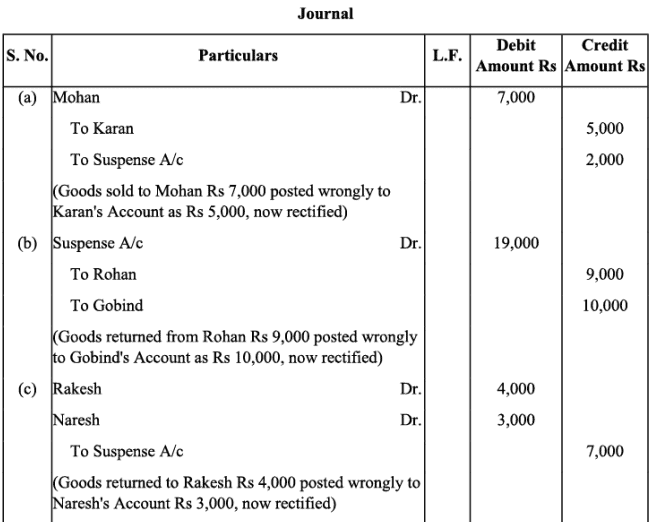
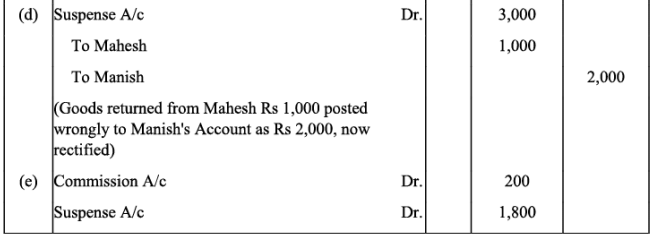
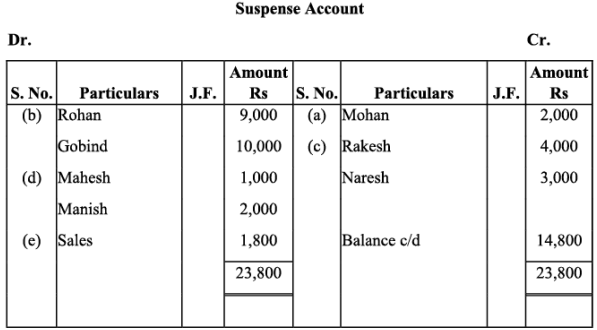
Q12: Rectify the following errors assuming that a suspense account was opened. Ascertain the difference in trial balance:
(a) Credit sales to Mohan Rs. 7,000 were posted to Karan as Rs. 5,000.
(b) Credit purchases from Rohan Rs. 9,000 were posted to the debit of Gobind as Rs. 10,000.
(c) Goods returned to Rakesh Rs. 4,000 were posted to the credit of Naresh as Rs. 3,000.
(d) Goods returned from Mahesh Rs. 1,000 were posted to the debit of Manish as Rs. 2,000.
(e) Cash sales Rs. 2,000 were posted to commission account as Rs. 200.
Ans:

Q13: Rectify the following errors assuming that a suspense account was opened. Ascertain the difference in trial balance:
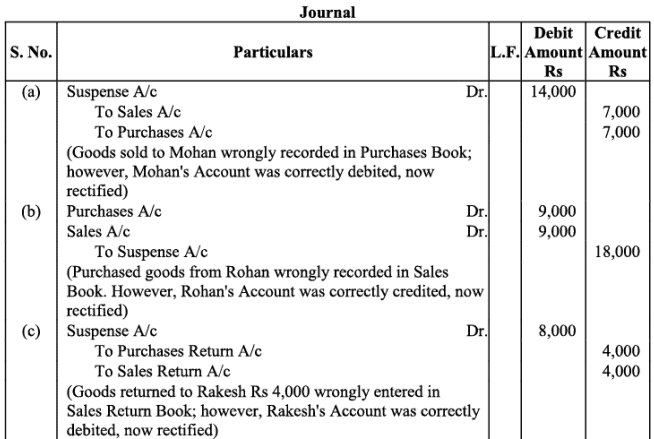
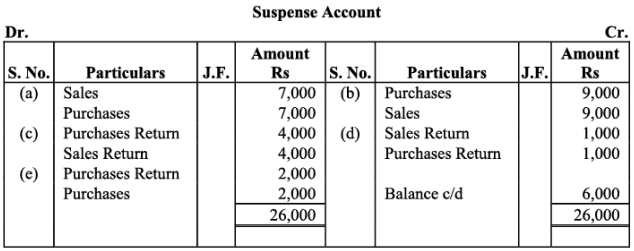
(a) Credit sales to Mohan Rs. 7,000 were recorded in Purchase Book. However, Mohan’s account was correctly debited.
(b) Credit purchases from Rohan Rs. 9,000 were recorded in Sales Book. However, Rohan’s account was correctly credited.
(c) Goods returned to Rakesh Rs. 4,000 were recorded in Sales Return Book. However, Rakesh’s account was correctly debited.
(d) Goods returned from Mahesh Rs. 1,000 were recorded through Purchases Return Book. However, Mahesh’s account was correctly credited.
(e) Goods returned to Naresh Rs. 2,000 were recorded through Purchases Book. However, Naresh’s account was correctly debited.
Ans:


Q14: Rectify the following errors:
(a) Furniture purchased for Rs. 10,000 was wrongly debited to Purchases Account.
(b) Machinery purchased on credit from Raman for Rs. 20,000 was recorded through Purchases Book.
(c) Repairs on machinery Rs. 1,400 were debited to Machinery Account.
(d) Repairs on overhauling of secondhand machinery purchased Rs. 2,000 were debited to Repairs Account.
(e) Sale of old machinery at book value of Rs. 3,000 was credited to Sales Account.
Ans: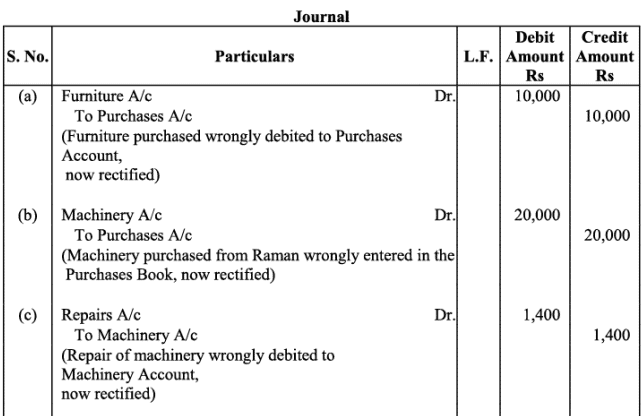

Q15: Rectify the following errors assuming that a suspense account was opened. Ascertain the difference in trial balance:
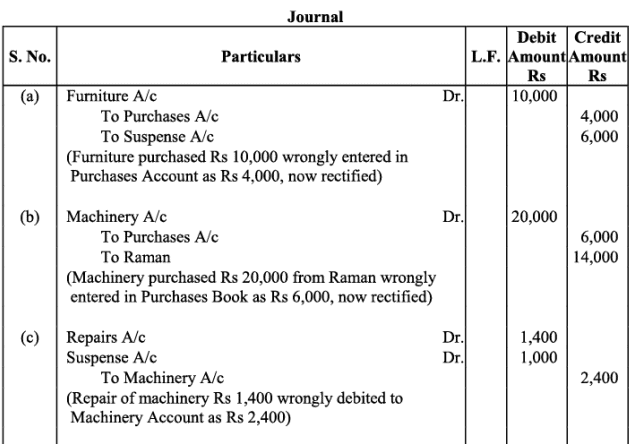
(a) Furniture purchased for Rs. 10,000 was wrongly debited to Purchase Account as Rs. 4,000.
(b) Machinery purchased on credit from Raman for Rs. 20,000 was recorded through Purchases Book as Rs. 6,000.
(c) Repairs on machinery Rs. 1,400 were debited to Machinery Account as Rs. 2,400.
(d) Repairs on overhauling of secondhand machinery purchased Rs. 2,000 were debited to Repairs Account as Rs. 200.
(e) Sale of old machinery at book value Rs. 3,000 was credited to Sales Account as Rs. 5,000.
Ans:

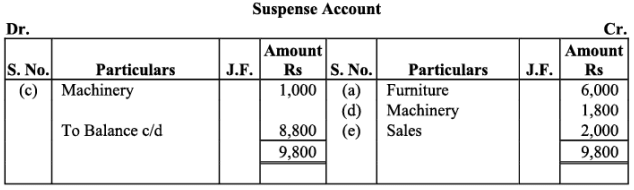
Q16: Rectify the following errors:
(a) Depreciation provided on machinery Rs. 4,000 was not posted.
(b) Bad debts written off Rs. 5,000 were not posted.
(c) Discount allowed to a debtor Rs. 100 on receiving cash from him was not posted.
(d) Discount allowed to a debtor Rs. 100 on receiving cash from him was not posted to discount account.
(e) Bill receivable for Rs. 2,000 received from a debtor was not posted.
Ans:
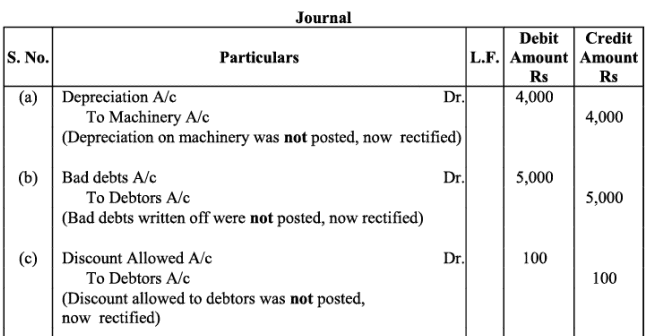

Q17: Rectify the following errors:
(a) Depreciation provided on machinery Rs. 4,000 was posted as Rs. 400.
(b) Bad debts written off Rs. 5,000 were posted as Rs. 6,000.
(c) Discount allowed to a debtor Rs. 100 on receiving cash from him was posted as Rs. 60.
(d) Goods withdrawn by proprietor for personal use Rs. 800 were posted as Rs. 300.
(e) Bill receivable for Rs. 2,000 received from a debtor was posted as Rs. 3,000.
Ans:
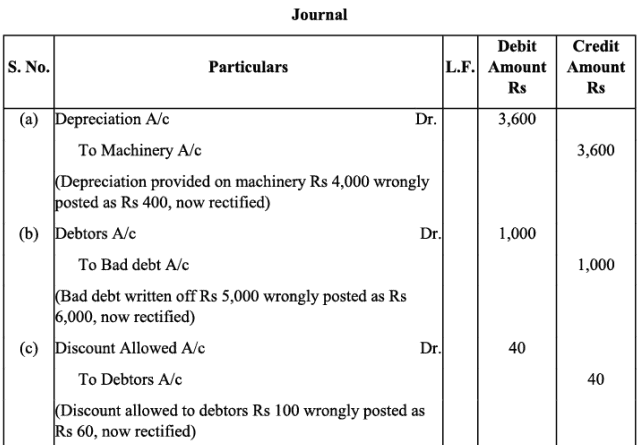

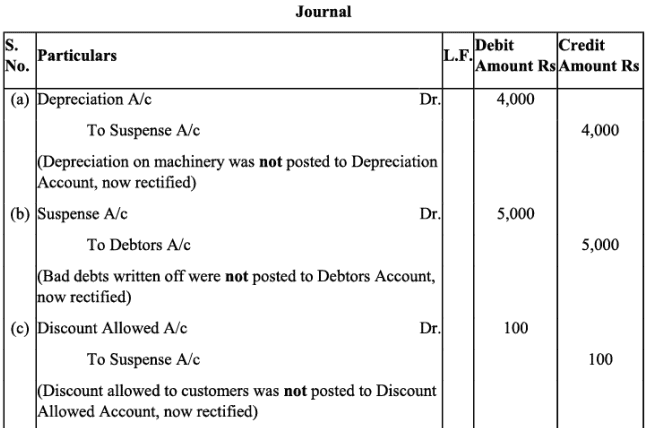
Q18: Rectify the following errors assuming that a suspense account was opened. Ascertain the difference in trial balance:
(a) Depreciation provided on machinery Rs. 4,000 was not posted to Depreciation account.
(b) Bad debts written off Rs. 5,000 were not posted to Debtors account.
(c) Discount allowed to a debtor Rs. 100 on receiving cash from him was not posted to discount allowed account.
(d) Goods withdrawn by proprietor for personal use Rs. 800 were not posted to Drawings account.
(e) Bill receivable for Rs. 2,000 received from a debtor was not posted to Bills receivable account.
Ans:

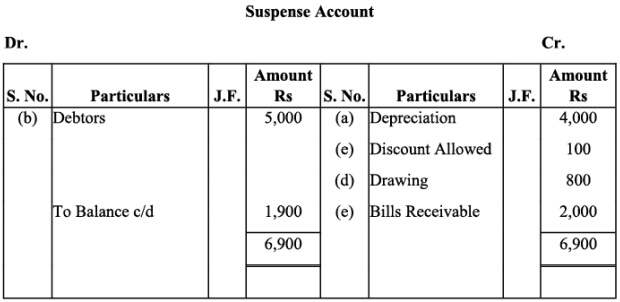
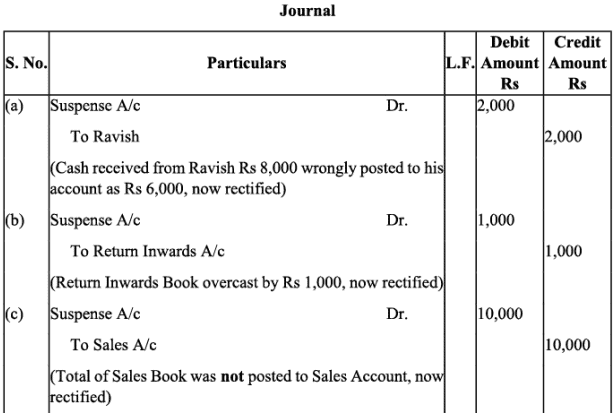
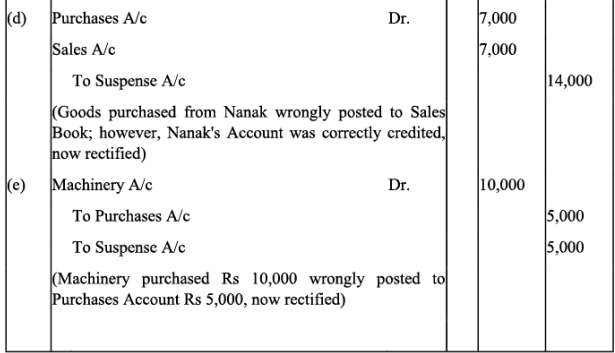
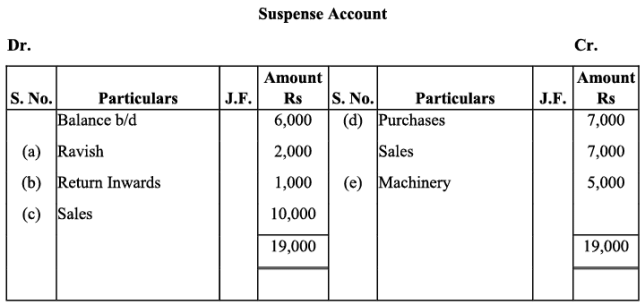
Q19: Trial balance of Anuj did not agree. It showed an excess credit of Rs. 6,000. He put the difference to suspense account. He discovered the following errors:
(a) Cash received from Ravish Rs. 8,000 was posted to his account as Rs. 6,000.
(b) Returns inwards book overcast by Rs. 1,000.
(c) Total of sales book Rs. 10,000 was not posted to Sales account.
(d) Credit purchases from Nanak Rs. 7,000 were recorded in Sales Book. However, Nanak’s account was correctly credited.
(e) Machinery purchased for Rs. 10,000 was posted to Purchases account as Rs. 5,000.
Rectify the errors and prepare suspense account.
Ans:
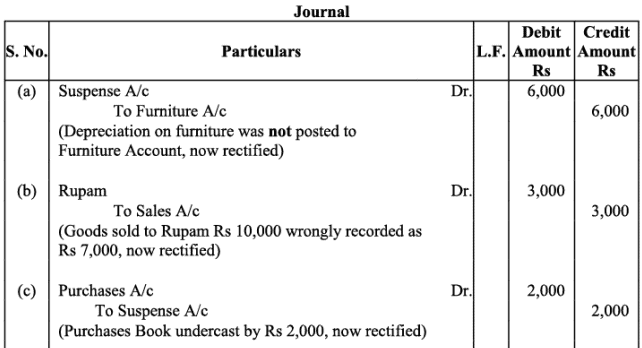
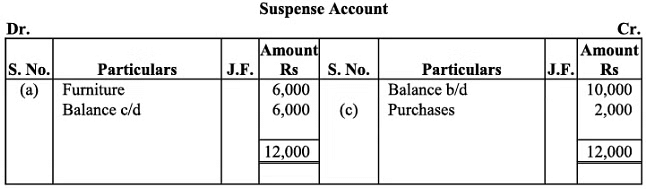
Q20: Trial balance of Raju showed an excess debit of Rs. 10,000. He put the difference to suspense account and discovered the following errors:
(a) Depreciation written-off the furniture Rs. 6,000 was not posted to Furniture account.
(b) Credit sales to Rupam Rs. 10,000 were recorded as Rs. 7,000.
(c) Purchases book undercast by Rs. 2,000.
(d) Cash sales to Rana Rs. 5,000 were not posted.
(e) Old Machinery sold for Rs. 7,000 was credited to Sales account.
(f) Discount received Rs. 800 from Kanan on paying cash to him was not posted.
Rectify the errors and prepare suspense account.
Ans:

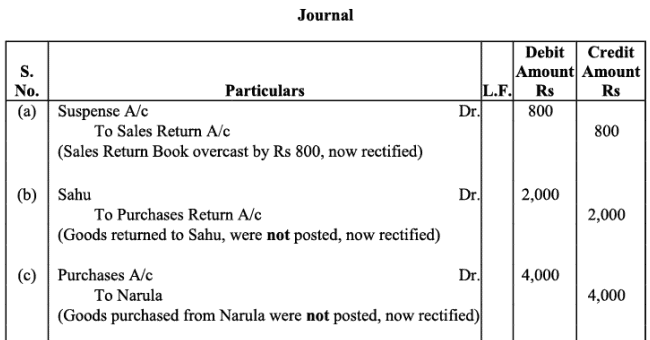
Q21: Trial balance of Madan did not agree, and he put the difference to suspense account. He discovered the following errors:
(a) Sales return book overcast by Rs. 800.
(b) Purchases return to Sahu Rs. 2,000 were not posted.
(c) Goods purchased on credit from Narula Rs. 4,000 were taken into stock, but no entry was passed in the books.
(d) Installation charges on new machinery purchased Rs. 500 were debited to sundry expenses account as Rs. 50.
(e) Rent paid for residential accommodation of Madan (the proprietor) Rs. 1,400 was debited to Rent account as Rs. 1,000.
Rectify the errors and prepare suspense account to ascertain the difference in trial balance.
Ans:

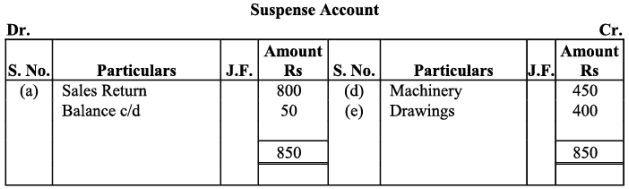
Note: As per the solution Suspense Account shows a credit balance of Rs. 50. However, as per the answer given in the book, it is a credit balance of Rs. 2050. In order to match answer with the book item (b) is taken as, ‘Purchases return to Sahu Rs. 2,000 were not posted to Sahu’s Account.’ Thus, the rectifying entry for this error will be as:
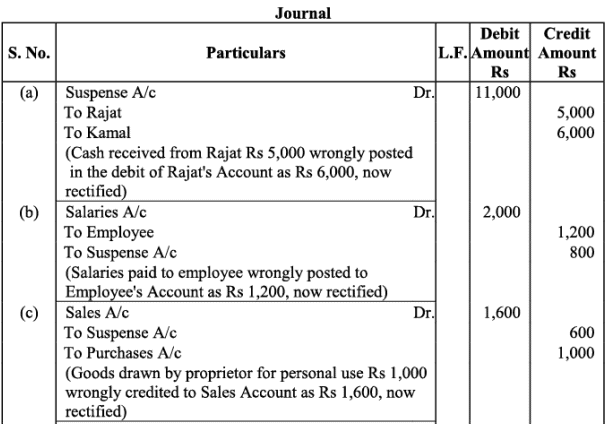
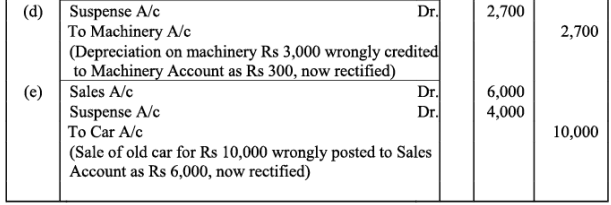
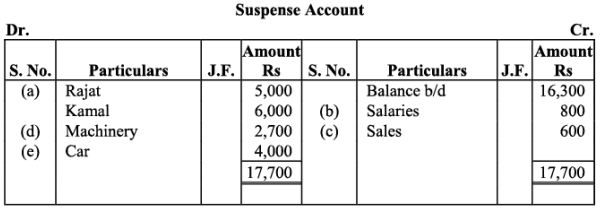
Q22: Trial balance of Kohli did not agree and showed an excess debit of Rs. 16,300. He put the difference to a suspense account and discovered the following errors:
(a) Cash received from Rajat Rs. 5,000 was posted to the debit of Kamal as Rs. 6,000.
(b) Salaries paid to an employee Rs. 2,000 were debited to his personal account as Rs. 1,200.
(c) Goods withdrawn by proprietor for personal use Rs. 1,000 were credited to sales account as Rs. 1,600.
(d) Depreciation provided on machinery Rs. 3,000 was posted to Machinery account as Rs. 300.
(e) Sale of old car for Rs. 10,000 was credited to sales account as Rs. 6,000.
Rectify the errors and prepare suspense account.
Ans:
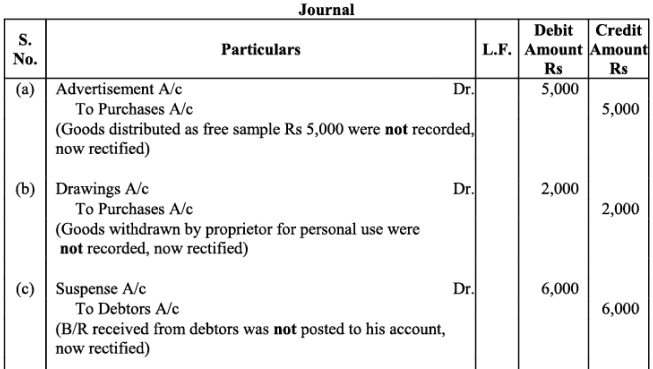
Q23: Give journal entries to rectify the following errors assuming that suspense account had been opened:
(a) Goods distributed as free sample Rs. 5,000 were not recorded in the books.
(b) Goods withdrawn for personal use by the proprietor Rs. 2,000 were not recorded in the books.
(c) Bill receivable received from a debtor Rs. 6,000 was not posted to his account.
(d) Total of Returns inwards book Rs. 1,200 was posted to Returns outwards account.
(e) Discount allowed to Reema Rs. 700 on receiving cash from her was recorded in the books as Rs. 70.
Ans:

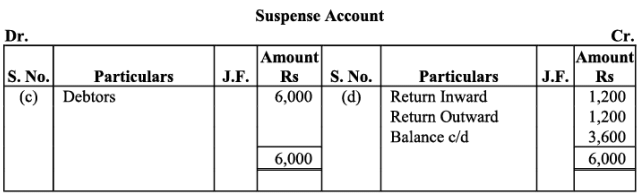
Q24: Trial balance of Khatau did not agree. He put the difference to suspense account and discovered the following errors:
(a) Credit sales to Manas Rs. 16,000 were recorded in the purchases book as Rs. 10,000 and posted to the debit of Manas as Rs. 1,000.
(b) Furniture purchased from Noor Rs. 6,000 was recorded through purchases book as Rs. 5,000 and posted to the debit of Noor as Rs. 2,000.
(c) Goods returned to Rai Rs. 3,000 were recorded through the Sales book as Rs. 1,000.
(d) Old machinery sold for Rs. 2,000 to Maneesh was recorded through sales book as Rs. 1,800 and posted to the credit of Manish as Rs. 1,200.
(e) Total of Returns inwards book Rs. 2,800 was posted to Purchase account.
Rectify the above errors and prepare suspense account to ascertain the difference in trial balance.
Ans:
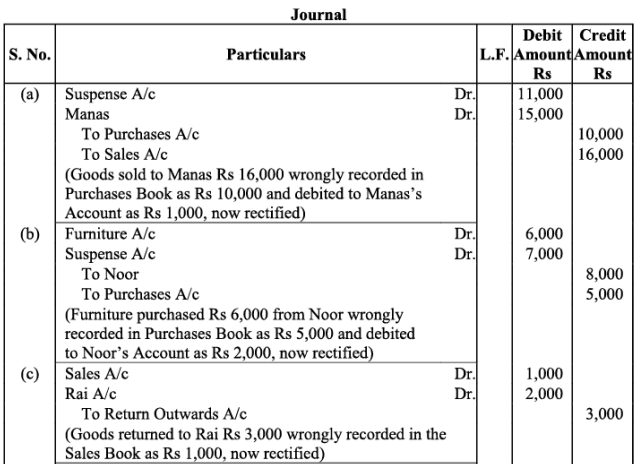

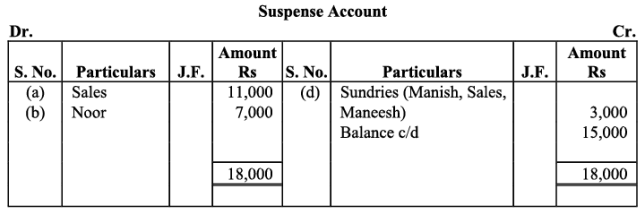
Q25: Trial balance of John did not agree. He put the difference to suspense account and discovered the following errors:
(a) In the sales book for January, total of page 2 was carried forward to page 3 as Rs. 1,000 instead of Rs. 1,200 and total of page 6 was carried forward to page 7 as Rs. 5,600 instead of Rs. 5,000.
(b) Wages paid for installation of machinery Rs. 500 was posted to wages account as Rs. 50.
(c) Machinery purchased from R & Co. for Rs. 10,000 on credit was entered in Purchases Book as Rs. 6,000 and posted from there to R & Co. as Rs. 1,000.
(d) Credit sales to Mohan Rs. 5,000 were recorded in Purchases Book.
(e) Goods returned to Ram Rs. 1,000 were recorded in Sales Book.
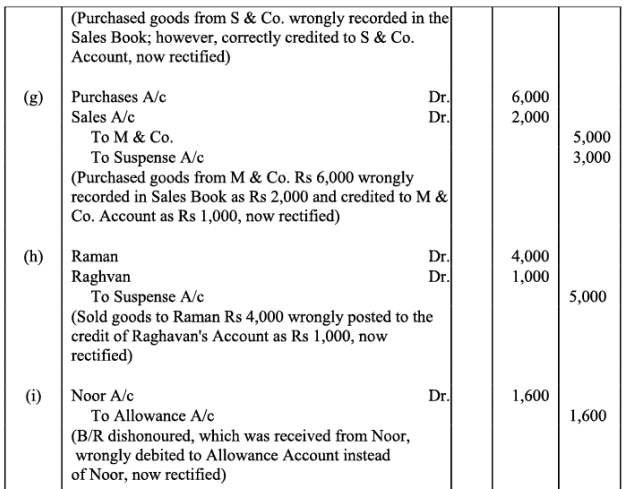
(f) Credit purchases from S & Co. for Rs. 6,000 were recorded in sales book. However, S & Co. was correctly credited.
(g) Credit purchases from M & Co. Rs. 6,000 were recorded in Sales Book as Rs. 2,000 and posted therefrom to the credit of M & Co. as Rs. 1,000.
(h) Credit sales to Raman Rs. 4,000 were posted to the credit of Raghvan as Rs. 1,000.
(i) Bill receivable for Rs. 1,600 from Noor was dishonoured and posted to the debit of Allowances account.
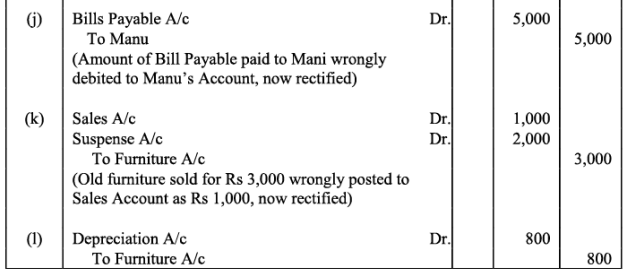
(j) Cash paid to Mani Rs. 5,000 against our acceptance was debited to Manu.
(k) Old furniture sold for Rs. 3,000 was posted to Sales account as Rs. 1,000.
(l) Depreciation provided on furniture Rs. 800 was not posted.
(m) Material Rs. 10,000 and wages Rs. 3,000 were used for construction of building. No adjustment was made in the books.
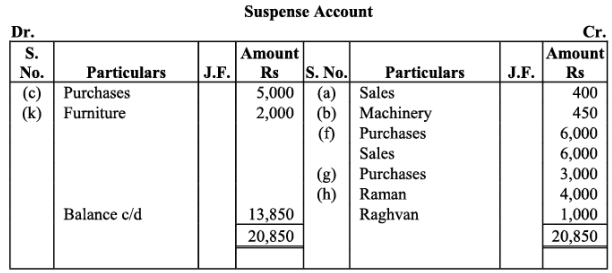
Rectify the errors and prepare suspense account to ascertain the difference in trial balance.
Ans:
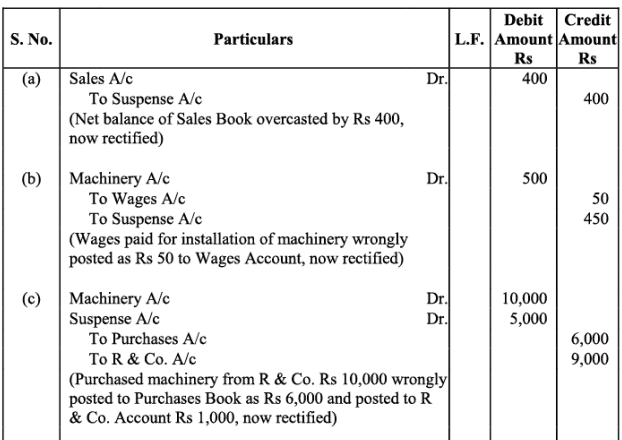


Note:In item (m), it has been assumed that the materials used in the construction of building are part of stock in trade.
|
61 videos|154 docs|35 tests
|
FAQs on NCERT Solution: Trial Balance and Rectification of Errors - Accountancy Class 11 - Commerce
| 1. What is a trial balance and why is it important in accounting? |  |
| 2. What are the common types of errors that can occur in accounting? |  |
| 3. How can errors in the trial balance be rectified? |  |
| 4. What is the difference between a suspense account and a correction account? |  |
| 5. How does the trial balance assist in preparing financial statements? |  |





















