Unit 7: Accounting Standards Chapter Notes | Accounting for CA Foundation PDF Download
Unit Overview
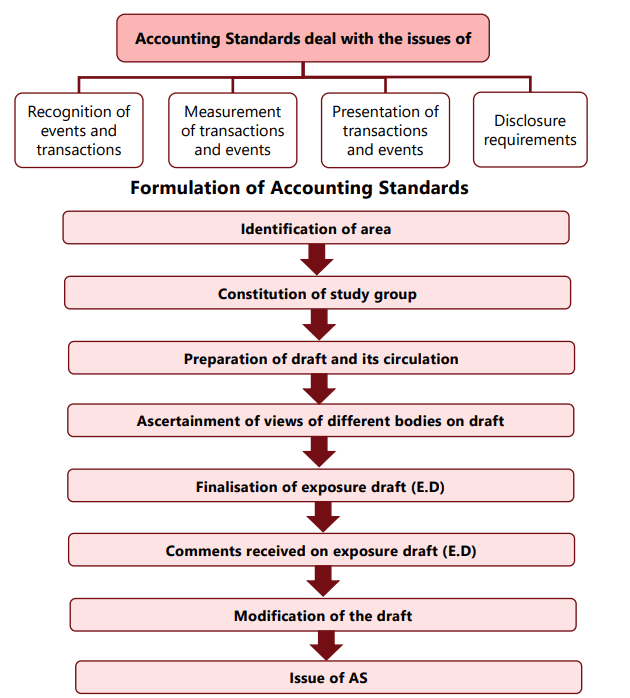
Introduction to Accounting Standards
Accounting serves as the essential "language of business," conveying the financial outcomes of a company to various stakeholders through financial statements. However, without proper regulation of the financial accounting process, there is a risk that these statements could be misleading, biased, and present a distorted view of the business rather than its true state. To guarantee transparency, consistency, comparability, adequacy, and reliability in financial reporting, it is crucial to standardize accounting principles and policies.
- Accounting Standards (ASs) offer a framework and set standard accounting policies for the treatment of transactions and events, making the financial statements of different enterprises comparable.
- Accounting standards are official policy documents created by expert accounting bodies, the government, or regulatory authorities. These documents address the recognition, measurement, presentation, and disclosure of accounting transactions and events in financial statements. The primary goal of standard-setting bodies is to promote the timely and useful dissemination of financial information to investors and other parties interested in a company's economic performance.
Accounting standards focus on several key issues:
- Recognition: Determining when events and transactions should be recognized in financial statements.
- Measurement: Assessing the value of these transactions and events.
- Presentation: Organizing and presenting these transactions and events in a way that is clear and understandable to readers.
- Disclosure: Outlining the information that must be disclosed to the public, stakeholders, and potential investors to provide insight into the financial statements and aid in informed decision-making.
Objectives of Accounting Standards
Accounting standards aim to harmonize the accounting policies and practices of different business entities. The goal is to standardize the diverse accounting practices used for various aspects of accounting. By doing so, accounting standards seek to:
- Eliminate non-comparability: Improve the reliability of financial statements by making them more comparable across different entities.
- Provide standard policies: Offer a set of standard accounting policies, valuation norms, and disclosure requirements.
Accounting standards reduce the range of accounting alternatives in financial statement preparation. This ensures comparability while maintaining rationality, allowing for meaningful comparisons of financial statements from different enterprises.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Accounting Standards
Accounting standards outline the principles, valuation methods, and application techniques for preparing and presenting financial statements to ensure they provide an accurate and fair representation. By establishing these standards, accountants gain several advantages:
Benefits of Accounting Standards
- Standardization of Accounting Treatments: Accounting standards minimize or eliminate confusing variations in the treatments used for preparing financial statements.
- Additional Disclosure Requirements: Standards may mandate disclosures that go beyond legal requirements in certain areas where important information is not statutorily required.
- Enhanced Comparability: The application of accounting standards facilitates, to some extent, the comparison of financial statements of companies across different countries and within the same country. However, it's important to note that variations in institutions, traditions, and legal systems lead to differences in accounting standards adopted by different countries.

Limitations of Accounting Standards
- Difficulties in Choosing Between Treatments: Certain accounting problems may have multiple viable solutions, making it challenging to choose between different alternative accounting treatments.
- Restricted Scope: Accounting standards cannot supersede statutory requirements. They must be formulated within the framework of existing laws and regulations.

Process of Formulation of Accounting Standards in India
Background: The Institute of Chartered Accountants of India (ICAI) is the leading accounting body in the country. In 1977, ICAI established the Accounting Standards Board (ASB) to take the initiative in formulating accounting standards. Role of ICAI and ASB: The ICAI plays a crucial role in setting and issuing accounting standards, ensuring that the process is consultative and transparent. The ASB, while being a part of the ICAI, operates independently in formulating accounting standards. Consideration of IFRS: The ASB takes into account International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS) when framing Indian Accounting Standards (AS), adapting them to the local context of laws, customs, and business practices. Composition of ASB: The ASB comprises representatives from various sectors, including industry associations (like ASSOCHAM, CII, FICCI), regulators, academics, and government departments. Independence of ASB: While the ASB is constituted by the ICAI Council, it has the autonomy to formulate accounting standards without interference. The ICAI Council cannot modify ASB's draft standards without consulting the board.
Standard-Setting Procedure by ASB:
- Identification of Areas: The ASB identifies broad areas where accounting standards need to be formulated.
- Constitution of Study Groups: Study groups are formed to focus on specific projects and prepare preliminary drafts of the proposed standards. These drafts include the standard's objectives, scope, definitions, recognition and measurement principles, and presentation and disclosure requirements.
- Consideration and Revision: The ASB reviews the preliminary draft prepared by the study group and makes revisions based on discussions.
- Circulation of Draft: The revised draft is circulated to ICAI Council members and specified outside bodies for comments.
- Meetings for Feedback: Meetings are held with representatives of outside bodies to gather their views on the draft.
- Finalisation of Exposure Draft: The exposure draft is finalised and issued for public comments.
- Consideration of Comments: Comments received on the exposure draft are considered, and the draft standard is finalised for submission to the ICAI Council.
- Approval and Issuance: The final draft is submitted to the ICAI Council for approval and issuance.
After considering the final draft of the proposed standard, the Council of the ICAI may modify it in consultation with the ASB if necessary. Subsequently, the ICAI issues the accounting standard for non-corporate entities. For unlisted corporate entities with a net worth of less than 250 crores, the accounting standards are issued by the Central Government of India.
There are three sets of Accounting Standards designed for different categories of entities based on their nature, size, and legal framework. These standards ensure that each entity follows appropriate accounting principles for financial reporting.
The three sets of Accounting Standards are:
- Indian Accounting Standards (Ind AS): These standards apply to all listed companies, Non-Banking Financial Companies (NBFCs), and unlisted companies and unlisted NBFCs with a net worth of INR 250 crores or more.
- Accounting Standards (AS) under Companies (Accounting Standards) Rules, 2021: These standards are applicable to companies not following Ind AS. These companies must apply Accounting Standards notified under the Companies Act as per the Companies (Accounting Standards) Rules, 2021.
- Accounting Standards (AS) prescribed by the ICAI: These standards apply to entities other than companies.
List of Accounting Standards in India
The Accounting Standards Board issues Accounting Standards that business entities must follow to ensure their financial statements are prepared according to generally accepted accounting principles (GAAP).
Here is the list of applicable accounting standards:

Introduction to Indian Accounting Standards (IND AS)
- The Institute of Chartered Accountants of India (ICAI) is responsible for setting accounting standards in India. In 2006, ICAI began the process of aligning Indian accounting standards with the International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS) issued by the International Accounting Standards Board (IASB). The goal was to enhance the acceptability and transparency of financial information provided by Indian corporates through their financial statements.
- The Indian government, in consultation with the ICAI, agreed to this move towards IFRS. However, instead of adopting IFRS outright, the decision was made to converge with them. This decision followed a detailed analysis of IFRS requirements and extensive discussions with various stakeholders.
- While formulating the IFRS-converged Indian Accounting Standards (Ind AS), efforts were made to align these standards closely with the corresponding IFRS. However, there were necessary departures to suit the Indian context. Additionally, certain changes were made to reflect the economic environment of India, which differs from the environment assumed by IFRS.
Key Points about Ind AS
- Origin: Ind AS was initiated by the ICAI in 2006 to align Indian accounting practices with global standards.
- Convergence vs. Adoption: The Indian government decided to converge with IFRS rather than adopt it blindly, ensuring necessary modifications for the Indian context.
- Stakeholder Consultation: The decision involved detailed analysis and discussions with various stakeholders to address the unique economic environment of India.
- Alignment with IFRS: Ind AS aims to be in line with IFRS, with deviations made only when essential.
- Economic Context: Adjustments were made in Ind AS to reflect India’s distinct economic conditions, which may differ from those assumed by IFRS.
List of Ind as on 1st August, 2024

Accounting Standards for Local Bodies
Accounting Standards for local bodies are designed for entities whose main goal is to provide services to the public, rather than making profits and offering returns to investors. These standards are crucial because the performance of such bodies cannot be fully assessed just by looking at their financial position, performance, and cash flows.
List of Accounting Standards for Local Bodies (ASLB) as on 1st August, 2024

Note: The above Ind AS and ASLB do not form part of the syllabus. They are included here for the students' knowledge only.
|
68 videos|160 docs|83 tests
|
FAQs on Unit 7: Accounting Standards Chapter Notes - Accounting for CA Foundation
| 1. What are the objectives of accounting standards in India? |  |
| 2. What are the advantages of implementing accounting standards? |  |
| 3. What is the process of formulation of accounting standards in India? |  |
| 4. What is the significance of Indian Accounting Standards (IND AS)? |  |
| 5. What are the accounting standards applicable to local bodies in India? |  |

|
Explore Courses for CA Foundation exam
|

|


















